* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
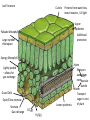
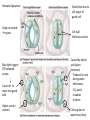
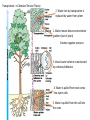
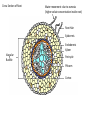
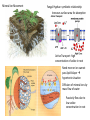
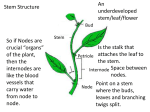
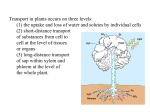
Stem Structure Bud Stem Petriole Internode Node Leaf Structure Cuticle Protects from water loss, insect invasion, UV light Upper epidermis Additional protection Palisade Mesophyll Large number chloroplast Spongy Mesophyll Xylem Transport water from Vein/ rootsVascular Lightly packed – allows for gas exchange bundle Phloem Transport sugar to rest of plant Lower epidermis Guard Cells Open/Close stomata Stomata Gas exchange CO2(g) H2O(g) Xylem Cells Dead Cells Thickened cellulose, lignified 2⁰ walls Strengthens cell walls Waterproofs plant Protects against pathogens Tapered to form continuous column Most modern plants Allows water to mover laterally Ancient plants Stomata Operations Open/close due to cell turgor of guard cell Bulge to outside opens Blue light triggers ATP powered pumps Causes K+ to move into guard cells Higher solute = osmosis Cell wall thickness uneven K+ Caused by absisic acid (plant hormone) Produced in root during water definicency CO2 levels circadian rhythms Cells sag due to water loss (close) Transpiration Cohesion-Tension Theory 2. Water lost by transpiration is replaced by water from xylem 1. Water moves down concentration gradient (out of plant) Creates negative pressure 3. Vessel water column is maintained by cohesion/adhesion 4. Water is pulled from root cortex into xylem cells 5. Water is pulled from the soil into the roots Root Structure Fully differentiated functional cells Root Hairs: increase surface area = more absorption of water/minerals x3 Enlarging cells (G1 phase) Start differentiating Zone of cell division (M phase) ‘Stem’ cells – undifferentiated cells Protects apical meristem Cross Section of Root Water movement: due to osmosis (higher solute concentration inside root) Root Hair Epidermis Endodermis Xylem Vascular Bundle Pericycle Phloem Cortex Mineral Ion Movement Fungal Hyphae: symbiotic relationship Increases surface area for absorption Active Transport: high concentration of solute in root Need more or ion cannot pass lipid bilayer hypertonic situation Diffusion of mineral ions by mass flow of water Passively flow due to low solute concentration in root Movement within roots All particles need to go symplastic at endodermis to get to xylem Water and Minerals Movement between cell walls Movement within cells – water/minerals pass through plasmodesmata Factors that affect transpiration Increase evaporation Reduces difference in water concentration gradient Removes humidity from stomata Less soil water, water stream stopped at roots, stomata close Increase kinetic energy - evaporation Cause guard cells to lose turgor – close stomata Xerophytes thickened Crypt/pit – increases humidity Reduced number Trap water vapor, increases humidity Decreases surface area for transpiration Go dormant in dry months Succulents – fleshy stems Alternative photosynthetic pathway CAM: stomata open at night C4: rapid uptake of CO2 Halophytes: high levels of salinity Sunken stomata Leaf surface area reduced Succulents: dilute salt concentration Compartmentalize Na+ and Cl- in vacuoles Prevents salt toxicity Salt glands: secrete salt