* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sample Exam 2 from 2003
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
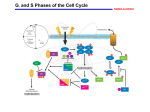
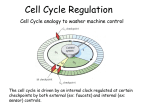
Bio 169 2003 Exam 2 Name___________________________________ Biology 169 -- Exam 2 February 25, 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat: Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific and concise as possible in each answer, noting the suggested length limits described for each problem. Please print name on top of each page! (In case pages get separated.) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------I certify that I have performed my work on this examination in full conformity with the provisions of the Honor Code. Signature___________________________________ 1. (3 points) What important property of the cell cycle was shown by fusing cells in G1 or cells in G2 with cells in S phase (1 or 2 sentences)? 2. (3 points) Describe an important difference between the cyclin dependent kinases that control the mammalian and yeast cell cycle (1 sentence). 3. (4 points) S. pombe cdc2 mutants and S. cerevisiae cdc28 temperature sensitive mutants arrest at different points in the cell cycle. At what point does each of these mutants arrest? Explain why they arrest at different cell-cycle phases (2 sentences). 4. (3 points) What activity prevents the re-initiation of origins of replication during S and G2 phase, and at what time during the cell cycle is this activity removed (2 sentences)? 1 Bio 169 2003 Exam 2 Name___________________________________ 5. (2 points) Human genes that regulate the cell cycle were first isolated by (circle one): a. Biochemical purification b. Complementation of yeast mutants c. Complementation of Xenopus mutants d. Positional cloning 6. (3 points) Describe the difference between a centromere and a kinetochore, and the role they play together during the cell cycle (2 sentences). 7. (2 points) Circle all of the following true statements about eukaryotic S phase. a. There is a single origin of replication in the genome. b. All chromosomes must have at least one origin of replication. c. Each chromosome is replicated twice during S phase of a mitotic cell cycle. d. There are multiple origins of replication in the genome. 8. (5 points) Investigators found that cyclin B concentration rises and falls in synchrony with mitotic events and MPF activity. However, correlation is not causality. How did they show that cyclin B was responsible for these cell cycle events (4-5 sentences)? 2 Bio 169 2003 Exam 2 Name___________________________________ 9. (2 points) Circle any of the following statements that are consistent with the known action of the p21 family of cdk inhibitors (i.e. there could be more than one). a. over expression arrests mammalian cells in G1 phase b. prevent the transcription of cdk genes c. simultaneously bind cyclin and cdk d. interact only with unbound cdk proteins 10. (2 points) Mitotic cyclin levels in early Xenopus embryos are regulated by (circle the best answer): a. phosphorylation b. synthesis and degradation of their mRNAs c. ubiquitination by APC during mitosis d. transcription by MPF 11. (2 points) Circle any of the following statements that are consistent with the known action of the S. pombe wee1 protein (i.e. there could be more than one). a. phosphorylates cdc2 on Tyr15 b. phosphorylates cdc2 on Thr 161 c. inhibits the kinase activity of cdc2 protein d. dephosphorylates and activates CAK kinase e. dephosphorylates Tyr15 of cdc2 13. (2 points) The restriction point in mammalian cells is equivalent to (circle one): a. the anaphase stage of M phase b. START in S. cerevisiae c. the point at which the spindle forms d. G2-M control in S. pombe 3 Bio 169 2003 Exam 2 Name___________________________________ 12. (2 points each) For each of the following situations in S. pombe, indicate whether a “wee” phenotype, characterized as small cells with a shortened G2 phase, or a G2 arrest phenotype would occur (write either “wee” or “G2 arrest” on the line provided). For temperature sensitive alleles (ts), assume the phenotype was scored at the restrictive temperature. ts mutation of cdc2 _______________ ts mutations of cdc13 _______________ ts mutation of cdc25 _______________ a wee1 mutation _______________ expression of a cdc2 mutant that cannot be phosphorylated on Tyr 15 _______________ expression of a cdc2 mutant that cannot be phosphorylated on Thr 161 _______________ over expression of cdc25 _______________ a dominant, hyperactive cdc2 allele _______________ 14. (1 point) Name one stimulus for quiescent (G0) cells to re-enter the cell cycle? ____________ Name 3 molecular events that occur within cells during G1 after such stimulation (“passage through the restriction point” is not what I’m looking for) (2 points each). 1) _______________________________________________________ 2) _______________________________________________________ 3) _______________________________________________________ 4 Bio 169 2003 Exam 2 Name___________________________________ 15. (2 points each) Assume that a wild type mammalian cell in G0 takes 8 hours to enter S phase after addition of growth factors, and that the Restriction Point occurs 5 hours before the beginning of S phase. Indicate by writing “YES” or “NO” whether a cell will divide at least once or not in each of the following experimental situations. Continuous incubation in cell culture medium containing serum _______________ Incubation in medium containing serum for 6 hours, followed by incubation in medium lacking serum _______________ Incubation in medium containing serum for 3 hours, followed by incubation in medium lacking serum _______________ Incubation in medium containing serum for 3 hours, followed by incubation in medium lacking serum for 30 min, followed by continuous incubation in medium containing serum _______________ 16. (2 points) Which causes cyclin D to be over expressed in mantle cell lymphoma (circle one)? a. gene amplification b. chromosome translocation c. point mutation d. mutation of both alleles to the recessive genotype 17. (1 point) E2F controls the transcription of genes encoding proteins that predominantly act in which phase of the cell cycle? ____________________ 18. (2 points) The components of the mammalian restriction point that when mutated lead to cancer include all of the following except (circle one): a. cyclin D b. p16 c. Rb d. cdc2 19. (2 points each) Name three criteria used to establish that the RB gene had been identified. 1)___________________________________________________________________ 2)___________________________________________________________________ 3)___________________________________________________________________ 5 Bio 169 2003 Exam 2 Name___________________________________ 20. (3 points) Why did Bob Weinberg think that Ted Dryja’s strategy for cloning the RB gene would fail (2 sentences)? 21. (2 points each) Indicated whether the following situations would tend to promote cell cycle progression, inhibit cell cycle progression, or do nothing (use those words). A cell with a mutant E2F that cannot bind to DNA __________________________ A cell with a mutant pRB that cannot bind to E2F __________________________ A cell with a mutant p16 protein that cannot bind to cdk4 __________________________ A cell with a mutant cdk4 that cannot bind to cyclin D __________________________ Expression of a mutant pRB that cannot be phosphorylated by cyclin D/cdk4 __________________________ Expression of a hyper-stable cyclin D protein __________________________ A deletion of the RB gene __________________________ A deletion of both the RB gene and the cyclin D gene __________________________ A deletion of both the RB gene and the E2F1 gene __________________________ Over expression of the p16 gene in an RB mutant cell __________________________ Over expression of the p16 gene in a normal cell __________________________ 6