NEED FOR THE STUDY Hypertension is the most important health
... 1913, the famous clinician Thomas Janeway described congestive heart failure as the manifestation of hypertensive cardiovascular disease4. Shortly after, the relationship between hypertension and hypertrophy of the left ventricle was established in observations linking cardiac findings to the then n ...
... 1913, the famous clinician Thomas Janeway described congestive heart failure as the manifestation of hypertensive cardiovascular disease4. Shortly after, the relationship between hypertension and hypertrophy of the left ventricle was established in observations linking cardiac findings to the then n ...
cardiovascular block
... Macroscopic and microscopic changes in myocardial infarction. Biochemical markers of myocardial infarction. Complications of myocardial infarction: immediate and late. ...
... Macroscopic and microscopic changes in myocardial infarction. Biochemical markers of myocardial infarction. Complications of myocardial infarction: immediate and late. ...
9.3 Natural Fluid systems
... – Humans are affected by air pressures (breathing) and fluid pressures (the circulatory and respiratory systems) • Water, and water balance, is vital for life • The human body is 66% water, and loses 2.1 L of water daily (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 ...
... – Humans are affected by air pressures (breathing) and fluid pressures (the circulatory and respiratory systems) • Water, and water balance, is vital for life • The human body is 66% water, and loses 2.1 L of water daily (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 ...
ISOLATED SYSTOLIC HYPERTENSION: Cardiovascular risk and
... and morbidity in patients with ISH. The results of several ongoing trials are expected to provide further information on possible additional advantage of newer promising agents. ...
... and morbidity in patients with ISH. The results of several ongoing trials are expected to provide further information on possible additional advantage of newer promising agents. ...
NAME
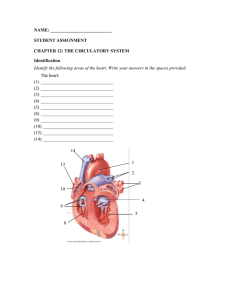
... D. bundle of His 30. What is the outside covering that surrounds and protects the heart called? A. endocardium B. myocardium C. pericardium D. ectocardium 31. What are the thin-walled upper heart cavities that receive blood from veins called? A. chordae tendineae B. atria C. pericardia D. ventricles ...
... D. bundle of His 30. What is the outside covering that surrounds and protects the heart called? A. endocardium B. myocardium C. pericardium D. ectocardium 31. What are the thin-walled upper heart cavities that receive blood from veins called? A. chordae tendineae B. atria C. pericardia D. ventricles ...
cvs-FB-2007
... • forms within the aterial circulation • is introduced into the arterial circulation • forms within the venous and has a conduit to th arterial circulation ì.e right to left shunt ...
... • forms within the aterial circulation • is introduced into the arterial circulation • forms within the venous and has a conduit to th arterial circulation ì.e right to left shunt ...
Measuring and Recording Blood Pressure
... • Normal range in adults is 30 to 50 mm/Hg. • Example: Systolic pressure is 120 mm/Hg and diastolic pressure is 80 mm/Hg, the pulse pressure is 40 mm/Hg. (120-80=40) ...
... • Normal range in adults is 30 to 50 mm/Hg. • Example: Systolic pressure is 120 mm/Hg and diastolic pressure is 80 mm/Hg, the pulse pressure is 40 mm/Hg. (120-80=40) ...
Unit2-KA6aNotesDone
... red and ______ white The blood is made of ______ blood cells) and a liquid called _____________. plasma biconcave Red blood cells are specialised by being _____________in nucleus shape, having no __________and containing haemoglobin _______________. oxygen This allows them to transport _____________ ...
... red and ______ white The blood is made of ______ blood cells) and a liquid called _____________. plasma biconcave Red blood cells are specialised by being _____________in nucleus shape, having no __________and containing haemoglobin _______________. oxygen This allows them to transport _____________ ...
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE
... • The walls of the blood vessels also contain adventitial fibroblasts that create an endomysial network. In HHD, • there is hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes and transition of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. ...
... • The walls of the blood vessels also contain adventitial fibroblasts that create an endomysial network. In HHD, • there is hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes and transition of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. ...
Cardiovascular System Unit Exam – Study Guide Differentiate
... 4. Discuss the events that are taking place in the cardiac cycle during the left ventricular systole. Indicate whether the other heart chambers are in systole or diastole and whether they are filling or emptying of blood. If they are emptying, state where the blood is going. If they are filling with ...
... 4. Discuss the events that are taking place in the cardiac cycle during the left ventricular systole. Indicate whether the other heart chambers are in systole or diastole and whether they are filling or emptying of blood. If they are emptying, state where the blood is going. If they are filling with ...
the circulatory system
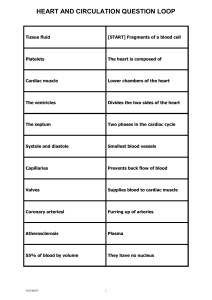
... 1. Blood is made up of 3 types of cell, name them. 2. What makes up the remaining 55% of blood? 3. Where are red blood cells produced? 4. What is the function of haemoglobin? 5. What is the main function of white blood cells 6. Why are platelets important in our blood? EXT: 1. What is meant by anaem ...
... 1. Blood is made up of 3 types of cell, name them. 2. What makes up the remaining 55% of blood? 3. Where are red blood cells produced? 4. What is the function of haemoglobin? 5. What is the main function of white blood cells 6. Why are platelets important in our blood? EXT: 1. What is meant by anaem ...
clinical practice guidelines for beta-blocker prophylaxis following an
... rate less than 60 bpm/Systolic arterial • Heart pressure less than 100 mm HG. ...
... rate less than 60 bpm/Systolic arterial • Heart pressure less than 100 mm HG. ...
The Cardiac Cycle
... i. This sends an electrical signal to the ____________ __ ________ and eventually to the _____________ ________ c. EKG, or ________________, measures the electrical activity of the heart. i. The ____ wave measures atrial depolarization ii. The _________ complex measures the ventricular depolarizatio ...
... i. This sends an electrical signal to the ____________ __ ________ and eventually to the _____________ ________ c. EKG, or ________________, measures the electrical activity of the heart. i. The ____ wave measures atrial depolarization ii. The _________ complex measures the ventricular depolarizatio ...
Secondary hypertension: etiology and mechanism of disease
... of 15 and 50 years, and involves the middle twothirds of the main renal artery. BOX 2 lists the situations in which RAS should specifically be investigated. While most experts agree that balloon angioplasty with bail-out stenting is the optimal treatment strategy for patients with hypertension due t ...
... of 15 and 50 years, and involves the middle twothirds of the main renal artery. BOX 2 lists the situations in which RAS should specifically be investigated. While most experts agree that balloon angioplasty with bail-out stenting is the optimal treatment strategy for patients with hypertension due t ...
File - Mrs. Ragsdale`s Science Page @ BHS
... back through the semilunar valve and collects in the left atria The blood moves into the left ventricle after passing through the atrio-ventricular valve before entering the aorta where it is distributed throughout the body ◦ Blood is always under low pressure in the veins, ...
... back through the semilunar valve and collects in the left atria The blood moves into the left ventricle after passing through the atrio-ventricular valve before entering the aorta where it is distributed throughout the body ◦ Blood is always under low pressure in the veins, ...
The Electrocardiogram
... Strength of heart contractions Heart rate Blood viscosity – thickness of blood ...
... Strength of heart contractions Heart rate Blood viscosity – thickness of blood ...
Title: Hypertension and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) Author
... What is Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH)? LVH represents an extreme increase in the left ventricular mass of the heart. The left ventricle is the part of the heart most responsible for pumping blood to our body, and like any muscle, grows in reaction to more rigorous use. Most cases of LVH ar ...
... What is Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH)? LVH represents an extreme increase in the left ventricular mass of the heart. The left ventricle is the part of the heart most responsible for pumping blood to our body, and like any muscle, grows in reaction to more rigorous use. Most cases of LVH ar ...
Heart Intro SJW
... The amount of blood pumped can be calculated: Heart Rate x Stroke Volume = Cardiac Output. Heart rate: The number of heart beats per minute. Stroke volume: The volume of blood pumped from heart with each beat. Cardiac output: The amount of blood pumped by heart in one minute. ...
... The amount of blood pumped can be calculated: Heart Rate x Stroke Volume = Cardiac Output. Heart rate: The number of heart beats per minute. Stroke volume: The volume of blood pumped from heart with each beat. Cardiac output: The amount of blood pumped by heart in one minute. ...
Hypertension and the JNC 8 Guidelines
... Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation,41 and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2003;42(6):1206–1252. ...
... Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation,41 and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2003;42(6):1206–1252. ...
Introduction to the Heart Health Program
... • 9 out of 10 Canadians over the age of 20 have at least one of the following risk factors: • smoking, • physical inactivity during leisure time, • less than recommended daily consumption of vegetables and fruit, • stress, • overweight or obesity, • high blood pressure, • or diabetes. ...
... • 9 out of 10 Canadians over the age of 20 have at least one of the following risk factors: • smoking, • physical inactivity during leisure time, • less than recommended daily consumption of vegetables and fruit, • stress, • overweight or obesity, • high blood pressure, • or diabetes. ...
Ch 37 Test Review- 3 points Bonus
... (Ch 38 review questions are incorporated in to your mandatory HW packet that is due Monday) What is the function of the heart? What type of muscle is the heart composed of? This muscle tissue in the heart forms a thick layer called? The structure separating the right and left sides of the heart that ...
... (Ch 38 review questions are incorporated in to your mandatory HW packet that is due Monday) What is the function of the heart? What type of muscle is the heart composed of? This muscle tissue in the heart forms a thick layer called? The structure separating the right and left sides of the heart that ...
Antihypertensive drug

Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used drugs are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.Which type of medication to use initially for hypertension has been the subject of several large studies and resulting national guidelines. The fundamental goal of treatment should be the prevention of the important endpoints of hypertension, such as heart attack, stroke and heart failure. Patient age, associated clinical conditions and end-organ damage also play a part in determining dosage and type of medication administered. The several classes of antihypertensives differ in side effect profiles, ability to prevent endpoints, and cost. The choice of more expensive agents, where cheaper ones would be equally effective, may have negative impacts on national healthcare budgets. As of 2009, the best available evidence favors the thiazide diuretics as the first-line treatment of choice for high blood pressure when drugs are necessary. Although clinical evidence shows calcium channel blockers and thiazide-type diuretics are preferred first-line treatments for most people (from both efficacy and cost points of view), an ACE inhibitor is recommended by NICE in the UK for those under 55 years old.