Experimental demonstration 1
... Safety precaution: since we use low voltage batteries, there is no risk. However, do not repeat any of this experiment using the higher voltage electricity outlets, which operate on 110V or higher! The batteries provide direct current (DC) in a closed circuit as opposed to the alternating current (A ...
... Safety precaution: since we use low voltage batteries, there is no risk. However, do not repeat any of this experiment using the higher voltage electricity outlets, which operate on 110V or higher! The batteries provide direct current (DC) in a closed circuit as opposed to the alternating current (A ...
Unit V: Electricity and Magnetism
... Compare and contrast conductors, semiconductors, and insulators Differentiate between neutral, charged, and polarized objects Calculate force due to static charges Draw and interpret electric field lines Describe how electrical potential varies around a circuit, including the role of batteries and o ...
... Compare and contrast conductors, semiconductors, and insulators Differentiate between neutral, charged, and polarized objects Calculate force due to static charges Draw and interpret electric field lines Describe how electrical potential varies around a circuit, including the role of batteries and o ...
Electricity (1)
... atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
... atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
14.3 Electrical Power, AC, and DC Electricity
... Electricity in Other Countries For large amounts of electricity, we use alternating current because it is easier to generate and to transmit over long distances. In many other countries, the current reverses itself 50 times per second rather than 60, When visiting Asia, Africa, or Europe, you ...
... Electricity in Other Countries For large amounts of electricity, we use alternating current because it is easier to generate and to transmit over long distances. In many other countries, the current reverses itself 50 times per second rather than 60, When visiting Asia, Africa, or Europe, you ...
Electricity and Magn.. - Caledonia High School
... have north and south poles Like poles repel, unlike poles attract Magnetic Field- where magnetic forces can act Earth ...
... have north and south poles Like poles repel, unlike poles attract Magnetic Field- where magnetic forces can act Earth ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... charged. As electrons leave an object it attains a positive charges. Charges interact with each other: Often when you remove clothes from the clothes dryer, they seem to stick together. This is because some of the clothes have gained electrons by rubbing against other clothes. The clothes losing ele ...
... charged. As electrons leave an object it attains a positive charges. Charges interact with each other: Often when you remove clothes from the clothes dryer, they seem to stick together. This is because some of the clothes have gained electrons by rubbing against other clothes. The clothes losing ele ...
Electromagnetic Waves come in many varieties, including radio
... ∂D/∂t, and so he reformulated Ampère’s law as ∇ ∇×H = J + ∂D/∂t. Maxwell’s equations are essential to the understanding of such things as the electrical and optical properties of matter, the ionosphere, ‘space weather’, solar dynamics and pulsars. New advances, the Large Hadron Collider, also depend ...
... ∂D/∂t, and so he reformulated Ampère’s law as ∇ ∇×H = J + ∂D/∂t. Maxwell’s equations are essential to the understanding of such things as the electrical and optical properties of matter, the ionosphere, ‘space weather’, solar dynamics and pulsars. New advances, the Large Hadron Collider, also depend ...
Seventh Grade Science Lesson Plans Week 23
... Product Target 4.6: Conduct an investigation that provides evidence that fields exist between objects exerting forces on each other even though they are not in contact. ...
... Product Target 4.6: Conduct an investigation that provides evidence that fields exist between objects exerting forces on each other even though they are not in contact. ...
Magnetic Materials Background: 2. Origins of Magnetism
... Origins of Magnetism Almost everyone is familiar with what a magnetic material can do but very few know how a magnet works. To understand this phenomenon one must first grasp the inextricable connection that exists between magnetism and electricity. A simple electromagnet can be produced by wrapping ...
... Origins of Magnetism Almost everyone is familiar with what a magnetic material can do but very few know how a magnet works. To understand this phenomenon one must first grasp the inextricable connection that exists between magnetism and electricity. A simple electromagnet can be produced by wrapping ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... A generator contains coils of wire that are stationary, and rotating magnets are rotated by turbines. Turbines are huge wheels that rotate when pushed by water, wind, or steam. Thus mechanical energy is changed to electrical energy by a generator. Smaller ...
... A generator contains coils of wire that are stationary, and rotating magnets are rotated by turbines. Turbines are huge wheels that rotate when pushed by water, wind, or steam. Thus mechanical energy is changed to electrical energy by a generator. Smaller ...
Presentation - El blog del Séneca
... force. He couldn’t explain the phenomenon. Two other scientists investigated further… ...
... force. He couldn’t explain the phenomenon. Two other scientists investigated further… ...
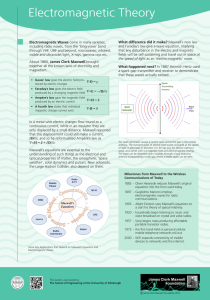
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.