* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Middle Ages Student Notes
Medieval Inquisition wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 11th century wikipedia , lookup
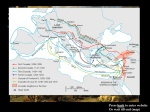
The European Middle Ages The Early Middle Ages What happened to Rome? • By the end of the 5th century, _____________________________ had destroyed the Roman Empire… The Impact of the Invasion… • Disruption of _____________ • Downfall of ___________________ • Population Shifts • Decline of ____________________ • Loss of ______________________________ • BUT, there was one institution that survived the fall of Rome… • The ________________________________________________ !! Between 400 & 600 ___________________________________________ replaced large Roman provinces In ____________________, a Germanic people called the _______________________ held power Influential Frankish Rulers: CLOVIS: Converted to _________________________________________ Gained _____________________________ of the Church in Rome United the _____________________________ into one kingdom Germanic Kingdoms Emerge Influential Frankish Rulers: CHARLES MARTEL: Defeated the _______________________________ at the Battle of Tours (732) He became a Christian ____________________________ His _____________________________ is Charlemagne (Charles the Great) Charlemagne Charlemagne’s Empire • 2/3 of ______________________________ • All of present day ___________________________ • Small part of _______________________________; All of German Saxony Charlemagne’s Accomplishments • Spread ____________________________ through his conquests of other lands • AD 800: Pope Leo III asks for Charlemagne’s help to crush an angry mob __________________ • In gratitude, the Pope _____________________Charlemagne & called him “_________________” WHY does this matter? Christian pope crowned a German king as the successor to the _____________________________ Gave him ________________________________ over the former Roman Empire Revived the idea of a UNITED CHRISTIAN _________________________________ Would eventually lead to future power _____________________ between the popes & emperors Charlemagne in Power Government: appointed _______________________ to rule over local regions; Strong, efficient, & orderly Revived ______________ learning: grammar, rhetoric, logic, arithmetic, geometry, music, astronomy Became educational _________________ for medieval _____________________________ The End of Charlemagne Charlemagne’s son (Louis the Pious) is ____________ to the throne; __________________________________ Louis’s sons _________________________ for control of the empire; civil war! Ends in 843; empire is divided into _________ kingdoms Charlemagne’s Legacy Extended ____________________________ into N. Europe Further blended ______________, ___________________& Christian traditions Educational ________________________;Government style is _________________________ by future leaders Rise of Feudalism & the Manor System Problems in Europe • • • • • • The destruction of Charlemagne’s empire led to widespread _____________________ in W. Europe Political turmoil, _________________________, enemy invasions & __________________________ Invaders attack! ______________________________ nomads, Muslims Central authority was __________________________________ to protect people from this chaos So who did Europeans look to for protection? ________________________________(aka ____________________) • • Led to a new system of ______________________________ & landholding Feudalism: Political, ___________________________ & __________________________ system based on mutual _________________________ between lords & vassals Emergence of Feudalism OBLIGATIONS STATUS Protection & land for his vassals Loyalty to his lord & defense of his lord’s land in exchange for a fief (_______________________________________); could be poor or wealthy Loyalty to his lord (military service, payments, & advice) in exchange for a _______________; could be wealthy nobles or serfs (__________________________) Social Classes are well-defined - The medieval feudal system divides people into 3 social groups: - Those who _________________(nobles, knights); those who ___________________ (monks, nuns); those who __________________ (peasants)- Social class is usually inherited; majority of people are __________________________ - Most peasants are ________________________ - people lawfully bound to a place of birth - Can’t be ___________________________________, can’t leave land without lord’s ____________________________; what they produce belongs to their ___________________ Manorialism • • • • • • • • • • • Manor: The Lord’s ______________________________ Manorialism: the ________________________________side of feudalism Manors varied in __________________ & included the lord’s _____________________, pastures and _____________________, forested areas, a church, & a village where _________________ lived The goal of every manor was to be ___________________________________; Why? The harshness of manor life Peasants pay _____________ to use mill, bakery, etc… Pay a __________________ to the priest Tithe: _________________________________; equal to 1/10 of a peasant’s income Serfs live in crowded cottages with _____________________ floors, ______________________ beds Daily life consists of raising crops & livestock; feeding and clothing family Poor diet, illness, malnutrition makes average life expectancy _______ years Serfs generally accept their lives as part of God’s ________________ • • • • Anatomy of a Castle Due to the lack of a strong central authority, ____________________ was VERY common during the Middle Ages Why were castles, or ___________________________ houses, needed? Medieval castles were designed in response to the ___________________ they had to withstand Common Features: Stone, thick walls, rounded towers, reinforced doors, moat & __________________ • • • • • The World of Nobles __________________ was a way of life Constant battle for _____________________ between nobles From boyhood many nobles were trained to become ______________________ Feudal lords raised private _____________________ of knights Knights rewarded with ___________________, which provides income; Other activities help knights __________________ for battle • Knighthood Age 7 (_________________): – Sent to the castle of a lord – Trained in weaponry, ______________________, & _________________________ • Age 14 (__________________): – Became a knight’s servant • Age 21 (__________________): – Full-fledged knighthood • Knights compete in __________________________: mock battles characterized by fierce __________________________; Gain experience • Warfare: battles generally fought near _______________________________ • Boiling water, hot oil, molten led & crossbows served to deter ______________________soldiers Code of Chivalry • Chivalry: A code of_______________________ followed by _____________________; a set of ideals for behavior • Required knights to be ____________________, _________________ & honest • Fight fairly; treat captured ______________________ well & with respect; Defend the ______________ • ________________________ & ________________________ women • __________________________________ adopted this view of women • Wrote & performed love songs, poems that praised _______________________ • Traveled; also recited/performed epic ___________________ about heroes and adventures Noblewomen • Lady of the Manor: • While husband was at war, women _________________________vassals & managed the ______________________ • They could inherit __________________, defend the castle, or send knights to _______________ on the lord’s request Role of Religion - During the Middle Ages, the ______________________ Church was the most powerful institution of W. Europe - Catholicism was the center of most people’s ___________________ - The Church taught that: - All people were dependent on God’s ______________________ - To receive God’s grace one had to take part in the _______________________: church rituals - Without sacraments/God’s grace, can’t go to heaven 7 Sacraments: ___________________, Penance, Eucharist, Confirmation, Holy Orders, Matrimony (marriage), Anointing of the sick The Power of Mass - Mass = name for Church services - Mass conducted in _____________________ - Most peasants did not understand it; gave priests lots of _____________________ over people - Peasants got their religious __________________________from statues, paintings, stained glass windows, etc… POPE . Catholic Church Organization . . The Power of the Church o o o o o o o Clergy: religious ________________ Includes Churchy hierarchy + monks/nuns who lived _______________________ from society Monastic Life Men (monks) live in monastery Women (nuns) live in __________________ Both dress simply; aid the community; live separate from the rest of the world Preserve ancient religions works & ancient ___________________ (copy books by hand) Medieval Catholic Church was a powerful political ______________________ Helped to ______________________ Western Europe during the Middle Ages; Canon Law = __________ law Disobedience to the Church could lead to: o Excommunication - __________________ from Church (can’t receive the sacraments, therefore can’t go to heaven) o Interdict: king’s land (& all people in it) would be banned from receiving ________________________ Church became very ______________________ from donations of land & money Donated by nobles who wanted to ensure their _____________________; As a result, nobles begin to dominate & control the Church During this time, monasteries tried to rid the Church of influence from the ______________________ 1059: __________________________ would no longer be chosen by political leaders; would now be chosen by religious figures only (cardinals) Heresy The Church as Judge o The Church was very powerful & had _______________________where it tried people for crimes against the Church o Heresy: denial of Church teachings; one of the biggest _______________________ o Heretics (people who committed heresy) were excommunicated o Heresy considered as bad as _________________________ The Inquisition o A _____________ set up to prosecute heretics in an attempt to outlaw heresy o People could be accused of heresy by their ________________; then they would be investigated by the Church o Often, heretics were tortured so they would _________________________ The Jewish Community o As the Catholic Church grew more powerful, the Jews were blamed for ALL _________________________ o As a result, they were often attacked & killed o Anti-Semitism: the _______________________________ of Jews o Main source of anti-semitism came from flawed interpretations of Christian doctrine The CRUSADES Background During the _________________________________________ in the European Middle Ages Byzantine emperor asks for help from Christian Western Europe against the threatening _____________ Turks Popes begin to call for Crusades – _______________________________ – to gain control of the Holy Land (Jerusalem) Crusaders are promised a place in ___________________________ if they die on a Crusade Over ________________ years several Crusades are launched; all become weaker & soldiers get greedy WHY go on a Crusade? The First Crusade The Second Crusade The Third Crusade Later Crusades Pope wants to reclaim ______________________________ & re-unite Christianity Kings use the Crusades as an excuse to send away ______________________knights Younger sons join Crusades in hopes of earning ___________ or winning _________ through fighting Merchants join the Crusades to gain _________________ through _________________________ Pope promises Crusaders who die a guaranteed place in _______________________ Pope ____________ launches the First Crusade to recover Jerusalem from Muslim rule (1095) Armies from Western Europe pass through ____________________________________________ Crusader armies captured Jerusalem in 1099 and _____________________ Muslim & Jewish residents 4 ‘Crusader states’ are created from captured land Launched after Muslims ____________________________ of a “Crusader State” in 1144 Christian armies ___________________________________________________ the Muslims ___________________________ leads the Seljuk Turks; conquers Jerusalem in 1187 “Crusade of _________________” 3 powerful rulers: ____________ the Lionhearted (England); Philip II (France); Frederick I (Germany) Richard I ____________________________________ with Saladin in 1192 Agreement between Saladin & King Richard gives Jerusalem to ___________________________, but allows Western pilgrims access to Christian _____________________________________________ Other popes call for later crusades, but each one is __________________________ than the last By the 13th century, the Western powers pose little ___________________________ for the Turks The Crusades weaken Constantinople & the _________________________ of the Byzantine Empire: during the 4th Crusade, Christians _________________________ Constantinople 2 other Crusades strike __________________________ but fail to weaken the Muslims Effects of the Crusades Crusades demonstrate the power of the _________________________________ Merchants expand trade, bringing goods to _________________________ from ________________________ Failure of later Crusades ________________________ pope & nobles, strengthens the power of _______________ Create a lasting ________________________________ between Christians & Muslims High Middle Ages: Changes in Medieval Culture Agricultural Changes Guilds The Commercial Revolution Horses used to plow fields; faster; increases _____________ production & supply The three-field system: Plant and sow __________ fields each year, let ___ field ‘rest’ Increases food production, which in turn increases the _______________________ Guilds: organizations of people with the same ______________________________ Included skilled artisans Set standards for _______________________, wages, prices, working conditions Provide _____________________________ for members Supervise ______________________________for new members Their ________________________ influences government & economy Commercial Revolution: changes in business & ________________________ Merchants develop _____________ to avoid carrying large sums of money around Merchants take out ____________________ to purchase goods Development of _________________________________ Economic changes lead to the growth of _______________ & jobs Between 1000-1150, Europe’s population rises to _______ million; Why? o Serfs leaving the _____________________for opportunities o The revival of ___________________ o Strong _____________________ to protect Towns are uncomfortable: crowded, ____________________, fire hazards The Growth of Cities The Revival of Culture Revival of trade spawns revival of _____________________ and learning Universities began as “_________________________”: An association of people organized for the purpose of teaching & learning Subjects included _______________, theology, & medicine Vernacular: the language of ___________________________ speech Instead of using ________________, people began to speak the language that had developed in their own country Gave each kingdom a separate __________________________________ Made literature accessible to more _____________________________ Dante Alighieri (13th century) Divine Comedy: describes an imaginary _________________ from hell to heaven Geoffrey Chaucer (14th century) Canterbury Tales: describes a group of ____________________ telling tales to entertain each other on the way to a shrine