* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson Plans Teacher: Robinson Dates: 3/24
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Mormon views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
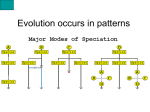
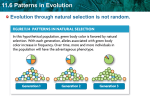
Lesson Plans Teacher: Robinson Dates: 3/24-4/8 Day 2 - (3/30-3/31) I can differentiate among I can critique data used by chemical evolution, scientists (e.g., Redi, organic evolution, and Needham, Spallanzani, the evolutionary steps Pasteur) to develop an along the way to aerobic understanding of heterotrophs and evolutionary processes and photosynthetic patterns. autotrophs. Use a Venn diagrams to compare Why did Malthus prokaryotes/eukaryotes, suggest world peace as protists/other eukaryotes, impossible, & how did fungi/plants, and this influence Darwin? plants/animals. 1. Chemical evolution Lyell – Studied geography. 2. Organic evolution He noticed that the 3. Sequence of continents moved…and this proposed provided Darwin and other evolutionary steps evolutionists with a means of within aerobic explaining how populations heterotrophs and could separate (become photosynthetic isolated) from one another so autotrophs they could develop isolated mutations. This provides a Summarize the work means for divergent done by Redi, Needham, evolution and adaptive Spallanzani, and radiation. Pasteur…and sequence to form the modern Discussion of summaries evolution theory. Even though LaMark made significant and accurate Which individual’s ideas contributions to of evolution theory are adaptation/evolution theory, most like those of what part of his contribution Darwins? Why? was incorrect? 315-232 definitions due 333-358 definitions due today, questions due next today, questions due next class class Workbook & Discussions Day 1 - (3/24-3/29) Learning Target Bell ringer Lesson (procedures, activities, materials) Wrap up/Reflection Homework Assessments Day 3 - (4/1-4/4) I can explain the steps of natural selection, including the mechanisms of speciation (e.g., mutations, adaptations, geographic isolation) and applications of speciation (e.g., pesticide and antibiotic resistance). How did Lyell’s work in geography provide a means for divergent & adaptive radiation? Definition adaptation and modern evolution theory. Discussion and examples for the proposed types of evolution. (Divergent, convergent, adaptive radiation, etc.) Review evidence for evolution (homologous, analogous, vestigial, genetics, etc.) Describe endosymbiotic theory. How are divergent evolution and adaptive radiation similar and different? Course: Biology I Day 4 - (4/5-4/6) Day 5 - (4/7-4/8) I can explain how organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups based upon their evolutionary relationships. (6a) I can identify if an organism displays asymmetry or type of symmetry. Identify what types of mutations occurred in the samples provided on the smart board. Draw example structures that display asymmetry, bilateral symmetry, and radial symmetry. Venn Diagrams comparing… 1. Bacteria/Archaea/Eukarya 2. Protista vs. prokaryotes (bacteria/archaea) 3. Protista vs. other Eukaryotes 4. Fungi vs Plantae 5. Plantae vs. Animalia Test Workbook review of pages 315-325. Define the various types of symmetry found in organisms and use examples on the smart board to familiarize the students with each type. Which Kingdom includes multicellular organisms that have cell walls that do well in dark moist areas, & includes yeasts? Are there more organisms at the family, class, order, or genus level of taxonomy? Justify your answer. 358-384 definitions due today, questions due next class Competency/Objective: 6. Demonstrate an understanding of principles that explain the diversity of life and biological evolution. a. Draw conclusions about how organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups based on similarities that reflect their evolutionary relationships. (DOK 2) • Characteristics of the six kingdoms • Major levels in the hierarchy of taxa (e.g., kingdom, phylum/division, class, order, family, genus, and species) • Body plans (symmetry) • Methods of sexual reproduction (e.g., conjugation, fertilization, pollination) • Methods of asexual reproduction (e.g., budding, binary fission, regeneration, spore formation) b. Critique data (e.g., comparative anatomy, Biogeography, molecular biology, fossil record, etc.) used by scientists (e.g., Redi, Needham, Spallanzani, Pasteur) to develop an understanding of evolutionary processes and patterns. (DOK 3) c. Research and summarize the contributions of scientists, (Darwin, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck, & Lyell) whose work led to the development of the theory of evolution. d. Analyze and explain the roles of natural selection, including the mechanisms of speciation (e.g., mutations, adaptations, geographic isolation) and applications of speciation (e.g., pesticide and antibiotic resistance). (DOK 3) e. Differentiate among chemical evolution, organic evolution, and the evolutionary steps along the way to aerobic heterotrophs and photosynthetic autotrophs. (DOK 2)