* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alkene reaction study guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
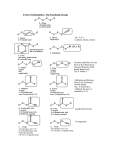
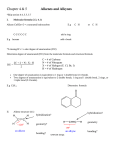
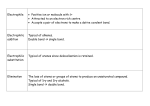
Alkene Reactions Study Guide Leader: Neal Campbell Course: Chem 331 Instructor: Date: Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Purpose Synthesis Name of Reaction Dehydration Dehydrohalogenation Reactions Electrophilic Strong Acid Addition Acid-catalyzed Addition of H20, ROH Oxymercuration Hydroboration Halogenation on Org. solvent Halogenation on Water Catalytic Hydrogenation Epoxide Formation I Epoxide Formation II Trans-1,2-Diol Formation Cis-1,2-Diol Formation Ozonolysis Cleavage Permanganate Cleavage Periodate Cleavage of diols What does it do? Reagents Special Features Removes water (H-OH) Form an alkene from an alcohol Remove H-X Form and alkene from alkane with halogens Addition of one Halogen across the double bond H2SO4, Δ, THF Form MOST substituted alkene –Zaitzev’s NaOH, Δ, EtOH Form MOST substituted alkene – Zaitzev’s HBr, HCl, HI/H3PO4 Addition of Water or alcohol across the double bond. Form alcohol or ether. Addition of Water across the double bond. Form an alcohol Addition of Water across double bond Form an alcohol Addition of two halogens across double bond Addition of halogen and OH across double bond. Form Halohydrins Reduction of double bond. Addition of two H Forms an epoxide across the double bond Start with halohydrin Eliminates water, -X and forms epoxide in between Start with epoxide Opens the epoxide, adds two OH on adjacent carbons Adds two OH on adjacent carbons of double bond Cuts through double bond and forms ketones/aldehydes Cuts through double bond and forms ketones, carboxylic acids and CO2 Start with 1,2 diol. Cuts in between and replaces OH with ketones H2O, ROH, H2SO4, Δ Br/Cl/I go to MOST substituted Carbon – Markovnikov’s OH or OR go to MOST substituted carbon – Markovnikov’s Markovnikov’s alcohol product. Anti Addition Hg(OAc)2, NaBH4,THF, H2O BH3, H2O2, -OH Cl2, Br2, NBS, DMSO, CH2CL2 Cl2, Br2, NBS, H2O H2, Pd/C or PtO2 in CH3COOH MCPBA Anti-Markovnikov’s alcohol product. Syn addition Anti Addition Markovnikov, -OH is the negative part Anti Addition Syn Addition. Only works with C=C bonds NaOH, EtOH H3O+ Anti Reaction – Trans products OsO4, Pyridine, Syn reaction – Cis NaHSO3, H2O products O3, Zn, CH3COOH Only works with C=C bonds + KMO4, H3O Only works with C=C bonds HIO4 Only works with 1,2 diols Radical Polimerization Dichloro Carbene Addition Simmons-Smith Reaction Start with alkene. Chain grows by reacting with monomers (repeating unit) Start with alkene. Form a cyclic propane (triangle) with 2 chlorines on the tip Start with alkene. From a cyclic propane (triangle). Initiator CHCl3, KOH Creates a 3-membered ring with chlorines CH2I2, Zn(Cu), Ether Creates a 3-membered ring Tips for Multistep Synthesis Problems: o Work Backwards – analyze the product and look for something “special” (alcohols, cyclopropane). o Think which reactions could have yielded the product given. o Look for differences between the original and the final compounds (for example, if there is a chlorine present at the beginning and none at the end, there must have been a dehydrohalogenation or epoxide formation from halohydrin). o If the starting compound is an alkane with no functional groups, the first step will be to do a radical chlorination or bromination (to add some functionality). o Pay careful attention to cis or trans position of groups at the end product – they will tell you something important about the reaction used. o Keep in mind that you can add 1 or 2 halogens as needed. o Keep in mind that you can change the position where the alcohol ends up (depending on where you need the alcohol)