* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra 1 Things to Know for SOL Factoring: find 2 #`s add to 4, multi
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
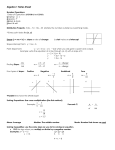
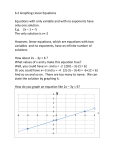
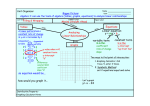
Algebra 1 Things to Know for SOL Factoring: x 4 x 3 find 2 #’s add to 4, multi. to 3 ( x 1)( x 3) factored 2 Absolute Value: 5 5 5 5 Represents distance Radicals √𝑥 4 = x2 (Divide exponent by 2 bring outside square root) Exponents: 3 2 3 n mn n m xn m x x x 2 m 20 1 x 1 43 3 4 1 n 1 n xm x mn n x xy n xn y n x 3 x 2 x x x 2 3 x 3 2 x2 5x 6 Divide: 𝟒𝒙𝟐 𝟐𝒙 1 = 2x or 2x (Divide your coefficients, subtract exponents Undefined slope: X = 4 ; Vertical line (Slope = undefined) Y = 4 : Horizontal line (Slope = 0) Identity: a b c ab ac a0 a Inverse: a a 0 Distributive Property: Zero Property √𝑥 5 =√𝑥 4 ∗ 𝑥 = x2 √𝑥 (List perfect squares for integers, and simplify) Graphing Inequalities: < , > sign = Dotted line ≤ ≥ sign = solid line (x,y) Test Point (0,0) to find shading If (0,0) makes true statement shade TOWARDS (0,0) False-Shade away from (0,0) Multiply: (distribute or FOIL) Properties of Real Numbers: Commutative Properties: a b b a ab ba Associative Properties: a b c a b c a bc ab c Variations: Direct y mx where m = constant of 𝑦 𝑥 variation (m = ) (Tables) Inverse y m x (m = xy) (Tables) Factor: Look for the GCF (greatest common factor first) 2x2 +8x + 6 = 2(x2 +4x + 3) = 2(x+3)(x+1) Equations of a Lines: y mx b slope intercept m = slope, b = y-intercept y y1 m x x1 point-slope Systems: y 2 x 1 Linear: Solution is where the lines y 2 x 9 are equal or intersect. to solve: substitution, elimination Graph – ordered pair where lines intersect a 1 a 1 a 1 a a 00 Degree : Degree of monomial = sum of exponents 4x 3 is a degree of 3 Degree of Polynomial = degree of highest monomial degree x 2 3x 1 is a degree of 2 Solving Equations: 1. Deal with any parentheses in the problem 2. Combine similar terms on same side of = sign 3. Get the needed variables on the same side of = sign 4. Isolate the needed variable by add or subtract 5. Find the needed variable by divide or multiply Solve Quadratic Equations: Parabola: 2 x 5x 6 0 Set = 0 y ax 2 bx c x 3 x 2 0 Factor Roots, Solutions, x 3 0, x 2 0 Set both factors = 0 Zeros, x-intercepts: x 3, x 2 Find roots (solve) Where the graph Solve Quadratic Equations: Quadratic crosses the x-axis. Put in standard form: Ax 2 Bx C 0 Equation. b b2 4ac 2a 2 3 x 2 x 7 0 , A = 3, B = 2, C = 7 x Slope: m vertical change rise y2 y1 horizontal change run x2 x1 Inequalities: Remember to 5 3x 13 x change direction 3x 8 x of inequality when 4x 8 multiply/divide by a negative x 2 Function: Passes the vertical line test. A set of ordered pairs in which each x element has only one y element associated with it. f x 3x 4 f 2 3 2 4 2 X and Y-intercept: X-intercept: plug in 0 for Y, solve for X Y-intercept: plug in 0 for X, solve for Y Combine Like Terms: must be same variable(s) and exponents, combine the number in front 4 x 2 3 x 2 6 3x 2 9 Perimeter: add the distance around the outside Area Rectangle: multiply the length and width Box-and-Whisker Plot: 25% 25% Minimum Q1 Statistics: Mean = average = x = Standard Deviation = z score = 25% Median Q3 25% Maximum z x Parallel and Perpendicular Line: Parallel: slopes are equal. Perpendicular: slopes are negative reciprocal (flip over and negate) Statistics: MAD = Mean Absolute Deviation |𝑵𝒖𝒎𝒃𝒆𝒓 − 𝑴𝒆𝒂𝒏| for each element in data set (Always Positive from absolute value) = or element mean standard deviation Find the mean of those values measures how many standard deviations from the mean the observed values is. Calculator Graphing Functions Y = to graph a lines or parabolas, must solve equations for y first ZOOM 6: ZStandard (for normal window) 9: ZoomStat (to fit graph) TRACE to put a curser on the graph 2nd TRACE CALC 2: zero (to find x intercept, zero, solution, root) 3: minimum (to find the lowest value, vertex of parabola) 4: maximum (to find the highest value, vertex of parabola) 5: intersect (to find point where two lines cross, solution) Statistics STAT for scatter plots and data sets 1: Edit to enter data into L1 , L2 → CALC (for mean, standard deviation, line of best fit, curve best fit) 1: 1 – Var Stats (for mean, standard deviation) 2: LinReg(ax+b) (for line of best fit) 3: QuadReg for curve of best fit Convert: decimal to fraction MATH 1: Frac ENTER ENTER Raise a number to an exponent 45 4 5 Clear the Calculator: 2nd + MEM 7: Reset… 1: All Ram ... 2: Reset 2nd + MEM 7: Reset… 2: Defalts … 2: Reset