* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download United India Association of New England Jointly Sponsors with
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
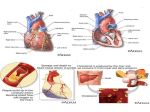
, Salil Midha, MD FACC Chief of Cardiology and Director of Cardiac Cath and Rehabilitation programs Melrose Wakefield Hospital, Melrose, MA President, Boston Cardiac Foundation www.bostoncardiac foundation.org Acknowledgements Thanks to the following web sites for the educational materials American Heart Association CADI Research foundation Mayo Clinic Cardiac Cath. Lab, Melrose, MA Heart Disease Overview Number one cause of death in the world More people die of heart disease than due to cancer and accidents combined Recent treatments have lowered the mortality due to the heart disease Heart Disease Overview Begins in childhood and slowly progresses Causes plaque formation Plaque rupture causes heart attacks and stroke No relation of severity of disease and symptoms Advanced warning of angina in 1/3 rd patients only Half of the sudden deaths occur in undiagnosed Good news – Can be detected by stress test, heart scan and cardiac Catheterization Heart Disease Prevalence Over Age 20 Deaths Due To Heart Diseases Mortality Trends in USA Heart Disease Indian Overview 1.2 Billion people 33% below age 15 50% below age 25 Life expectancy is 64 years in 2008 (USA 75 for men and 78 for females) Only 5.5 % over 65( 65 million) vs. 13% in USA (41 million our of 300 million people) 2.3 million died of heart disease in India vs. 404,000 in USA Coronary Artery Disease in Indians Mortality Ratios In UK Vs. Asia Ethnic Differences Cardiac Mortality in India Stroke Mortality Ethnic Difference Heart Disease Definitions Coronary Artery Disease Angina Heart Attack/ Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart failure Valular Heart disease Arrhythmia like Atrial Fibrillation and Ventricular tachycardia Congenital Heart disease Coronary artery Disease Heart supplies the blood and Oxygen to the rest of the body. Average heart rate is 70 and BP is 120/80 Heart is supplied by three arteries which are known as coronary arteries. These are Left Anterior Descending, left Circumflex and the right coronary arteries Coronary Arteries and Atherosclerosis Heart Attack A heart attack occurs when one or more of the arteries supplying your heart with oxygen-rich blood (coronary arteries) become blocked. Coronary artery can become narrowed from the buildup of cholesterol. This buildup — collectively known as plaques — in arteries throughout the body is called atherosclerosis. Causes of Heart Attack During a heart attack, one of these plaques can rupture and a blood clot forms on the site of the rupture. If the clot is large enough, it can completely block the flow of blood through the artery and cause heart attack Atherosclerosis & Plaque Rupture Angina Condition when patient complain of chest pain due to the lack of blood supply to the heart muscle This generally happens slowly with some warning signs However frequently there is sudden blockage of the vessel due to acute plaque rupture and closure of the artery with clot build up. Symptoms of Heart Disease Pressure, a feeling of fullness or a squeezing pain in the center of your chest that lasts for more than a few minutes Pain extending beyond your chest to your shoulder, arm, back, or even to your teeth and jaw Increasing episodes of chest pain Prolonged pain in the upper abdomen Shortness of breath Sweating Impending sense of doom Fainting Nausea and vomiting Prevalence of Heart Disease Annual Rate of First Heart Attack Estimated 10 Risk of Heart Attack Deaths Due To Heart Disease In USA RISK FACTORS IN ASIAN INDIANS LDL Major risk factor Age Adjusted CAD Death Rates High Calcium Score and LDL Regional Differences In India Overview of Diet Significantly modifiable risk Change saturated and trans fats with poly and monounsaturated foods Olive and Canola oils are monounsaturated Soybean and sunflower oils are polyunsaturated Total fat calories should be 25% of diet and saturated foods should be less than 7% Omega 3 and 6 are found in oily fish, nuts and seeds. Decrease salt intake and increase fruits and vegetables Corn Oil v Coconut Oil Metabolic Syndrome for Indians Increased risk of Diabetes and heart attack Abdominal obesity High cholesterol High Blood pressure Low LDL( good cholesterol) High triglycerides Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence of Obesity in USA Obesity Overview Major modifiable risk Over 400 million people are obese Over 1.6 billion people are overweight Caused by overeating and lack of physical activity Incidence of Diabetes increased 3 fold in men and 5 fold in women Preventable Shortens life span by 3 years Progression of Obesity Prevalence of Hypertension Diabetes Awareness, Treatment and Control Annual Cost of Heart and Stroke Effects of Niacin on Cholesterol Projected Annual Cost By 2030 Indians Vs. White Populations 2-4 fold prevalence rate 10 years earlier incidence of heart attack 10 fold increase in young adults( below age 40) 3 vessel disease in young postmenopausal women Higher chance of death with heart attack Disease occurs with low body index and with near normal BP and cholesterol. Obesity in Asian Indians Risk factors for Heart Disease Age over 40 High Cholesterol and triglycerides Cigarette smoking Hypertension Diabetes Mellitus Family History of heart disease Lack of physical activity Obesity Stress Illegal drug use Prevalence of Smoking Heart Attack Rx & Medications Aspirin Blood thinner Super Aspirins like Plavix(clopidogrel) Nitroglycerin Beta blockers Cholesterol-lowering medications Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors Coronary angioplasty and stenting Coronary artery bypass surgery Statin Treatment Difference Risk Factors INTERHEART Study Elevated cholesterol ratio. High Apo B combined with low Apo A levels Smoking Diabetes Hypertension Abdominal Obesity Stress and depression Failure to eat vegetables and fruit daily Failure to exercise Failure to drink small amount of alcohol Support and Coping after Heart Attack Anger Guilt Depression Cardiac Rehabilitation Support groups Calories by Beverages in USA Framingham Risk Score-10 year While male 16% White female 11% Indian male 32% Indian female 22% Risk for Indians is at least twice as compared to White population. Body Mass Index BMI = Weight in pounds / Height in inches Your body mass index (BMI) is an estimate of your body fat that is based on your height and weight. Doctors use BMI, along with other health indicators, to assess an adult’s current health status and potential health risks. Exercise guidelines 100 % of your heart rate = 220 – your age If your are 30 220-30 = 210 Achieve 70% of your peak heart rate for 30 minutes of exercise 3 days per week Life Style Changes for Prevention Lifestyle changes Medications compliance Not smoking Controlling certain conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol and diabetes Staying physically active Eating healthy foods Maintaining a healthy weight Reducing and managing stress Life Style and Home Remedies Smoking cessation- Single most important thing Avoid second hand smoke –no ash trays in home Check your cholesterol – know your HDL and LDL Control your Blood Pressure –Ideal below 120/80 Exercise regularly Maintain healthy weight-know your BMI-waist line Eat Healthy diet- low fat/saturated fats Vegetarian diet and white meat only-avoid red meat Manage stress decease alcohol content CAD Risk in 60 Year Old Helpful Guides This presentation can be viewed anytime at www.bostoncardiacfoundation.org Other helpful sites CADI research American Heart Association Mayo Clinic Recommended Treatment For Indians thank you for listening!