Quantum Mechanics
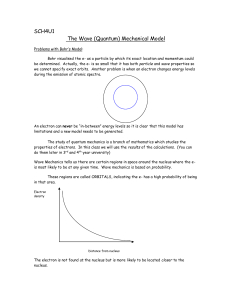
... The wave function, Y (psi) represents the displacement as a function of time and position Thus, Y2 is the probability of finding a certain electron at the given position and time The Y2 function gives us the shapes of the ...
... The wave function, Y (psi) represents the displacement as a function of time and position Thus, Y2 is the probability of finding a certain electron at the given position and time The Y2 function gives us the shapes of the ...
lect10
... QM is a complete theory that tells us that the world, at the quantum level, is governed by statistical law. It rules out “classical” or “naïve” realist views of nature. As an example, consider the following applet demonstrating the Hydrogen atom. ...
... QM is a complete theory that tells us that the world, at the quantum level, is governed by statistical law. It rules out “classical” or “naïve” realist views of nature. As an example, consider the following applet demonstrating the Hydrogen atom. ...
1.1 What has to be explained by Quantum mechanics?
... But ”free” and ”occupied” states within a band, sizes of band gaps, etc. classify metals, semiconductors, and insulators. • Why, in contrast, must photons be Bosons?!? (One single QM state macroscopically measurable) • What is: Schrödinger equation, Operator, commutator, probability function, wave ...
... But ”free” and ”occupied” states within a band, sizes of band gaps, etc. classify metals, semiconductors, and insulators. • Why, in contrast, must photons be Bosons?!? (One single QM state macroscopically measurable) • What is: Schrödinger equation, Operator, commutator, probability function, wave ...
File - SPHS Devil Physics
... a. Observations: Much of the work towards a quantum theory of atoms was guided by the need to explain the observed patterns in atomic spectra. The first quantum model of matter is the Bohr model for hydrogen. (1.8) b. Paradigm shift: The acceptance of the wave–particle duality paradox for light and ...
... a. Observations: Much of the work towards a quantum theory of atoms was guided by the need to explain the observed patterns in atomic spectra. The first quantum model of matter is the Bohr model for hydrogen. (1.8) b. Paradigm shift: The acceptance of the wave–particle duality paradox for light and ...
Modern Physics Guide
... What events take place (collisions, emission and absorption, and so forth) What events cause others. The mass of an object. What measurements change from one observer to another? Simultaneity of events separated in space. Elapsed time Length in direction of motion Early Quantum: Discovery of electro ...
... What events take place (collisions, emission and absorption, and so forth) What events cause others. The mass of an object. What measurements change from one observer to another? Simultaneity of events separated in space. Elapsed time Length in direction of motion Early Quantum: Discovery of electro ...
Quantum Mechanics
... The nature of a system can be described by probabilistic values; probability of an event is equal to the square of the amplitude of the wavefunction (|ψ|²). Impossible to know all properties of a system at the same time, each must be given by probabilistic values (uncertainty principle). Matter exhi ...
... The nature of a system can be described by probabilistic values; probability of an event is equal to the square of the amplitude of the wavefunction (|ψ|²). Impossible to know all properties of a system at the same time, each must be given by probabilistic values (uncertainty principle). Matter exhi ...
PHYS 481/681 Quantum Mechanics Stephen Lepp August 29, 2016
... Introduction to Quantum Mechanics nd the interpretation of its solutions, the uncertainty principles, one-dimensional problems, harmonic oscillator, angular momentum, the hydrogen atom. 3 credits. • Class MW 11:30-12:45 BPB 249. • Office Hours TTh 12:45-1:30 or by arrangement. • Textbook “Quantum Me ...
... Introduction to Quantum Mechanics nd the interpretation of its solutions, the uncertainty principles, one-dimensional problems, harmonic oscillator, angular momentum, the hydrogen atom. 3 credits. • Class MW 11:30-12:45 BPB 249. • Office Hours TTh 12:45-1:30 or by arrangement. • Textbook “Quantum Me ...
Slide 1 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Chapter 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom 7.1 The Wave Nature of Light 7.2 Quantum Effects and Photons 7.3 The Bohr Theory of the Hydrogen Atom 7.4 Quantum Mechanics 7.5 Quantum Numbers and Atomic Orbitals ...
... Chapter 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom 7.1 The Wave Nature of Light 7.2 Quantum Effects and Photons 7.3 The Bohr Theory of the Hydrogen Atom 7.4 Quantum Mechanics 7.5 Quantum Numbers and Atomic Orbitals ...
Torres: Copenhagen Quantum Mechanics
... None of this could happen on the visible scale “it becomes important to remember that science is concerned only with observable things and that we can observe an object only by letting it interact with some outside influence” -Dirac This interaction, observation, causes a disturbance on the quan ...
... None of this could happen on the visible scale “it becomes important to remember that science is concerned only with observable things and that we can observe an object only by letting it interact with some outside influence” -Dirac This interaction, observation, causes a disturbance on the quan ...