General Psychology Notes - Social Psychology
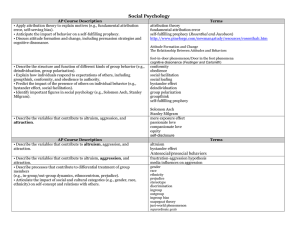
... * Anxiety or discomfort one feels when they are holding two inconsistent beliefs, or when behavior is inconsistent with your belief. * Because of discomfort you become motivated to change a belief. D. Prejudice and Stereotypes 1. Stereotype - false assumption that all group members have the same fea ...
... * Anxiety or discomfort one feels when they are holding two inconsistent beliefs, or when behavior is inconsistent with your belief. * Because of discomfort you become motivated to change a belief. D. Prejudice and Stereotypes 1. Stereotype - false assumption that all group members have the same fea ...
The use of social network analysis and technology acceptance
... Information System (IS) implementations are a risky business with studies showing only a 16% 29% success rate. This research explores the use of social capital to support technology implementations. This research brings together two distinct bodies of knowledge: social network analysis and technolog ...
... Information System (IS) implementations are a risky business with studies showing only a 16% 29% success rate. This research explores the use of social capital to support technology implementations. This research brings together two distinct bodies of knowledge: social network analysis and technolog ...
Theories of Group Cohesion
... drop in motivation when people believe they are taking part in a group task. Social loafing is a very important idea for Sport Psychology, because coaches are trying to get the best out of their teams and a team with players who aren‟t pulling their weight will lose to one where social loafing has b ...
... drop in motivation when people believe they are taking part in a group task. Social loafing is a very important idea for Sport Psychology, because coaches are trying to get the best out of their teams and a team with players who aren‟t pulling their weight will lose to one where social loafing has b ...
File
... The scientific study of how we think _____________________________________ Social thinking involves thinking about others, especially when they engage in doing things that are ______________________ ...
... The scientific study of how we think _____________________________________ Social thinking involves thinking about others, especially when they engage in doing things that are ______________________ ...
Ms. Cabrera AP Psychology 2015-2016 Unit I
... 10 class periods (8 Block, 2 Short) This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and other social phenomena. Essential Questions: How do people explain (or attribute) the behavior of ot ...
... 10 class periods (8 Block, 2 Short) This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and other social phenomena. Essential Questions: How do people explain (or attribute) the behavior of ot ...
These are the AP Unit goals for social psychology
... cognitive dissonance (Festinger and Carlsmith) ...
... cognitive dissonance (Festinger and Carlsmith) ...
Lesson Plan week #2
... fall in love with a person of another race? Religion? How would your friends feel? How would your family fell? ...
... fall in love with a person of another race? Religion? How would your friends feel? How would your family fell? ...
SI: March 12, 2012 Chapter 15 part 1 Part I: Warm
... Part IV: True/False Choose the correct answer to the following multiple choice questions True/False: Attitudes are especially likely to affect behavior when internal influences are minimal. True/False: Attitudes can influence behavior. True/False: The smaller the dissonance, the more motivated we ar ...
... Part IV: True/False Choose the correct answer to the following multiple choice questions True/False: Attitudes are especially likely to affect behavior when internal influences are minimal. True/False: Attitudes can influence behavior. True/False: The smaller the dissonance, the more motivated we ar ...
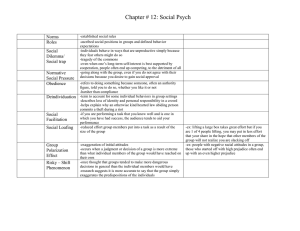
Norms - Manhasset Schools
... -instrumental aggression: aggression committed to gain something of value -the principle that frustration – the blocking of an attempt to achieve some goal – creates anger, which can generate aggression -zero-sum game analyzing human cooperation and trust -refers to the error by which we generalize ...
... -instrumental aggression: aggression committed to gain something of value -the principle that frustration – the blocking of an attempt to achieve some goal – creates anger, which can generate aggression -zero-sum game analyzing human cooperation and trust -refers to the error by which we generalize ...
Sociology and You - Freeman Public Schools
... • An in-group requires extreme loyalty from its members to the exclusion of others. • The in-group feels opposition, antagonism, or competition toward the out-group. ...
... • An in-group requires extreme loyalty from its members to the exclusion of others. • The in-group feels opposition, antagonism, or competition toward the out-group. ...
Unit 14 Reading Guide
... Explain how the ‘foot-in-the-door’ effect explains Milgram’s experiment results. ...
... Explain how the ‘foot-in-the-door’ effect explains Milgram’s experiment results. ...
Social Psych Outline
... Explain how the foot-in-the-door effect explains Milgrim’s experiment results. ...
... Explain how the foot-in-the-door effect explains Milgrim’s experiment results. ...
Social Psych Unit reading guide
... Explain how the foot-in-the-door effect explains Milgrim’s experiment results. ...
... Explain how the foot-in-the-door effect explains Milgrim’s experiment results. ...
Formation
... For each of the three interpersonal needs—Inclusion, Control, and Affection—the FIRO instrument also provides a measure of how much each need is Expressed or Wanted by you. EXPRESSED The extent to which you will initiate the behavior. WANTED The extent to which you want or will accept that behav ...
... For each of the three interpersonal needs—Inclusion, Control, and Affection—the FIRO instrument also provides a measure of how much each need is Expressed or Wanted by you. EXPRESSED The extent to which you will initiate the behavior. WANTED The extent to which you want or will accept that behav ...
Ch. 3
... – Assumes prejudice can be linked to categorization, or how we group - usually based on stereotypes – Try to expand our schema for a particular group – What qualities are shared between groups? ...
... – Assumes prejudice can be linked to categorization, or how we group - usually based on stereotypes – Try to expand our schema for a particular group – What qualities are shared between groups? ...
Social Psychology
... Social psychology is the study of how people and groups interact. Scholars in this interdisciplinary area are typically either psychologists or sociologists, though all social psychologists use both the individual and the group as their subject to study. Their approach to the field focuses on the in ...
... Social psychology is the study of how people and groups interact. Scholars in this interdisciplinary area are typically either psychologists or sociologists, though all social psychologists use both the individual and the group as their subject to study. Their approach to the field focuses on the in ...
Document
... • Conformity – Solomon Asch (1950s) – Classic experiment • Group size • Group unanimity ...
... • Conformity – Solomon Asch (1950s) – Classic experiment • Group size • Group unanimity ...
Chapter 14
... Affect our Behavior? Situationism – View that environmental conditions influence people’s behavior as much or more than their personal dispositions do (Person vs. Situation) ...
... Affect our Behavior? Situationism – View that environmental conditions influence people’s behavior as much or more than their personal dispositions do (Person vs. Situation) ...
Attributing Behavior (p.644-645): List and describe attribution
... Social Influence: Conformity & Obedience (p.650-657): Explain the concepts of obedience & conformity through the research of Asch & Milgram. ...
... Social Influence: Conformity & Obedience (p.650-657): Explain the concepts of obedience & conformity through the research of Asch & Milgram. ...
Sociology Course Descriptions
... perspectives, key concepts, and related research methods of sociology. Analysis of social issues in their institutional context may include topics such as social stratification, gender, race/ethnicity, and deviance. SOCI 1306. Social Problems Application of sociological principles and theoretical pe ...
... perspectives, key concepts, and related research methods of sociology. Analysis of social issues in their institutional context may include topics such as social stratification, gender, race/ethnicity, and deviance. SOCI 1306. Social Problems Application of sociological principles and theoretical pe ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Set of expectations about social position Defines how those in position ought to ...
... Set of expectations about social position Defines how those in position ought to ...
Study Guide 16 Social Psychology
... 10. Your book doesn’t mention this concept, but Robert Cialdini has also researched “door-in-the-face technique” as a method of persuasion. In this technique, the persuader attempts to convince someone to comply with a request by first making an extremely large request that the respondent will obvio ...
... 10. Your book doesn’t mention this concept, but Robert Cialdini has also researched “door-in-the-face technique” as a method of persuasion. In this technique, the persuader attempts to convince someone to comply with a request by first making an extremely large request that the respondent will obvio ...
Personality in Social Psychology
... social comparison than would individuals facing either embarrassing or ambiguous situations. ...
... social comparison than would individuals facing either embarrassing or ambiguous situations. ...
PowerPoints
... Stanley Milgram wondered about this and conducted an experiment to determine how many people would resist authority figures who made immoral requests. ...
... Stanley Milgram wondered about this and conducted an experiment to determine how many people would resist authority figures who made immoral requests. ...
Social loafing

In the social psychology of groups, social loafing is the phenomenon of people exerting less effort to achieve a goal when they work in a group than when they work alone. This is seen as one of the main reasons groups are sometimes less productive than the combined performance of their members working as individuals, but should be distinguished from the accidental coordination problems that groups sometimes experience.Social loafing can be explained by the ""free-rider"" theory and the resulting ""sucker effect"", which is an individual’s reduction in effort in order to avoid pulling the weight of a fellow group member.Research on social loafing began with rope pulling experiments by Ringelmann, who found that members of a group tended to exert less effort in pulling a rope than did individuals alone. In more recent research, studies involving modern technology, such as online and distributed groups, have also shown clear evidence of social loafing. Many of the causes of social loafing stem from an individual feeling that his or her effort will not matter to the group.