* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Roman Republic - White Plains Public Schools
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Structural history of the Roman military wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
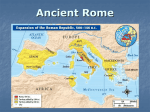
The Roman Republic World History/Napp “According to legend, the city of Rome was founded in 753 B.C. by Romulus and Remus, twin sons of the god Mars and a Latin princess. The twins were abandoned on the Tiber River as infants and raised by a she-wolf. The twins decided to build a city near the spot. In reality, it was men not immortals who built the city, and they chose the spot largely for its strategic location and fertile soil. Rome was built on seven rolling hills at a curve on the Tiber River, near the center of the Italian peninsula. It was midway between the Alps and Italy’s southern tip. Rome also was near the midpoint of the Mediterranean Sea. The earliest settlers on the Italian peninsula arrived in prehistoric times. From about 1000 to 500 B.C., three groups inhabited the region and eventually battled for control. They were the Latins, the Greeks, and the Etruscans. The Latins built the original settlement at Rome, a cluster of wooden huts atop one of its seven hills, Palatine Hill. These settlers were considered to be the first Romans. Between 750 and 600 B.C., the Greeks established colonies along southern Italy and Sicily. The cities became prosperous and commercially active. They brought all of Italy, including Rome, into closer contact with Greek civilization. The Etruscans were native to northern Italy. They were skilled metalworkers and engineers. The Etruscans strongly influenced the development of Roman civilization. They boasted a system of writing, for example, and the Romans adopted their alphabet. They also influenced Rome’s architecture, especially the use of the arch. Around 600 B.C., an Etruscan became king of Rome. In the decades that followed, Rome grew from a collection of hilltop villages to a city that covered nearly 500 square miles. Various kings ordered the construction of Rome’s first temples and public centers – the most famous of which was the Forum, the heart of Roman political life. The last king of Rome was Tarquin the Proud. A harsh tyrant, he was driven from power in 509 B.C. The Romans declared they would never again be ruled by a king. Instead, they established a republic, from the Latin phrase res publica, which means ‘public affairs.’ A republic is a form of government in which power rests with citizens who have the right to vote for their leaders. In Rome, citizenship with voting rights was granted only to free-born male citizens.” ~ World History Identify and explain the following terms: Romulus and Remus Tiber River Latins, Greeks and Etruscans Palatine Hill Tarquin the proud Republic - What do you consider to be the key characteristic of the early Roman Republic? Why? - How did Rome’s location benefit its people? Patricians, Plebeians and Twelve Tables - Patricians were wealthy landowners who held most of the power in Rome - Plebeians were the common farmers, artisans, and merchants who made up the majority of the population Government Army - Rome had two officials called consuls - The Romans placed - For hundreds of great value on the years after the military founding of the republic, Rome - All citizens who sought to expand its owned land were territories through required to serve in trade and conquest the army - By 265 B.C., the - Roman soldiers Romans were were organized into masters of nearly all large military units Italy called legions - Rome’s location - The Roman legion gave it easy access to was made up of some the riches of the 5,000 heavily armed lands around the foot soldiers Mediterranean Sea (infantry) - However, other - A group of soldiers large and powerful on horseback cities interfered with (cavalry) supported Roman access to the each legion Mediterranean - Consuls commanded the army and directed the government - But a consul’s term was only one year long and one consul could always - Patricians inherited overrule, or veto, the their power and other’s decisions claimed that their ancestry gave them - The senate had the authority to both legislative and make laws for Rome administrative functions in the - The plebeians were republic citizens of Rome with the right to vote - Its 300 senators but could not hold were chosen from the most important the upper class of government Roman society positions - Later, plebeians - In time, Rome’s were allowed in the leaders allowed Senate the plebeians to form their own assembly - In times of crisis, and elect the republic could representatives appoint a dictator – called tribunes a leader who had absolute power to - The written laws of make laws and Rome were called command the army the Twelve Tables and established - A dictator’s power the idea that all free lasted for only six citizens had a right months to the protection of the law - Legions were divided into smaller groups of 80 men, each of which was called a century - The military organization and fighting skill of the Roman army were key factors in Rome’s rise to greatness Expansion - One such city was Carthage, once a colony of Phoenicia - Carthage was located in North African - Rome and Carthage fought three wars known as the Punic Wars - When Rome finally defeated Carthage, it set the city afire and its 50,000 inhabitants were sold into slavery Identify and explain the following terms: Patricians Plebeians Tribunes Twelve Tables Consuls Legions Cavalry Punic Wars - What limits were there on the power of the Roman consuls? - What was the significance of the Twelve Tables? - Do you think the Roman Republic owed its success more to its form of government or its army? Why? - Do you agree with claims that early Rome had achieved a “balanced” government? - How and why did geography turn Rome and Carthage into rivals? - Why did the Carthaginian general, Hannibal, enter Roman territory by crossing the Alps? Mountains are difficult to cross. What was his motivation for such a daring move? The benefit of written laws is that A) A ruler in a bad mood cannot simply change the punishment to satisfy his anger B) consistency is the hobgoblin of small minds – there is no benefit C) Create punishments that are never harsh D) None of the above Rome and Carthage battled over the Mediterranean Sea because A) the best beaches in the world are located on the Mediterranean coast B) by controlling the sea, the victor controlled a very profitable trade route C) none of the above – the sea is not as important as the land - What similarities do you see in the governments of the Roman Republic and the United States? - Which government seems more democratic? Why? Hannibal 247–183 B.C. “When Hannibal was only a boy of nine, his father, Hamilcar Barca, a general in Carthage’s army, made him swear that he would always hate Rome and seek to destroy it. After his defeat at the battle of Zama and Carthage’s loss in the Second Punic War, Hannibal took refuge among Rome’s enemies. He fought against Roman forces as an ally of the kings of Syria and Bithynia. When Roman agents came for him in Bithynia on the Black Sea in Anatolia in 183 B.C., he committed suicide rather than submit to Rome.” - How did Hannibal’s father influence him?