Social Psychology Chapter 16
... Ex: A friend tells you that they believe Coach Stove is a mean teacher. You may feel dislike for Coach Stove, and act unfriendly. ...
... Ex: A friend tells you that they believe Coach Stove is a mean teacher. You may feel dislike for Coach Stove, and act unfriendly. ...
Chapter 14:Social Psychology
... Dilution or weakening of each group member’s obligation to act when responsibility is perceived to be shared with all group members ...
... Dilution or weakening of each group member’s obligation to act when responsibility is perceived to be shared with all group members ...
Social Structure and Social Interaction
... • relationship of people and groups to one another • people learn different behaviors and attitudes because of their location in the social structure • major components of social structure • culture: language, beliefs, values, norms, behaviors, and material objects that constitute a people’s way of ...
... • relationship of people and groups to one another • people learn different behaviors and attitudes because of their location in the social structure • major components of social structure • culture: language, beliefs, values, norms, behaviors, and material objects that constitute a people’s way of ...
Now!
... 14-9: How does psychology’s definition of aggression differ from everyday usage? What biological factors make us more prone to hurt one another? 14-10: What psychological and social-cultural factors may trigger aggressive behavior? ...
... 14-9: How does psychology’s definition of aggression differ from everyday usage? What biological factors make us more prone to hurt one another? 14-10: What psychological and social-cultural factors may trigger aggressive behavior? ...
18SocialPsychology
... Social Facilitation improved performance of tasks in the presence of others occurs with simple or well-learned tasks but not with tasks that are difficult or not yet mastered ...
... Social Facilitation improved performance of tasks in the presence of others occurs with simple or well-learned tasks but not with tasks that are difficult or not yet mastered ...
Social Psychology
... highest number will receive a reward. The offer to form a pair is made by extending your hand to another person, as if to offer a handshake. The other person can choose either to accept or reject your offer. If your offer is accepted, stand together with your partner at the edge of the room. ...
... highest number will receive a reward. The offer to form a pair is made by extending your hand to another person, as if to offer a handshake. The other person can choose either to accept or reject your offer. If your offer is accepted, stand together with your partner at the edge of the room. ...
Otherness
... Rather than talking about the individual characteristics or personalities of different individuals, which is generally the focus for psychology, sociologists focus on social identities. Social identities reflect the way individuals and groups internalize established social categories within their so ...
... Rather than talking about the individual characteristics or personalities of different individuals, which is generally the focus for psychology, sociologists focus on social identities. Social identities reflect the way individuals and groups internalize established social categories within their so ...
PPT
... Social thinking • Attribution theory - our interpretation about the cause of someone else’s behavior – Dispositional attribution – Situational attribution ...
... Social thinking • Attribution theory - our interpretation about the cause of someone else’s behavior – Dispositional attribution – Situational attribution ...
Fundamentals of Psychology
... Social loafing Occurs when people working on a group task that lacks individual evaluation perform at a lower level than they would if they worked alone. ...
... Social loafing Occurs when people working on a group task that lacks individual evaluation perform at a lower level than they would if they worked alone. ...
Conformity ASCH`S STUDY
... • Norms & roles can help you know how to behave in new situations. • Violating norms/roles can cause discomfort. • Social roles may affect behavior more than personality in certain situations. • Attitudes are also influenced by social roles. ...
... • Norms & roles can help you know how to behave in new situations. • Violating norms/roles can cause discomfort. • Social roles may affect behavior more than personality in certain situations. • Attitudes are also influenced by social roles. ...
Diapositive 1 - Coach in VET
... Roughly, two opposite considerations : A strong social belonging ...
... Roughly, two opposite considerations : A strong social belonging ...
social psychology social categorization Implicit personality theory
... social categorization categorizing people into stereotyped groups based upon their shared characteristics (is done using Implicit Personality Theory) ...
... social categorization categorizing people into stereotyped groups based upon their shared characteristics (is done using Implicit Personality Theory) ...
This is Where You Type the Slide Title
... social categorization categorizing people into stereotyped groups based upon their shared characteristics (is done using Implicit Personality Theory) ...
... social categorization categorizing people into stereotyped groups based upon their shared characteristics (is done using Implicit Personality Theory) ...
Chapter 12: Social Psychology
... Describe how the controversy surrounding the murder of Kitty Genovese triggered the study of bystander helping behavior. ...
... Describe how the controversy surrounding the murder of Kitty Genovese triggered the study of bystander helping behavior. ...
Module 56
... Normative Social Influence: influence resulting from a person’s desire to gain approval or avoid rejection. Respecting normative behavior, because price may be severe if not followed. Informative Social Influence: The group may provide valuable information, only stubborn people will never listen to ...
... Normative Social Influence: influence resulting from a person’s desire to gain approval or avoid rejection. Respecting normative behavior, because price may be severe if not followed. Informative Social Influence: The group may provide valuable information, only stubborn people will never listen to ...
Social thinking: involves thinking about others, especially when they
... 7. Cognitive dissonance: the state of psychological tension, anxiety, and discomfort that occurs when a person’s attitude and behavior are inconsistent. Most people modify attitudes to reduce the dissonance. Ex. Take the example of smokers who knows that smoking is bad for them. How do they reduce t ...
... 7. Cognitive dissonance: the state of psychological tension, anxiety, and discomfort that occurs when a person’s attitude and behavior are inconsistent. Most people modify attitudes to reduce the dissonance. Ex. Take the example of smokers who knows that smoking is bad for them. How do they reduce t ...
B). Group behaviors
... 5. Norm and role-Compliance and Conformity How likely are we to be obedient to an authority? (Milgram’s study) Why do people in groups often agree with the majority, even when they have exactly the opposite opinion, or the majority’s ideas are wrong? (Asch’s study) 6. Social facilitation, Effect of ...
... 5. Norm and role-Compliance and Conformity How likely are we to be obedient to an authority? (Milgram’s study) Why do people in groups often agree with the majority, even when they have exactly the opposite opinion, or the majority’s ideas are wrong? (Asch’s study) 6. Social facilitation, Effect of ...
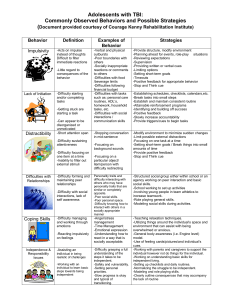
Adolescents with TBI: Commonly Observed Behaviors and Possible
... -Establishing schedules, checklists, calendars,etc. -Break tasks into small steps -Establish and maintain consistent routine -Attainable reinforcement programs -Identifying and building off success -Positive feedback -Slowly increase accountability -Provide triggers/cues to begin tasks ...
... -Establishing schedules, checklists, calendars,etc. -Break tasks into small steps -Establish and maintain consistent routine -Attainable reinforcement programs -Identifying and building off success -Positive feedback -Slowly increase accountability -Provide triggers/cues to begin tasks ...
social psychology - Peoria Public Schools
... Social psychology is th’e study of how people interact with each other. Some interaction occurs one on one, while some takes place in groups. ...
... Social psychology is th’e study of how people interact with each other. Some interaction occurs one on one, while some takes place in groups. ...
Conformity and Social Norms
... their attitudes or behavior to adhere to existing social norms. • - ORCrane’s Definition: The tendency to adjust one’s thoughts, feelings, or behavior in ways that are in agreement with those of a particular individual or group, or with social norms. ...
... their attitudes or behavior to adhere to existing social norms. • - ORCrane’s Definition: The tendency to adjust one’s thoughts, feelings, or behavior in ways that are in agreement with those of a particular individual or group, or with social norms. ...
Intro Psych Jan28
... were in their forties. I moved into a male body, and my partner, who is an Older Member in the Level Above Human, took a female body. (We called these bodies "vehicles," for they simply served as physical vehicular tools for us to wear while on a task among humans. They had been tagged and set aside ...
... were in their forties. I moved into a male body, and my partner, who is an Older Member in the Level Above Human, took a female body. (We called these bodies "vehicles," for they simply served as physical vehicular tools for us to wear while on a task among humans. They had been tagged and set aside ...
Moduels 37, 38, and 39
... -Milgran (1965, 1974): Participants (teachers) obeyed to an experimenter and administered electrical shocks to other participants (learners) (63% to the last switch). -“I was simply following orders.” “Ordinary people can become agents in a terrible destructive process.” -Deception or stressful? Eth ...
... -Milgran (1965, 1974): Participants (teachers) obeyed to an experimenter and administered electrical shocks to other participants (learners) (63% to the last switch). -“I was simply following orders.” “Ordinary people can become agents in a terrible destructive process.” -Deception or stressful? Eth ...
Groups, Cliques and Social Behaviour - Hale
... Temporary/short-term relationships Interested in a narrow aspect of the person More formal/written communication Ex: School, business, team ...
... Temporary/short-term relationships Interested in a narrow aspect of the person More formal/written communication Ex: School, business, team ...
Social loafing

In the social psychology of groups, social loafing is the phenomenon of people exerting less effort to achieve a goal when they work in a group than when they work alone. This is seen as one of the main reasons groups are sometimes less productive than the combined performance of their members working as individuals, but should be distinguished from the accidental coordination problems that groups sometimes experience.Social loafing can be explained by the ""free-rider"" theory and the resulting ""sucker effect"", which is an individual’s reduction in effort in order to avoid pulling the weight of a fellow group member.Research on social loafing began with rope pulling experiments by Ringelmann, who found that members of a group tended to exert less effort in pulling a rope than did individuals alone. In more recent research, studies involving modern technology, such as online and distributed groups, have also shown clear evidence of social loafing. Many of the causes of social loafing stem from an individual feeling that his or her effort will not matter to the group.