File - Mr Sosebee History
... War without and direct military conflict that developed between the US and the Soviet Union after WWII, 1945-1989 US policy of providing direct economic and military aid to free nations whose right to self determination were threatened by communist forces Program in which the US supplied $13 million ...
... War without and direct military conflict that developed between the US and the Soviet Union after WWII, 1945-1989 US policy of providing direct economic and military aid to free nations whose right to self determination were threatened by communist forces Program in which the US supplied $13 million ...
File
... Democracy would control the world. Weapons were propaganda, competitions (including sports) and diplomacy. Sometimes there were small military actions. When World War II ended, the Soviet Union occupied Eastern Europe. Countries controlled by the Soviet Union were called satellites. The Soviet Union ...
... Democracy would control the world. Weapons were propaganda, competitions (including sports) and diplomacy. Sometimes there were small military actions. When World War II ended, the Soviet Union occupied Eastern Europe. Countries controlled by the Soviet Union were called satellites. The Soviet Union ...
The Cold War
... The Marshall Plan, 1948 Post-war European aid (food, $, infrastructure, etc.) WHY? ...
... The Marshall Plan, 1948 Post-war European aid (food, $, infrastructure, etc.) WHY? ...
The Cold War
... • 3) Future of Germany • 4) Economic reconstruction of Europe • 5) International policies toward the atomic bomb and atomic energy ...
... • 3) Future of Germany • 4) Economic reconstruction of Europe • 5) International policies toward the atomic bomb and atomic energy ...
From World War to Cold War Sec. 5
... Postwar hunger and poverty made Western European lands fertile ground for communist ideas. To strengthen democratic governments, the U.S. offered a massive aid package, called the Marshall Plan. Under it, the U.S. funneled food and economic assistance to Europe to help countries rebuild. Billions Am ...
... Postwar hunger and poverty made Western European lands fertile ground for communist ideas. To strengthen democratic governments, the U.S. offered a massive aid package, called the Marshall Plan. Under it, the U.S. funneled food and economic assistance to Europe to help countries rebuild. Billions Am ...
File
... Stalin continued to influence Eastern European nations and by 1946 Poland, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Albania all had Communist governments. Churchill described it as an iron-curtain, the name stuck. ...
... Stalin continued to influence Eastern European nations and by 1946 Poland, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Albania all had Communist governments. Churchill described it as an iron-curtain, the name stuck. ...
Patrick Wright. Iron Curtain: From Stage to Cold War. New York
... truth-obscuring metaphors. All credit then to Patrick Wright for inquiring into the origins of the “iron curtain,” a ubiquitous metaphor of the Cold War era. The term is indelibly associated with Winston Churchill, who made it the central image of his famous speech at Westminster College in Fulton, ...
... truth-obscuring metaphors. All credit then to Patrick Wright for inquiring into the origins of the “iron curtain,” a ubiquitous metaphor of the Cold War era. The term is indelibly associated with Winston Churchill, who made it the central image of his famous speech at Westminster College in Fulton, ...
The End of WW2 - Mr Barck`s Classroom
... • _________________________ – the policy of limiting communism to the areas already under Soviet control • Marshall Plan – __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ • _____________________________________________ (NA ...
... • _________________________ – the policy of limiting communism to the areas already under Soviet control • Marshall Plan – __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ • _____________________________________________ (NA ...
Origins of the Cold War
... The Truman Doctrine • State department officials developed a plan to provide American aid to Greece and Turkey after the British could no longer help keep Soviets out • March 1947, Truman called on the U.S. to take a leadership role in a statement of principles known as the Truman Doctrine. • Congr ...
... The Truman Doctrine • State department officials developed a plan to provide American aid to Greece and Turkey after the British could no longer help keep Soviets out • March 1947, Truman called on the U.S. to take a leadership role in a statement of principles known as the Truman Doctrine. • Congr ...
Chapter 23 THE COLD WAR ERA • “An iron curtain has descended
... After WWII, Soviet Expansion threatened to enslave Europe “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent.” o Winston Churchill Symbol of division: o Communist world, dominated by the Soviet Union o Free world, led by the United States Decad ...
... After WWII, Soviet Expansion threatened to enslave Europe “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent.” o Winston Churchill Symbol of division: o Communist world, dominated by the Soviet Union o Free world, led by the United States Decad ...
Why was 1945 a critical year in United States foreign relations?
... • East Germany: To make sure Germany could not threaten his nation again, Stalin established a totalitarian government, naming the state the German Democratic Republic. • Finland and Yugoslavia: Both countries maintained their independence from Soviet control – Finland, by signing a treaty of cooper ...
... • East Germany: To make sure Germany could not threaten his nation again, Stalin established a totalitarian government, naming the state the German Democratic Republic. • Finland and Yugoslavia: Both countries maintained their independence from Soviet control – Finland, by signing a treaty of cooper ...
THE COLD WAR - Rankin County School District
... 1. 3/12/1946: Fulton, Missouri 2. Winston Churchill visited Westminster College and summed up Soviet relations with the US and GB: “From Stettin on the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an Iron Curtain has descended across the Continent.” ...
... 1. 3/12/1946: Fulton, Missouri 2. Winston Churchill visited Westminster College and summed up Soviet relations with the US and GB: “From Stettin on the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an Iron Curtain has descended across the Continent.” ...
Study Guide Unit 4 - Warren County Schools
... Weimar government Sudetenland Bataan Death March Marshall Plan Détente Perestroika Iron curtain ...
... Weimar government Sudetenland Bataan Death March Marshall Plan Détente Perestroika Iron curtain ...
Containing Communism
... Containing Communism Containment, the Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan ...
... Containing Communism Containment, the Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan ...
cold war beginnings - apusmiskinis2012-2013
... Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia; all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must ...
... Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia; all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must ...
Cold War Begins - St. Francis School District
... United States House of Representatives for being communists The committee held nine days of hearings Over three-hundred artists were boycotted by their studios ...
... United States House of Representatives for being communists The committee held nine days of hearings Over three-hundred artists were boycotted by their studios ...
The Cold War
... 2. Promote democracy throughout the world, especially in Asia and Africa 3. Stop the spread of communism 4. Fear of communism and spying in the United States ...
... 2. Promote democracy throughout the world, especially in Asia and Africa 3. Stop the spread of communism 4. Fear of communism and spying in the United States ...
Guided Notes- Allies Become Enemies and Eastern
... ● Towards the end of the war the Nazi troops occupied a trip of countries along the Soviet Union’s western border ● Stalin ignored the Yalta agreement and installed and secured Communist governments in Albania, Bulgaria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Romania, Poland, and Yugoslavia ● Franklin D. Roosevel ...
... ● Towards the end of the war the Nazi troops occupied a trip of countries along the Soviet Union’s western border ● Stalin ignored the Yalta agreement and installed and secured Communist governments in Albania, Bulgaria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Romania, Poland, and Yugoslavia ● Franklin D. Roosevel ...
United States and Europe after World War II
... 1. In February 1945, Germany was close to surrendering to the Allied Powers as World War II was coming to an end. President Franklin D. Roosevelt of the United States, Prime Minister Winston Churchill of Great Britain, and Premier Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union – the Big Three leaders of the A ...
... 1. In February 1945, Germany was close to surrendering to the Allied Powers as World War II was coming to an end. President Franklin D. Roosevelt of the United States, Prime Minister Winston Churchill of Great Britain, and Premier Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union – the Big Three leaders of the A ...
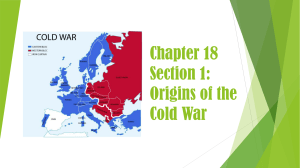
Chapter 18 Section 1: Origins of the Cold War
... • American capitalism: Private citizens controlled almost all economic activity • Potsdam Conference between the Big Three ...
... • American capitalism: Private citizens controlled almost all economic activity • Potsdam Conference between the Big Three ...
The Cold War
... 2. Promote democracy throughout the world, especially in Asia and Africa 3. Stop the spread of communism 4. Fear of communism and spying in the United States ...
... 2. Promote democracy throughout the world, especially in Asia and Africa 3. Stop the spread of communism 4. Fear of communism and spying in the United States ...
READING GUIDE: CHAPTER 21 – SECTION 1
... 29. How much money did the Marshall Plan supply in grants and loans to nations in Western Europe? 30. What did the program provide? 31. What happened to the aid offered to the Soviet satellite states in Eastern Europe? 32. Where was the front line of the Cold War? 33. What 3 countries combined their ...
... 29. How much money did the Marshall Plan supply in grants and loans to nations in Western Europe? 30. What did the program provide? 31. What happened to the aid offered to the Soviet satellite states in Eastern Europe? 32. Where was the front line of the Cold War? 33. What 3 countries combined their ...
Reading Guide: Chapter 21 – Section 1
... 18. What is different about Truman’s education than any other President in the 20th century? 19. What was Truman’s motto? What did it mean? 20. What two countries were battling communist forces? 21. Who was the only country in a position to help these countries? 22. What did Truman request from Con ...
... 18. What is different about Truman’s education than any other President in the 20th century? 19. What was Truman’s motto? What did it mean? 20. What two countries were battling communist forces? 21. Who was the only country in a position to help these countries? 22. What did Truman request from Con ...
Iron Curtain
The Iron Curtain was the ideological conflict and physical boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas from the end of World War II in 1945 until the end of the Cold War in 1991. The term symbolized efforts by the Soviet Union to block itself and its satellite states from open contact with the west and non-Soviet-controlled areas. On the east side of the Iron Curtain were the countries that were connected to or influenced by the Soviet Union. On either side of the Iron Curtain, states developed their own international economic and military alliances: Member countries of the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance and the Warsaw Pact, with the Soviet Union as the leading state Member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization and with the United States as the leading countryPhysically, the Iron Curtain took the form of border defenses between the countries of Europe in the middle of the continent. The most notable border was marked by the Berlin Wall and its Checkpoint Charlie which served as a symbol of the Curtain as a whole.The events that demolished the Iron Curtain started in discontent in Poland, and continued in Hungary, the German Democratic Republic (East Germany), Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, and Romania. Romania was the only communist state in Europe to violently overthrow its government.The term's use as a metaphor for strict separation can be traced to the early 19th century. It was originally a reference to fireproof curtains in theaters. Its popularity as a Cold War symbol is attributed to its use in a speech Winston Churchill gave in March 1946 in Fulton, Missouri.