* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter vocabulary graphic organizer
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
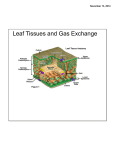
Chapter 1: Plants and How They Grow Concept web Leaves make sugar and oxygen Leaves use water, carbon dioxide, and energy from sunlight Chapter vocabulary graphic organizer Kinds of Trees deciduous coniferous Interacting Parts of a System seedling seed leaf Events in the Life of a Plant pollinate germinate Plant Types No Longer Living fossil extinct system: a set of parts that work with one another deciduous: loses leaves in fall and grows new ones in spring pollinate: move pollen from that part of a flower that makes pollen, to the part of a flower that makes seeds. coniferous tree: a tree that produces seeds in cones seed leaf: part of a seed that has stored food germinate: begins to grow (pg. 20) seedling: a new, small plant that grows from a seed fossil: remains or mark of a living thing from long ago extinct: no longer lives on Earth Lesson 1 What are the main parts of a plant? There are 4 main parts: leaves, roots, stems, and flowers What do all living things need? Living things need food, water, air and space. Plants make their own food by using energy from the sun Why Plants Need leaves. Leaf system Oxygen Plants make and let out oxygen gas when they make sugar Gas Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through tiny holes on its underside. Sun Plants need energy from the Sun to change carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen Leaf Veins Tiny tubes called leaf veins deliver water to the leaf. They also carry sugar made in the leaves to the rest of the plant Sugar The leaves make sugar for food that passes through the stems to the rest of the plant Water enters the leaf from the roots and stem What are other ways leaves help plants? They balance the amount of water plants take in by letting some water out through the tiny holes on the underside. In dry places leaves have waxy or fuzzy coatings to help keep water in Leaves help a plant from being eaten because they can be poisonous, sharp, or tough to chew. Using the above information students should be able to answer the following questions: 1. How are plants and animals similar? They need food, air, water and space to live and grow 2. What can plants do that animals cannot? Plants can make their own food. 3. How is the structure of an oak tree the same as a tomato plant? An oak tree and tomato plant are both plants. They both have leaves, roots, stems and flowers. 4. What is the purpose of the tiny holes in a leaf? They allow oxygen to pass out of the leaf and carbon dioxide to enter the leaf. 5. Explain how a leaf helps a plant control its water amount. A leaf lets out water through its tiny holes if there is too much water in the plant. In dry places, leaves have fuzzy or waxy coatings that help keep water in. 6. What might happen to a plant if you taped the bottom of its leaves? The plant would die because it could not get or gives off the gases it needs or give off water. Lesson 2 Why do plants need roots and stems? Roots help plants Hold the plant in the ground Take in water and materials called minerals from the soil. Store food made by the plant Taproots are large roots such as carrots, dandelions and beets Water and minerals travel up the root through tubes to the stem and leaves Water enters the root through the root hairs Stems help plants Holds up the leaves, flowers, and fruits They have tubes that move water and minerals from the roots of the plant to the leaves. Other tubes carry food from the leaves of plants to the stems and roots Parts of some stems grow underground. A potato is this kind of stem. These kinds of stems can sprout new stems from buds such as the potato’s “eyes.” They grow upward to form a new plant. Different kinds of stems Stolons: thin and grow along the surface of the ground. They can grow roots and a new plants Vines: grow parts that wrap around objects that support the plant Cactus stems These swell us as they store water/ the stems shrink as the plant uses water They also have thick, waxy covering to help keep them from losing water Have spines growing out of it which is a special kind of leaf that keeps animals from eating it Using the above information students should be able to answer the following questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is a taproot One large root that grows deed into the soil How do tiny root hairs help a plant? They take in water Why do you think carrots and beets are such thick roots? They hold a lot of water, nutrients, and food for the plant How do roots help a plant? They hold up the plant, take in water and minerals and store food made in plant leaves. What materials do the stem tubes move? Water, minerals and food 6. How is the movement of water different from the movement of food in plant stems? Water moves from the roots to the leaves, while food moves from the leaves to the stems and roots. 7. How do stems help a plant? Stems support leaves, flowers and fruits. They carry food from the leaves to the roots. Some stems help protect the plant form enemies 8. How are roots and stems alike and different? Alike: they help support plant and transport materials. Different: roots are below ground, while stems are usually above round; some stems help make food or store water, some roots store food. 9. Suppose that the stem branch of a plant is cut. Why do the leaves on the cut branch wilt and turn yellow while the other leaves remain healthy? The tubes that carry water and minerals from the roots to the leaves have been cut, so the leaves on the cut branch do not get the materials they need to survive.