Line Spectra and the Bohr Model
... Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Limitations of the Bohr Model • Can only explain the line spectrum of hydrogen adequately. • Can only work for (at least) one electron atoms. • Cannot explain multi-lines with each color. • Electrons are not completely described as small particles. • Electrons can ha ...
... Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Limitations of the Bohr Model • Can only explain the line spectrum of hydrogen adequately. • Can only work for (at least) one electron atoms. • Cannot explain multi-lines with each color. • Electrons are not completely described as small particles. • Electrons can ha ...
- Lorentz Center
... chains of our preconceptions […] but we must on the contrary adjust our ideas to experience.” “Even though the demand […] for Anschaulichkeit is partly legitimate and healthy, still this demand should never count in physics as an argument for the retention of fixed conceptual systems. Once the new c ...
... chains of our preconceptions […] but we must on the contrary adjust our ideas to experience.” “Even though the demand […] for Anschaulichkeit is partly legitimate and healthy, still this demand should never count in physics as an argument for the retention of fixed conceptual systems. Once the new c ...
spectral lines
... Bohr to the rescue In 1905, Einstein had proposed the wave/particle duality of light with the photon. In 1913, Bohr used the concept in creating a quantum model of the atom. ...
... Bohr to the rescue In 1905, Einstein had proposed the wave/particle duality of light with the photon. In 1913, Bohr used the concept in creating a quantum model of the atom. ...
Quantum Mechanics
... it doesn’t account for splitting of some spectral lines… it doesn’t account for interactions between atoms… and we haven’t explained “stationary states.” Looks like we’ve got some work to do. You may be on the right track, but… you’ll get run over if you just keep sitting there. ...
... it doesn’t account for splitting of some spectral lines… it doesn’t account for interactions between atoms… and we haven’t explained “stationary states.” Looks like we’ve got some work to do. You may be on the right track, but… you’ll get run over if you just keep sitting there. ...
Physics 115A Spring 2006
... Two thoughts to keep in mind when you get confused during this course: “Because atomic behavior is so unlike ordinary experience, it is very difficult to get used to, and it appears peculiar and mysterious to everyone—both to the novice and to the experienced physicist. Even the experts do not under ...
... Two thoughts to keep in mind when you get confused during this course: “Because atomic behavior is so unlike ordinary experience, it is very difficult to get used to, and it appears peculiar and mysterious to everyone—both to the novice and to the experienced physicist. Even the experts do not under ...
Quantum mechanics for Advaitins
... probability waves that carry no energy or momentum and are themselves unobservable. • The theory is interpreted in terms of the probabilities of observations that can be predicted from the waves. • There are many interpretations but we still don’t know if there is a “correct” one. • We will discuss ...
... probability waves that carry no energy or momentum and are themselves unobservable. • The theory is interpreted in terms of the probabilities of observations that can be predicted from the waves. • There are many interpretations but we still don’t know if there is a “correct” one. • We will discuss ...
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... a photon knocks the electron off its course. • The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. ...
... a photon knocks the electron off its course. • The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. ...
PHYS1220 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Even macroscopic objects that are made up of many atoms are governed by probability rather than strict determinism. eg QM predicts a finite (though negligibly small) probability that an thrown object (comprising many atoms) will suddenly curve upward rather than follow a parabolic trajectory ...
... Even macroscopic objects that are made up of many atoms are governed by probability rather than strict determinism. eg QM predicts a finite (though negligibly small) probability that an thrown object (comprising many atoms) will suddenly curve upward rather than follow a parabolic trajectory ...
Lecture 2
... It was at C. That means quantum mechanics is incomplete theory. Why? Well, the particle was at C, but quantum mechanics could not predict it. Therefore, does not give the whole story and we need additional information (hidden variables) to provide a complete description of the particle. Answer #2. T ...
... It was at C. That means quantum mechanics is incomplete theory. Why? Well, the particle was at C, but quantum mechanics could not predict it. Therefore, does not give the whole story and we need additional information (hidden variables) to provide a complete description of the particle. Answer #2. T ...
Quantum Problems 1. Consider a quantum system whose state at
... where |ψ1 i and |ψ2 i are energy eigenstates with eigenvalues E1 and E2 respectively. (E1 6= E2 .) (a) Calculate the uncertainty ∆E of the system, as well as the first time t2 > t1 at which |Ψ(t2 )i becomes orthogonal to |Ψ(t1 )i. Show that (∆E)(∆t) ≥ h̄, where ∆t = t2 − t1 . (b) Assume that the abo ...
... where |ψ1 i and |ψ2 i are energy eigenstates with eigenvalues E1 and E2 respectively. (E1 6= E2 .) (a) Calculate the uncertainty ∆E of the system, as well as the first time t2 > t1 at which |Ψ(t2 )i becomes orthogonal to |Ψ(t1 )i. Show that (∆E)(∆t) ≥ h̄, where ∆t = t2 − t1 . (b) Assume that the abo ...
Chapter 7 Student Learning Map
... photoelectric effect in describing the behavior of the electron and light? ...
... photoelectric effect in describing the behavior of the electron and light? ...
Heisenbergs
... titled "On the Perceptual Content of Quantum Theoretical Kinematics and Mechanics". Jha, A. (2013, November 30). Retrieved from http://www.theguardian.com/science/2013/nov/10/what-isheisenbergs-uncertainty-principle ...
... titled "On the Perceptual Content of Quantum Theoretical Kinematics and Mechanics". Jha, A. (2013, November 30). Retrieved from http://www.theguardian.com/science/2013/nov/10/what-isheisenbergs-uncertainty-principle ...
Physics PHYS 356 Spring Semester 2013 Quantum Mechanics (4 credit hours)
... In this class I would like for you to develop a “quantum worldview” – by which I mean that I would like to re-examine some of the concepts that you have previously, in classes like classical mechanics and electricity and magnetism, held as starting assumptions. In doing this, you will need to learn ...
... In this class I would like for you to develop a “quantum worldview” – by which I mean that I would like to re-examine some of the concepts that you have previously, in classes like classical mechanics and electricity and magnetism, held as starting assumptions. In doing this, you will need to learn ...
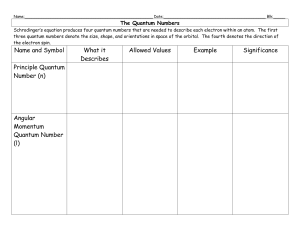
Quantum numbers
... Schrödinger & de Broglie Both felt the electron acted like a standing wave. (see slinky) Theorizing that the electron acts like a wave, and has a wave function That represents the x, y and z coordinates of the electron. A specific wave function is often called an orbital. ...
... Schrödinger & de Broglie Both felt the electron acted like a standing wave. (see slinky) Theorizing that the electron acts like a wave, and has a wave function That represents the x, y and z coordinates of the electron. A specific wave function is often called an orbital. ...
Slides from Lecture 9-11
... all those with infinite energy, i.e. outside the domain of the energy operator, Ĥ, (e.g. discontinuous wave functions). Should other operators (x ? p ?) have finite expected ...
... all those with infinite energy, i.e. outside the domain of the energy operator, Ĥ, (e.g. discontinuous wave functions). Should other operators (x ? p ?) have finite expected ...
correctly
... R = 2Ze2/ (40 x KE) = 2 x 9 x 109 x 1.6 x 10-19 x Z 1.2 x 10-12 J = 3.8 x 10-16 Z meters = 3.0 x 10-14 m for Z=79 (Gold) ...
... R = 2Ze2/ (40 x KE) = 2 x 9 x 109 x 1.6 x 10-19 x Z 1.2 x 10-12 J = 3.8 x 10-16 Z meters = 3.0 x 10-14 m for Z=79 (Gold) ...
Read Notes #1 - Faculty Website Listing
... electron) can only be explained by the particle representation while others can only be explained with the wave picture. ...
... electron) can only be explained by the particle representation while others can only be explained with the wave picture. ...
CLASSICAL-QUANTUM CORRESPONDENCE AND WAVE PACKET SOLUTIONS OF THE DIRAC
... The idea of wave mechanics leads naturally to assume the well-known relation E = ~ω in the specific form H = ~W , where H is the classical Hamiltonian of a particle and W is the dispersion relation of the sought-for wave equation. We derive the expression of H in a curved space-time with an electrom ...
... The idea of wave mechanics leads naturally to assume the well-known relation E = ~ω in the specific form H = ~W , where H is the classical Hamiltonian of a particle and W is the dispersion relation of the sought-for wave equation. We derive the expression of H in a curved space-time with an electrom ...
Quantum mechanics
... Quantum mechanics – The new way that was developed at the beginning of the 20th century to interpret & predict behaviors of microscopic objects such as atoms, electrons, .. ...
... Quantum mechanics – The new way that was developed at the beginning of the 20th century to interpret & predict behaviors of microscopic objects such as atoms, electrons, .. ...