Lecture32
... Gauss’s laws, Ampere’s law and Faraday’s law all combined! They are nearly symmetric with respect to magnetism and electricity. The lack of magnetic monopoles is the main reason why they are not completely symmetric. ...
... Gauss’s laws, Ampere’s law and Faraday’s law all combined! They are nearly symmetric with respect to magnetism and electricity. The lack of magnetic monopoles is the main reason why they are not completely symmetric. ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... core of the earth gives the earth a magnetic field much like a bar magnet. ...
... core of the earth gives the earth a magnetic field much like a bar magnet. ...
Document
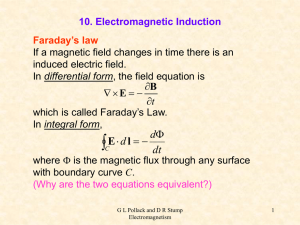
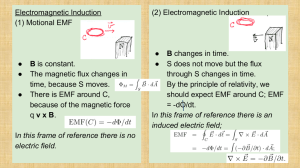
... 10. Electromagnetic Induction Faraday’s law If a magnetic field changes in time there is an induced electric field. In differential form, the field equation is B E t which is called Faraday’s Law. In integral form, ...
... 10. Electromagnetic Induction Faraday’s law If a magnetic field changes in time there is an induced electric field. In differential form, the field equation is B E t which is called Faraday’s Law. In integral form, ...
Document
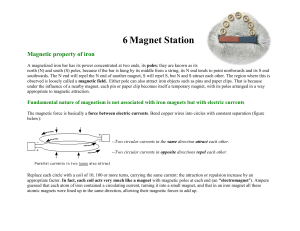
... Replace each circle with a coil of 10, 100 or more turns, carrying the same current: the attraction or repulsion increase by an appropriate factor. In fact, each coil acts very much like a magnet with magnetic poles at each end (an "electromagnet"). Ampere guessed that each atom of iron contained a ...
... Replace each circle with a coil of 10, 100 or more turns, carrying the same current: the attraction or repulsion increase by an appropriate factor. In fact, each coil acts very much like a magnet with magnetic poles at each end (an "electromagnet"). Ampere guessed that each atom of iron contained a ...
buds public school, dubai physics worksheet
... I Very Short Answer Type Questions 1. What is the frequency of an alternating current if its direction changes after 0.01S? 2. How can it be shown that a magnetic field at a point near a wire related to the strength of the electric current flowing in a wire? 3. Name the physical quantity whose SI un ...
... I Very Short Answer Type Questions 1. What is the frequency of an alternating current if its direction changes after 0.01S? 2. How can it be shown that a magnetic field at a point near a wire related to the strength of the electric current flowing in a wire? 3. Name the physical quantity whose SI un ...
Physics 3: Electricity and Magnetism
... The course trains physics, with a focus on both basic principles of electricity and magnetism and practical applications. The purpose of the course is to: i) make the students familiar with the numerous practical applications of electrical circuits and their components as well as magnetic and electr ...
... The course trains physics, with a focus on both basic principles of electricity and magnetism and practical applications. The purpose of the course is to: i) make the students familiar with the numerous practical applications of electrical circuits and their components as well as magnetic and electr ...
Section F22: Electric Motors and Electromagnetic Induction
... a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field, Electromagnetic effects (part 1) Section Questions (1) to (4) and how this effect is applied in simple 5 – Lesson 9 – Electromagnetic effects d.c. electric motors and loudspeakers 6.13 use the left hand rule to predict the direction of the resulting force ...
... a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field, Electromagnetic effects (part 1) Section Questions (1) to (4) and how this effect is applied in simple 5 – Lesson 9 – Electromagnetic effects d.c. electric motors and loudspeakers 6.13 use the left hand rule to predict the direction of the resulting force ...
Unit A – “Life Science”
... 6. Be able to identify the material that conducts electric current poorly. an insulator 7. What happens if a bulb burns out in a series circuit? the other lights will go out 8. How can the strength of an electromagnet be increased? by using more turns in the metal coil 9. Be familiar with what Micha ...
... 6. Be able to identify the material that conducts electric current poorly. an insulator 7. What happens if a bulb burns out in a series circuit? the other lights will go out 8. How can the strength of an electromagnet be increased? by using more turns in the metal coil 9. Be familiar with what Micha ...
Chapter 37: Electromagnetic Induction
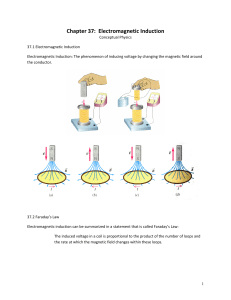
... Chapter 37: Electromagnetic Induction Conceptual Physics 37.1 Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction: The phenomenon of inducing voltage by changing the magnetic field around the conductor. ...
... Chapter 37: Electromagnetic Induction Conceptual Physics 37.1 Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction: The phenomenon of inducing voltage by changing the magnetic field around the conductor. ...
Jeopardy - Petoskey Public Schools
... Find the current produced if the voltage is 56 volts and the resistance is 7 ohms. ...
... Find the current produced if the voltage is 56 volts and the resistance is 7 ohms. ...
Electricity and Magnetism Unit
... • Magnet: an object that attracts the metals iron, cobalt, and nickel • Magnetism: the force of a magnet • Magnetic field: the area around a magnet where its magnetism acts • Electromagnet: a temporary magnet made when electric current flows through a wire coil wrapped around an iron or steel core ...
... • Magnet: an object that attracts the metals iron, cobalt, and nickel • Magnetism: the force of a magnet • Magnetic field: the area around a magnet where its magnetism acts • Electromagnet: a temporary magnet made when electric current flows through a wire coil wrapped around an iron or steel core ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.