Document
... What is an electrical Current?? • An electric current of Electrons, flowing through wires and electronic components. As the electrons are pushed through pipes by a pump, electric current is pushed through wires by a ...
... What is an electrical Current?? • An electric current of Electrons, flowing through wires and electronic components. As the electrons are pushed through pipes by a pump, electric current is pushed through wires by a ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 1. Define capacitance of a capacitor. 2. What is meant by dielectric constant of a medium? 3. What is Thomson effect? 4. State Faraday’s laws of electrolysis 5. A circular coil has a radius of 0.1m and number of turns 50. Calculate the magnetic induction at a distance of 0.2m from the centre when a ...
... 1. Define capacitance of a capacitor. 2. What is meant by dielectric constant of a medium? 3. What is Thomson effect? 4. State Faraday’s laws of electrolysis 5. A circular coil has a radius of 0.1m and number of turns 50. Calculate the magnetic induction at a distance of 0.2m from the centre when a ...
Chapter 3
... 3) Charge carriers in a metal are electrons rather than protons because electrons are A) smaller. B) loosely bound. C) negative. D) all of these. E) none of these. ...
... 3) Charge carriers in a metal are electrons rather than protons because electrons are A) smaller. B) loosely bound. C) negative. D) all of these. E) none of these. ...
Article #1: How Does An Electrical Generator Work?
... An electrical generator is a simple device that moves a huge magnet near a wire to create a steady flow of electrons, known as an electric current. In large power generators, the coils remain stationary, and the magnetic field rotates. This produces the same effect. The magnet rotates with the turbi ...
... An electrical generator is a simple device that moves a huge magnet near a wire to create a steady flow of electrons, known as an electric current. In large power generators, the coils remain stationary, and the magnetic field rotates. This produces the same effect. The magnet rotates with the turbi ...
Document
... the approximate appearance of the electric field around the fixed charges in each part of the figure below. Include arrows to show the directions of the field lines. ...
... the approximate appearance of the electric field around the fixed charges in each part of the figure below. Include arrows to show the directions of the field lines. ...
Introduction to Physics (in a nutshell) Based on the Physics Worktext
... Isaac Newton – formulated the laws of motion, gravity, discovered the nature and composition of light Aristotle – believed that all things are made of four elements: earth, air, fire, and water Johannes Kepler – discovered that planets follow an elliptical orbit which can be calculated for use in fl ...
... Isaac Newton – formulated the laws of motion, gravity, discovered the nature and composition of light Aristotle – believed that all things are made of four elements: earth, air, fire, and water Johannes Kepler – discovered that planets follow an elliptical orbit which can be calculated for use in fl ...
Real Contents
... Conductors in electrostatic equilibrium Potential difference and electric potential Potential differences in a uniform electric field Electric potential and potential energy due to point charges Electric potential due to continuous charge distributions ...
... Conductors in electrostatic equilibrium Potential difference and electric potential Potential differences in a uniform electric field Electric potential and potential energy due to point charges Electric potential due to continuous charge distributions ...
Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide Name KEY LT 1: I can
... Make sure that battery is fresh and has good connections with wires on both terminals. Check for an “breaks” in the circuit. 4. What causes static electricity? A buildup of electrical charges. Charges can be built up in a particular object, such as a balloon or someone’s hair, or charges can jus ...
... Make sure that battery is fresh and has good connections with wires on both terminals. Check for an “breaks” in the circuit. 4. What causes static electricity? A buildup of electrical charges. Charges can be built up in a particular object, such as a balloon or someone’s hair, or charges can jus ...
Magnets presentation
... Static Electricity occurs when there is a change of matter in an object. Almost all the time matter is electrically neutral. That means that it has the same amount of positive charges and negative charges. When these electrical charges builds up on an object the results are static electricity. ...
... Static Electricity occurs when there is a change of matter in an object. Almost all the time matter is electrically neutral. That means that it has the same amount of positive charges and negative charges. When these electrical charges builds up on an object the results are static electricity. ...
Key words
... A circuit where there is only one loop of wire. A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. A magnet will attract iron, nickel and cobalt. The pattern of attraction around a magnet. This can be seen by using iron ...
... A circuit where there is only one loop of wire. A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. A magnet will attract iron, nickel and cobalt. The pattern of attraction around a magnet. This can be seen by using iron ...
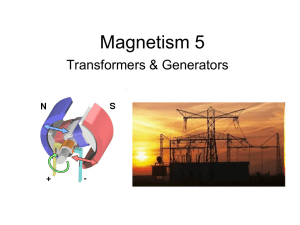
Magnetism 5 Transformers/Generators
... magnets in the generator. Coils of wire surrounding the spinning magnets cut through the magnetic field which induces a current. The current made by the generator goes to the power lines. Power lines bring the electricity to your homes, ...
... magnets in the generator. Coils of wire surrounding the spinning magnets cut through the magnetic field which induces a current. The current made by the generator goes to the power lines. Power lines bring the electricity to your homes, ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.