* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resistor Circuits Lab
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
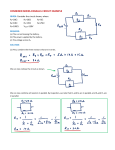
Name: ________________________________ PHYC 101 Summer 2016 RESISTANCE AND RESISTOR CIRCUITS Objectives: use a computer simulation to construct simple resistor circuits examine how changes in resistance affect current examine how changes in battery voltage affect current use simulated multi-meters to measure current through, and potential difference across, one or more resistors determine the result of connecting resistors in series determine the result of connecting resistors in parallel Background: Resistance is defined to be the ratio of electric potential difference (voltage) to current. When the electric potential difference is measured in Volts and the current is measured in Amps, the resistance will be measured in Ohms. Materials: Circuit Construction Kit found at http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/circuit-construction-kit-dc Example: 3 resistors in parallel This free computer simulation allows you to construct resistor circuits in multiple arrangements, choose the battery’s electric potential difference, and choose each resistor’s resistance. You will get better results if you choose these values carefully. The simulation’s voltmeter and non-contact ammeter can be used to obtain readings of these values for the entire circuit and for each circuit element. Since the non-contact ammeter only records to the hundredths place, you should make your battery voltage high enough to give you current readings greater than 1.00 A, but not so high that it “catches fire.” The following suggestions will help you immensely in building your circuits, determining potential difference and current, and responding to the lab questions. To determine the total current in a circuit, place the non-contact ammeter over the wire immediately after the power supply. To determine the current entering a resistor, place the non-contact ammeter over the wire immediately before the resistor. To determine the current leaving a resistor, place the non-contact ammeter over the wire immediately after the resistor. To determine the total potential difference (voltage) in a circuit, place the voltmeter in parallel across the power supply. The total resistance of a circuit will be the circuit’s total voltage divided by its total current (RT = VT/IT). To determine the potential difference (voltage) across a particular resistor, place the voltmeter in parallel across that resistor. “Right-clicking” on a circuit element gives you options for changing values, deleting, etc… Using the “Non-Contact Ammeter” will save you a lot of time! 1 Name: ________________________________ PHYC 101 Summer 2016 Your answers to the questions in this lab activity are to be posted on Blackboard. Go to Blackboard and select Resistor Circuits Laboratory Activity. You only get one opportunity to receive a score on this lab activity, so choose your responses carefully and do not exit Blackboard before recording all of your responses. A Single Resistor Use the computer simulation to construct a simple circuit containing a battery (power supply), a switch, wire, and a single resistor. Use a voltmeter and an ammeter in the circuit so that the circuit’s total voltage and total current can be determined, as well as the current and voltage of the resistor. Manipulate the battery’s voltage and the resistor’s resistance in order to answer the following questions. 1. How do changes in the battery’s electric potential difference (voltage) affect the total voltage of the circuit? 2. How do changes in the battery’s electric potential difference (voltage) affect the voltage across the single resistor? 3. How does the current entering the power supply compare with the current leaving the power supply? 4. How does the current entering the resistor compare with the current leaving the resistor? 5. What happens to the total current in the circuit as the resistor’s resistance is increased? 6. What happens to the voltage across the resistor as the resistor’s resistance is increased? 2 Name: ________________________________ PHYC 101 Summer 2016 Multiple Resistors in Series Use the computer simulation to construct a simple circuit containing a battery (power supply), a switch, wire, and multiple resistors in series. Use a voltmeter and an ammeter in the circuit so that the circuit’s total voltage and total current can be determined, as well as the current through and voltage across the individual resistors. Manipulate the battery’s voltage and the resistors’ resistances in order to answer the following questions. 7. Examine the total current when the circuit has a single resistor, two resistors in series, three resistors in series, etc… What happens to the total current in the circuit as more and more resistors are connected in series? 8. What is the relationship between the total resistance in a circuit and the resistance values of the individual resistors when multiple resistors are connected in series? 9. What is the relationship between the total voltage in the circuit and the voltages across the individual resistors? 10. What is the relationship between the total current in the circuit and the current through each individual resistor? Equal Resistors in Parallel Use the computer simulation to construct a simple circuit containing a battery (power supply), a switch, wire, and multiple resistors in parallel. Use a voltmeter and an ammeter in the circuit so that the circuit’s total voltage and total current can be determined, as well as the current through and voltage across the individual resistors. Manipulate the battery’s voltage and the resistors’ resistances in order to answer the following questions. Each resistor should have the same resistance value in this section. 3 Name: ________________________________ PHYC 101 Summer 2016 11. Examine the total current when the circuit has a single resistor, two equal resistors in parallel, three equal resistors in parallel, etc… What happens to the total current in the circuit as more and more identical resistors are connected in parallel? 12. What is the relationship between the total resistance in a circuit and the resistance values of the individual resistors when multiple resistors having identical resistances are connected in parallel? 13. What is the relationship between the total voltage in the circuit and the voltages across the individual resistors? 14. What is the relationship between the total current in the circuit and the current through each individual resistor? Unequal Resistors in Parallel Use the computer simulation to construct a simple circuit containing a battery (power supply), a switch, wire, and multiple resistors in parallel. Use a voltmeter and an ammeter in the circuit so that the circuit’s total voltage and total current can be determined, as well as the current through and voltage across the individual resistors. Manipulate the battery’s voltage and the resistors’ resistances in order to answer the following questions. Each resistor should have different resistance value in this section. 15. Examine the total current when the circuit has a single resistor, two unequal resistors in parallel, three unequal resistors in parallel, etc… What happens to the total current in the circuit as more and more unequal resistors are connected in parallel? 16. What can you say about the total resistance in a circuit when more than one resistor is connected in parallel if the resistors are not identical? 17. What is the relationship between the total voltage in the circuit and the voltages across the individual resistors? 18. What is the relationship between the total current in the circuit and the current through each individual resistor? 4 Name: ________________________________ PHYC 101 Summer 2016 Resistors in Combination Many circuits contain resistors that are not totally in series or totally in parallel. Use the simulation to construct a circuit containing a battery comprised of several dry cells in series, an ammeter, a switch, a voltmeter, and two identical resistors in parallel (R1 and R2) that are in series with an additional resistor (R3). Manipulate the values of the 3 resistors (always keeping R1 = R2) in order to develop a method for determining the total resistance of this combination circuit. Experiment with various values until you establish a method for determining the total resistance when 3 resistors are in this type of arrangement. 19. What is the total resistance when R1 = R2 = ? Ohms and R3 = ? Ohms? 20. What is the total resistance when R1 = R2 = ? Ohms and R3 = ? Ohms? Summary Questions #21-24 will appear on Blackboard. 5