* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes Sheet
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
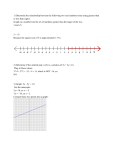
Algebra 1 Notes Sheet Number Operations Order of Operations (PEMDAS or GEMS) Grouping ( ), [ ] Exponents 5² Multiply & divide Subract & add Distributive Property: 5 (2x – 7) = 10x – 35 Multiply the number outside by everything inside. **Every point looks like (x, y) Linear (y = mx + b) m: slope or rate of change b: start value or y-intercept Slope-intercept form: y = mx + b Point-Slope form: y – y1 = m (x – x1) * Use when you are given a point and a slope. Example: write the equation of a line through (-4, 2) with a slope of 3 y – 2 = 3 (x + 4) y = 3x + 12 + 2 y = 3x + 14 Finding Slope: rise run Four types of slope: m= y 2 y1 x 2 x1 Positive m= y change x change Negative 1 m= 3 m=5 Undefined Zero 4 m= 0 m= 0 10 *Parallel lines have the SAME slope! Solving Proportions: Use cross-multiplication (the fish method) Example: x 3 5 10 Percents % _is_ = of %_ 100 15 x 10 x 1 .5 Mean: Average Median: The middle number Solving Inequalities: use the same steps as you do for solving an equation. FLIP the sign when you multiply or divide by a negative number. Examples: x + 2 > 15 12< 3x < 24 x > 13 3 3 3 4<x <8 Mode: Number that shows up most Graphs: Greater than (x >___) Less than (x < ____) Greater than or Equal to (x > ) Greater than or Equal to (x > ) Dot Open (o) Open (o) Closed Closed Absolute Value: The distance from 0. Example: Arrow --- ----- --- x 8 x is 8 away from 0. x = -8 and x = 8 Exponential y A(1 r ) t Exponent Rules: Multiplication Add Exponents A: Start value r: rate % (change to decimal) t: time Division Subtract Exponents Power to a Power Multiply Exponents 4x5 2x 4 1 2x (5 x 5 ) 2 25 x10 x 3 ( x11 ) x14 Scientific Notation: A decimal times 10 to a power. Example: 456,320,000 = 4.5632 x10 8 0.000213 = 2.13 x 10 4 y ax 2 bx c Quadratics Combine Like Terms: Only things with the same variable (letter) and exponent (little number) can go together. Example: (2 x 2 9 x 10) (5 x 2 2 x 4) 7 x 2 11x 6 *Distribute Negatives! (2x + 4) – (4x – 8) = 2x + 4 – 4x + 8 Multiplying Binomials (FOIL): Multiply the First, Outside, Inside, and Last Terms (x + 4) (x – 2) x 2 2x 4x 8 x 2 2x 8 Factor the quadratic expressions (un-FOIL): BOX METHODWhat numbers multiply to be the last term and add to be the middle term? x 2 2x 8 4(-2) = -8 4 + (-2) = 2 (x + 4) (x – 2) The quadratic formula is 2 b b 4ac x 2a Probability = number of favorable outcomes total outcomes Odds = number of favorable number of unfavorabl e *Multiply your number of choices and the probabilities of individual events in order to find totals. Example: What is the probability of rolling a 3 then rolling an odd number? Solution: 13 3 1 6 6 36 12