* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3: Plate Tectonics: Test Review
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
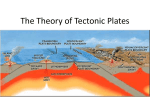
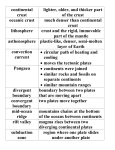
Unit 3: Plate Tectonics: Test Review Continental Drift 1. What is the large landmass when continents were joined together? Pangea 2. What is the hypothesis of continental drift? Continents drifted to their current location after Pangea. 3. Who proposed the hypothesis of continental drift? Wegener 4. What are the three evidence clues for continental drift? - Climate Clues - Rock Clues - Fossil Clues 5. What was the Glossopteris? A fern-like plant which only grows in warm climates. Found in Antarctica. 6. Where was it found? Antarctica, South America, India, Africa and Australia. 7. How did it prove the existence of Pangaea? The continents which are now in cooler climates, could not have supported the growth of Glossopteris proving the continents must have been in a warmer climate at one time. Plate Tectonics 8. In which layer of the Earth is magma formed? Mantle/Asthenosphere 9. Which layer provides the heat? Core 10. What do we call the large sections of the Earth’s crust? Plates 11. What are convection currents? A cycle of heating, rising, cooling, and sinking which is thought to be the force behind plate tectonics. 12. Is hot water more or less dense than cold water? Less dense 13. What causes magma to rise to the surface? Heat and density. 14. What causes Earth’s plates to move? Convection Currents 15. What could cause the plates to stop moving? No heat source/Outer core became solid 16. What are the three types of plate boundaries? Transform, Convergent, and divergent 17. What Geologic activities occur at each type of boundary? Transform: Earthquakes Convergent: Earthquakes, Mountains, Volcanoes, Subduction Zone/Trench Divergent: Ridges/ Mountains, Volcanoes, Rift Valleys and Seas, Earthquakes 18. What is the “zone” where continental and oceanic crust meet and the oceanic crust sinks below the continental crust? Subduction Zone 19. What type of plate boundary causes this “zone”? convergent 20. What type of boundary is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge an example? Divergent 21. Which two plates are to the left of the Mid- Atlantic Ridge? North American and South American 22. Which two plates are to the right of the Mid- Atlantic Ridge? African and Eurasian 23. What type of boundary is the San Andreas Fault? Transform 24. What occurs at the San Andreas Fault? (Earthquakes, Mountains and/or volcanoes)? Earthquakes 25. What type of plate boundary is found at the location of the Himalayan Mountains? Convergent 26. What occurs at the Himalayan Mountains? (Earthquakes, Mountains and/or volcanoes) Mountains, Earthquakes Sea Floor Spreading 27. Who came up with the theory of Sea Floor Spreading? Hess 28. What happens during this process? Hot, less dense material rises to the surface and cools to form a ridge/ mountains. 29. What type of boundary does it occur along? Why? Divergent, because it is spreading. 30. Is new crust created, destroyed or neither? Created 31. What happens when continental crust meets continental crust? Mountains