* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cold War
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
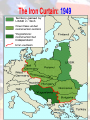
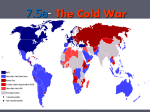
The Cold War: The Beginnings Five Major Causes • 1) Poland: “The Big Apple in the Barrel” • 2) Structure of governments in other E. European countries • 3) Future of Germany • 4) Economic reconstruction of Europe • 5) International policies toward the atomic bomb and atomic energy • “. . . as the war drew to an end, virtually none of the critical issues on the agenda of postwar relationships had been resolved. Preferring to postpone decisions rather than to confront the full dimension of the conflicts that existed, FDR evidently hoped that his own political genius, plus the exigencies of postwar conditions, would pave the way for a mutual accommodation that would somehow satisfy both America’s commitment to a world of free trade and democratic rule, and the Soviet Union’s obsession with national security and safely defined spheres of influence.” Chafe. The Unfinished Journey; American since WWII p. 53 Yalta Conference • Meeting of the Big 3 • Stalin took back free elections in Poland and banned democratic parties • Soviet Army in E. Europe = West could do little U.S. GOALS IN E. EUROPE: • Self-governing countries • Access to raw materials and markets • Rebuild European govs. • U.S. wanted to polarize Germany into small farms = FAILED SOVIET GOALS IN E. EUROPE • Encourage communism • Rebuild its economy by using E. European resources • Control E. Europe to balance U.S. influence in W. Europe • Keep Germany divided so it could not threaten the Soviet Union again. Satellite Nations • Stalin wanted a barrier between E. Europe and W. Europe. • Satellite Nations: countries dominated by the Soviet Union. U.S. Policy of Containment • Feb. 1946: George F. Kennan, U.S. diplomat proposed the policy of containment: – U.S. would take all measures to prevent any extension of communist rule to other countries. The Iron Curtain: 1949 The Truman Doctrine • March 12, 1947: Declaration that the U.S. should support free countries trying resist communist pressure. – 1947 – 1950: U.S. sent $400 million in aiding Greece and Turkey The Marshall Plan • June 1947: Sec. of State George Marshall: The Marshall Plan • U.S. provide aid ($) to all European nations that needed it. • By 1952, 16 countries received some $13 billion in aid Post-War Germany The Berlin Airlift • West Berlin held hostage by Stalin • U.S. and Great Britain flew in supplies for 327 days – 277,000 flights – 2.3 million tons of supplies • May 1949, Soviets lifted the blockade. NATO • NATO: North Atlantic Treaty Organization. • Formation of 12 countries unified by increased Soviet aggression • Military support if one of the NATO countries was attacked • 1st time in history the U.S. was involved in a military alliance during peacetime. Vasili Alexandrovich Arkhipov • • • • • Executive Officer aboard a Hotel class ballistic missile submarine B-59 during the Cuban Missile Crisis Caught behind the quarantine line during the Cuban Missile Crisis – In the middle of one U.S. carrier and 11 battleships U.S. dropped depth charges to force the subs to the surface Capt. of the sub loaded a nuclear torpedo to be used against the U.S. ships – Believed the war “already” has started Moscow had left the decision to use one of these nukes with the captain of the submarine but with a proviso. If he felt the need to use the weapon the next two officers in terms of rank had to agree to its use as well. The political officer on board said yes. The Executive Officer, Arkhipov, said no. McCarthyism • Joseph McCarthy, Republican from Wisconsin • Unfair tactic of accusing people of disloyalty w/o providing evidence. Finding Suspected Communists • HUAC = House Committee on UnAmerican Activities – Investigations in and outside the government – Investigated “thought to be” Communists in Hollywood The Hollywood 10 • Resist to cooperate with HUAC – Thought hearings were Unconstitutional • Blacklist: a list of people who were condemned for having a Communist background. Spy Cases