Name: Date: Period: Who is the Father of Atomic Theory? What
... 8. What allows atoms to combine together? 9. Name and describe the type of electrons that are involved in chemical bonds. Name: Describe: 10. Name and describe the two major types of chemical bonds? Bond 1: Describe: Bond 2: Describe: 11. Ionic bonds form between and atoms. ...
... 8. What allows atoms to combine together? 9. Name and describe the type of electrons that are involved in chemical bonds. Name: Describe: 10. Name and describe the two major types of chemical bonds? Bond 1: Describe: Bond 2: Describe: 11. Ionic bonds form between and atoms. ...
Slide 1
... Matter is made of different natural elements: lightest Hydrogen (1 proton), heaviest Uranium (92 protons) Smallest particle of an element is atom, made up of a nucleus (protons and neutrons), and orbiting electrons Electrons and protons attract as opposite electrical charges, NOT gravitationally lik ...
... Matter is made of different natural elements: lightest Hydrogen (1 proton), heaviest Uranium (92 protons) Smallest particle of an element is atom, made up of a nucleus (protons and neutrons), and orbiting electrons Electrons and protons attract as opposite electrical charges, NOT gravitationally lik ...
Example solution to the exercise 1
... Find a way to express the total energy as a function of the radius r. After this you can use the Larmor equation and the chain rule df (x) df (x) dx ...
... Find a way to express the total energy as a function of the radius r. After this you can use the Larmor equation and the chain rule df (x) df (x) dx ...
PYP001-121 Major-I Solution. In all the questions, choice
... D) Every type of atom has a different number of protons. E) The change of state from a gas to a liquid is called condensation. Q2. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A) Carbon dioxide, water, and table salt are examples of compounds. B) Two or more atoms combine to form an isotope. C) The pr ...
... D) Every type of atom has a different number of protons. E) The change of state from a gas to a liquid is called condensation. Q2. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A) Carbon dioxide, water, and table salt are examples of compounds. B) Two or more atoms combine to form an isotope. C) The pr ...
Chemistry II Demonstration Assessment
... Background Information: Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, rearranged, and/or joined in a new way. In this experiment you will decompose the chemical compound you synthesized in the laboratory yesterday. Energy is always required to break the bonds of a compound. You will use a 9 vol ...
... Background Information: Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, rearranged, and/or joined in a new way. In this experiment you will decompose the chemical compound you synthesized in the laboratory yesterday. Energy is always required to break the bonds of a compound. You will use a 9 vol ...
HL Chemistry: Notes Atomic Theory
... All matter can be discussed this way, but since large pieces of matter have such short wavelengths and since very small photons have such small mass, it is easier to discuss them as either matter or energy. However, electrons can be seen to exhibit both wave and particle natures. 5. Atomic spectra o ...
... All matter can be discussed this way, but since large pieces of matter have such short wavelengths and since very small photons have such small mass, it is easier to discuss them as either matter or energy. However, electrons can be seen to exhibit both wave and particle natures. 5. Atomic spectra o ...
Final Review
... Eqn. Be able to come up with the Schrodinger eqn in either Cartesian or Spherical Polar Coordinates. What is din each of these? What are the moment of inertia, center of mass, and reduced mass? What is the angular momentum. What is the magnitude of the angular momentum, and the magnitude of the zt ...
... Eqn. Be able to come up with the Schrodinger eqn in either Cartesian or Spherical Polar Coordinates. What is din each of these? What are the moment of inertia, center of mass, and reduced mass? What is the angular momentum. What is the magnitude of the angular momentum, and the magnitude of the zt ...
CH101 General Chemistry
... Energy of the light is proportional to its Intensity only (intense red light > dim blue light) Waves can have any amounts of energy Kinetic energy of electrons should increase with the light intensity ...
... Energy of the light is proportional to its Intensity only (intense red light > dim blue light) Waves can have any amounts of energy Kinetic energy of electrons should increase with the light intensity ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy
... When a photon of energy is absorbed by a molecule, it causes electronic excitation or mechanical motion to occur. The electronic excitations and motions of a particular molecule are also quantized so only certain frequencies of radiation are able to be absorbed. An analysis of the frequencies of ele ...
... When a photon of energy is absorbed by a molecule, it causes electronic excitation or mechanical motion to occur. The electronic excitations and motions of a particular molecule are also quantized so only certain frequencies of radiation are able to be absorbed. An analysis of the frequencies of ele ...
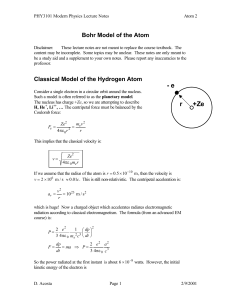
In 1913 Bohr proposed his quantized shell model of the atom to
... electrons in the Rutherford model was unstable because, according to classical mechanics and electromagnetic theory, any charged particle moving on a curved path emits electromagnetic radiation; thus, the electrons would lose energy and spiral into the nucleus. To remedy the stability problem, Bohr ...
... electrons in the Rutherford model was unstable because, according to classical mechanics and electromagnetic theory, any charged particle moving on a curved path emits electromagnetic radiation; thus, the electrons would lose energy and spiral into the nucleus. To remedy the stability problem, Bohr ...
3. atomic structure
... When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy usually in the form of light. This is known as a bright line spectrum, and can be used to identify an element like a fingerprint. ...
... When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy usually in the form of light. This is known as a bright line spectrum, and can be used to identify an element like a fingerprint. ...
Quantum Mechanics
... waves, what else can they do? • They can setup standing waves – Waves with particular wavelength/frequency that appear to not be travelling ...
... waves, what else can they do? • They can setup standing waves – Waves with particular wavelength/frequency that appear to not be travelling ...
atomic theory - unit a
... 1) Each element is composed of small particles called atoms. 2) All atoms of an element are identical to each other. 3) Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. 4) Atoms of one element are different than atoms of another element. 5) Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine. molecul ...
... 1) Each element is composed of small particles called atoms. 2) All atoms of an element are identical to each other. 3) Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. 4) Atoms of one element are different than atoms of another element. 5) Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine. molecul ...
The Wave Nature of Light
... • Therefore, if one knows the wavelength of light, one can calculate the energy in one photon, or packet, of that light: ...
... • Therefore, if one knows the wavelength of light, one can calculate the energy in one photon, or packet, of that light: ...
报告海报
... from the New York University, USA, then He received ITAMP postdoctoral Fellow. Current research interest: Spectroscopy and scattering in atomic and molecular physics for applications to astrophysics, light science, and ultra-low temperature collisions; Calculations of long-range forces between pairs ...
... from the New York University, USA, then He received ITAMP postdoctoral Fellow. Current research interest: Spectroscopy and scattering in atomic and molecular physics for applications to astrophysics, light science, and ultra-low temperature collisions; Calculations of long-range forces between pairs ...
Developing 100 ps-resolved X-ray structural
... gap of U36 is wider than 18 mm, one of two graphite heat absorbers can be removed from the beam path because the heat load on the monochromator is relatively low. The spectrum from U20, which has a smooth energy distribution in the energy range 13–18 keV, is useful for experiments using a white beam ...
... gap of U36 is wider than 18 mm, one of two graphite heat absorbers can be removed from the beam path because the heat load on the monochromator is relatively low. The spectrum from U20, which has a smooth energy distribution in the energy range 13–18 keV, is useful for experiments using a white beam ...
Practice Problems_sources
... (a) Find the internal quantum efficiency and the internal power level. (b) If the refractive index of the medium is 3.5, find the power emitted from the device. (Ans. (a) 0.7826 and 25.9 mW (b) 0.366 mW) 4. (a)A GaAlAs laser diode has a 500 micron cavity length which has an effective absorption coef ...
... (a) Find the internal quantum efficiency and the internal power level. (b) If the refractive index of the medium is 3.5, find the power emitted from the device. (Ans. (a) 0.7826 and 25.9 mW (b) 0.366 mW) 4. (a)A GaAlAs laser diode has a 500 micron cavity length which has an effective absorption coef ...
Light trapping by photon frequency management
... Fluorescent collectors: trapping light by frequency shift Tom Markvart Solar Energy Lab, Engineering Sciences University of Southampton, UK. Fluorescent collectors have been under consideration for some time, with the aim of reducing the size – and therefore the cost – of solar cells. We shall show ...
... Fluorescent collectors: trapping light by frequency shift Tom Markvart Solar Energy Lab, Engineering Sciences University of Southampton, UK. Fluorescent collectors have been under consideration for some time, with the aim of reducing the size – and therefore the cost – of solar cells. We shall show ...
UNM Physics 262, Problem Set 12, Fall 2006
... all your work, write clearly, indicate directions for all vectors, and be sure to include the units! Credit will be awarded for clear explanations as much, if not more so, than numerical answers. Avoid the temptation to simply write down an equation and move symbols around or plug in numbers. Explai ...
... all your work, write clearly, indicate directions for all vectors, and be sure to include the units! Credit will be awarded for clear explanations as much, if not more so, than numerical answers. Avoid the temptation to simply write down an equation and move symbols around or plug in numbers. Explai ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.