* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6.3 Gravity and Orbits
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Giant-impact hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
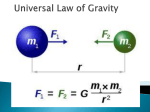
Chapter 6 the Solar System Lesson 3 Gravity and Orbit Vocabulary Gravity (318) – is a force of attraction or pull between two objects Orbit (320) – path one object takes around another object Inertia (320) – a tendency of a moving object to keep moving in a straight line. Ellipse (321) - a nearly circular orbit Tide (322) – the rise and fall of the ocean’s surface Main Idea The force of gravity keeps the planets in their orbits around the sun. What is gravity? Main Idea The pull of gravity depends on the masses of two objects and the distance between them Supporting Details Each planet in the solar system is drawn towards the sun by its gravity. Gravity is the force of attraction, or pull, between two objects. o Gravity is affected by: The mass of two objects The distance between the two objects Gravity is stronger when objects are closer Gravity is weaker the farther apart the objects are. Since all objects have mass, all objects are pulled towards one another by gravity. Mass stays the same, but weight can change depending on the gravity. o Weight is the product of gravity and mass. o One’s weight is less on the moon as the moon’s gravity is less than the Earth because its mass is less than the Earth. o One’s weight is greater on Jupiter as Jupiter’s gravity is greater than the Earth because its mass is greater than the Earth. What keeps objects in orbit? Main Idea An object stays in orbit because the pull of gravity is balanced by its forward motion. Supporting Details An orbit is a path one object takes around another object. o Planets orbit around the sun o Moons orbit around planets Planets are held in their orbits by the force of gravity and each planet. All objects have a property called inertia. o Inertia is the tendency of a moving object to keep moving in a straight line. It is a type of motion. Inertia balanced with gravity causes a planet to revolve around the sun and a moon to revolve around a planet. o Without inertia, the planets would be pulled into the sun o Without gravity, the planets would float into space in a straight line. o Also applies to objects orbiting the Earth. If the inertia is greater than the force of gravity, the object would continue going into space. If the inertia is less than gravitational force, the object would be pulled towards the Earth’s surface. o The effect of the two motions is a nearly circular orbit called ellipse. What causes the tides? Main Idea Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the Sun and the moon on the Earth. Supporting Details The pull of gravity from the moon and the sun causes a bulge or bump on the Earth’s surface. o The affect is slight on the earth’s land. o The affect can be seen in the movement of the ocean’s surface in the form of tides As the moon orbits the Earth each day, its gravity pulls on the ocean surface closest to it. o Low tide occurs when the moon passes over an area. The moon’s gravity is the strongest over the water surface below it It pulls the water away from the land o High tide occurs when the moon is on the opposite side of the Earth. The moon’s gravity is the weakest at this time. Water moves closer to the land Twice a month, the sun and the moon line up o The gravitational effect is greater at this time The effect causes greater high tides and low tides called spring tides. Spring tides occur during full moon and new moons o For the other parts of the planet experiencing 1st quarter and third quarter moons tides are more moderate. Sun and moon are pulling opposite direction partially canceling each other. These tides are called neap tides.