* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiratory System Team-Game
Survey
Document related concepts
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
High-altitude adaptation in humans wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
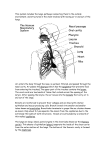
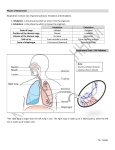
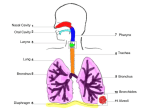
Respiratory System Team-Game-Tournament Review Game Questions 1. The entrance of air into and out of the lungs is called… 2. The exchange of gases between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the pulmonary capillaries is called… 3. The exchange of gases between the body cells and the blood in the systemic capillaries is called … 4. In body cells, the use of oxygen and glucose to produce ATP is called… 5. Name three functions that are performed by the conducting portion of the respiratory system? 6. Name the chamber behind the oral cavity and beneath the nasal cavity? 7. Name the piece of tissue that prevents food or drink from entering the trachea? 8. Name three structural adaptations that the nasal cavity has in order to filter, moisten and warm incoming air? 9. Where are your vocal cords located? 10. Name the cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi. 11. Name the two tubes that branch from the trachea and lead to the bronchioles? 12. Name the numerous, tiny tubes that lead to the alveoli? 13. What surrounds the exterior of every alveolus? 14. Name the cartilaginous structure that serves as a passageway fro air between the pharynx and the trachea? 15. What adaptation does that trachea have that ensures air is always able to pass through to the lungs? 16. What adaptation does the trachea have that ensures that particulate matter is swept out of the lungs, through the trachea and out of the respiratory system? 17. What is the primary function of the alveolus? 18. Name three structural adaptations that the alveoli have that facilitate gas exchange? 19. What are two functions of the surfactant present in the alveolus? 20. Name the bones that form the thoracic cavity. 21. Name the dome-shaped horizontal sheet of muscle that forms the base of the thoracic cavity? 22. The lungs are enclosed by two membranes called the … 23. The space between the pleural membrane lining the lungs and the pleural membrane lining the thoracic cavity is called…? 24. What happens to the diaphragm and rib cage during inhalation? 25. What happens to the diaphragm and rib cage during exhalation? 26. What is the primary stimulus for inhalation? 27. What is the primary stimulus for exhalation? 28. What is the secondary stimulus for inhalation? 29. What part of the brain contains the respiratory center? 30. What part of the body measures declining oxygen levels as a stimulus for inhalation? 31. How is the bulk of oxygen carried in the blood? 32. What is the name of hemoglobin when it is bound to oxygen? 33. What is the name of hemoglobin when it is bound to carbon dioxide? 34. What is the name of hemoglobin when it is bound to hydrogen ions? 35. How is the majority of carbon dioxide transported in the blood? 36. Name the enzyme that catalyzes the reversible reaction between carbon dioxide and water? 37. What does hemoglobin prefer to bind to first and foremost? 38. What are the temperature and the pH in the body tissues? 39. What are the temperature and the pH in the lungs? 40. How does low temperature and high pH affect hemoglobin’s binding of oxygen? 41. How does high temperature and low pH affect hemoglobin’s binding of oxygen? 42. How many polypeptides are contained in one hemoglobin molecule? 43. How many oxygen atoms can one hemoglobin molecule carry at one time? 44. Name the metal ion associated with the hemoglobin molecule? 45. Even though hydrogen ions are produced during internal respiration, the pH of the blood in the systemic capillaries does not decrease dramatically. Why? 46. In external respiration, hydrogen ions must recombine with bicarbonate ions to release carbon dioxide from the blood. Where do these hydrogen ions come from? 47. Describe three functions of bicarbonate ions in the human body? 48. Why must the thoracic cavity be airtight in order for breathing to occur? 49. Is inhalation under autonomic nervous system or central nervous system control? 50. The maximum amount of air that can be moved into the lungs plus the maximum amount of air that can be moved out of the lungs on a single breath is called…? Respiratory System Team-Game-Tournament Review Game Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. breathing external respiration internal respiration cellular respiration bulk flow of air to alveoli; filter air; moisten air; warm air pharynx epiglottis hair, mucus, blood capillaries larynx trachea bronchi bronchioles blood capillaries larynx rings of cartilage keep the trachea open cilia gas exchange by diffusion large surface collectively; one cell layer thick; surfactant on interior of alveolus; blood capillaries surrounding exterior of alveolus facilitate diffusion, and prevent collapse of alveolus on exhalation rib cage diaphragm pleural membranes interpleural space diaphragm contracts and flattens out; rib cage moves up and out diaphragm relaxes and forms a dome; rib cage moves down and in rising carbon dioxide levels stretch receptors surrounding each alveolus are stimulated falling oxygen levels medulla oblongata carotid bodies in carotid arteries, and aortic bodies in aorta attached to hemoglobin as oxyhemoglobin oxyhemoglobin carbaminohemoglobin reduced hemoglobin as a bicarbonate ion carbonic anhydrase oxygen 38 C and pH 7.38 37 C and pH 7.40 at low temperature and high pH, hemoglobin is in excess of 90% saturated with oxygen at high temperature and low pH, hemoglobin is only about 60-70% saturated with oxygen 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. four eight iron the hydrogen ions are grabbed by hemoglobin to form reduced hemoglobin reduced hemoglobin gives up the hydrogen ions in order to grab oxygen from the alveoli buffer pH in the cells; neutralize acidic chyme from stomach; transport carbon dioxide in the blood if there is a hole in the thoracic cavity, air will rush into the thoracic cavity and squeeze on the exterior of the lung, thereby preventing inhalation autonomic nervous system control, with conscious influence vital capacity