* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
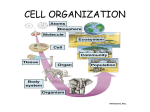
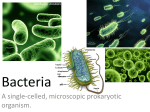
5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms [176216] Student Class Date 1. Which statement would most likely be found in an article about multi-celled organisms like plants? A. Plants have a simple structure. B. Plants contain only one cell that performs all functions. C. Plants do not need to eat, remove waste, or reproduce. D. Plants contain many specialized cells that perform different functions. 2. How is a plant different from bacteria? A. A plant is a multi-celled organism in which each cell performs a specific function. Bacteria is a single-celled organism in which one cell performs all functions. B. Bacteria is a multi-celled organism in which each cell performs a specific function. A plant is a single-celled organism in which one cell performs all functions. C. A plant is a multi-celled organism in which one cell performs 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 1/13 all functions. Bacteria is a single-celled organism in which each cell performs a specific function. D. Bacteria is a multi-celled organism in which one cell performs all functions. A plant is a single-celled organism in which each cell performs a specific function. 3. Why do humans require many different types of cells to survive? A. Human cells are identical and work together to perform the same function. B. Human cells are specialized and work together to perform the same function. C. Human cells are identical and work independently to perform different functions. D. Human cells are specialized and work independently to perform different functions. 4. Fungi and bacteria are both single-celled organisms. What do they most likely have in common? A. Both fungi and bacteria are large organisms. B. Both fungi and bacteria can carry out all life functions in their one cell. 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 2/13 C. Both fungi and bacteria need sunlight and nutrients from the soil to be able to grow. D. Both fungi and bacteria are highly specialized to do only one job so they must work with other cells to obtain food. 5. Which must a single-celled and a multi-celled organism both be able to do? A. hunt B. mate C. get nutrients D. talk to each other 6. Bacteria often live inside the body of a living host, such as a dog. Which best describes how bacteria carry out the processes necessary for survival? A. Bacteria borrow cells from the host to carry out life processes. B. Bacteria use their many different cells to carry out life processes. 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 3/13 C. Bacteria are made up of one cell which is responsible for carrying out all life processes. D. Bacteria use their many different cells as well as cells from the host to carry out life processes. 7. An organism can only be seen through a microscope. Which is most likely true of that organism? A. It is a plant. B. It is an animal. C. It is multicellular. D. It is single-celled. 8. How is it possible for single-celled organisms to survive? A. They are small and can easily avoid predators. B. They have all of their needs met within one cell. C. They have adapted to live only in specific environments. D. They depend on other cells to obtain food, water, and other 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 4/13 resources. 9. Which is an example of a single-celled organism? A. bird B. spider C. human D. amoeba 10. Which organism only requires one cell to carry out all life processes? A. tree B. snake C. bacteria D. mushroom 11. What is the main distinction between multi-celled and single- celled organisms? 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 5/13 A. size B. shape C. number of cells 12. Which device works similar to the way kidneys work in the human body? A. A refrigerator stores food similar to the way kidneys store nutrients the body needs. B. A thermostat controls temperature similar to the way kidneys control body conditions. C. A wire transports electrical energy similar to the way kidneys transport energy to cells. D. A strainer separates water from noodles similar to the way kidneys remove waste from cells. 13. Which is responsible for providing oxygen to cells? A. skeletal system B. digestive system C. muscular system D. circulatory system 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 6/13 14. Which best describes the relationship between the skeletal system and the circulatory system? A. The skeletal system transports red blood cells after the circulatory system produces them. B. The skeletal system protects red blood cells and the circulatory system pumps those cells through veins and arteries. C. The skeletal system produces red blood cells and the circulatory system transports those cells where they need to go. D. The skeletal system helps put oxygen in red blood cells and the circulatory system helps those cells rid the body of carbon dioxide. 15. In which system does the heart work to move blood throughout the body? A. digestive system B. muscular system C. respiratory system D. cardiovascular system 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 7/13 16. Which is an example of a function the muscular system performs? A. Voluntary muscles pump blood through the body. B. Skeletal muscles keep a body’s joints working properly. C. Cardiac muscles move bones and hold a body’s skeleton in place. D. Smooth muscles help move food through the organs they surround. 17. How does the circulatory system work with the digestive system? A. Blood is used to build muscle strength. B. Food is broken down in the bloodstream. C. Blood carries nutrients throughout the body. D. Food waste is filtered by the heart and blood vessels. 18. Which body system is responsible for supplying the body with oxygen and removing carbon dioxide? 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 8/13 A. nervous B. digestive C. muscular D. respiratory 19. Which two systems work together to help a person stand erect? A. skeletal and muscular B. skeletal and digestive C. skeletal and respiratory D. skeletal and cardiovascular 20. Why is the digestive system important? A. It transports blood that cells need. B. It provides oxygen that cells need. 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 9/13 C. It provides nutrients that cells need to produce energy. D. It carries carbon dioxide and oxygen away from the body. 21. How does the muscular system depend on the nervous system? A. The nervous system transports blood to the muscles. B. The nervous system provides support for the muscles. C. The nervous system supplies food and oxygen to the muscles. D. The nervous system sends signals to the muscles to cause movement. 22. How does the skeletal system benefit the digestive system? A. It protects organs within the system. B. It supplies blood to organs within the system. C. It provides oxygen to organs within the system. D. It provides nutrients to organs within the system. 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 10/13 23. How does the skeletal system benefit the nervous system? A. It protects the lungs. B. It protects the heart. C. It protects the brain and spinal cord. D. It protects the esophagus and stomach. 24. Which system is responsible for creating red blood cells? A. skeletal B. nervous C. muscular D. circulatory 25. Which best describes the system of the human body that breaks down food for cell energy? A. cardiovascular system 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 11/13 B. respiratory system C. circulatory system D. digestive system 26. Which body system coordinates and communicates with all other body systems? A. respiratory system B. circulatory system C. digestive system D. nervous system 27. Why do the other body systems depend on the circulatory system? A. It protects the organs of other body systems. B. It produces energy for the other body systems. C. It picks up waste materials from other body systems. 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 12/13 D. It sends messages from the brain to the other body systems. 5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Page 13/13