Skills Lab 1
... Report incident to supervisor (2 purple tops & file incident report) Obtain history from the source patient (HIV, Hepatitis or risk factors) ...
... Report incident to supervisor (2 purple tops & file incident report) Obtain history from the source patient (HIV, Hepatitis or risk factors) ...
Abundance of the invertebrate polychaete host
... • Enzootic to the Pacific NW of the United States. – Particularly prevalent in the Klamath River • One of the primary causes of juvenile salmonid death in the Klamath River. • 54% infected in 2008, compared to 10% in other rivers in the West. ...
... • Enzootic to the Pacific NW of the United States. – Particularly prevalent in the Klamath River • One of the primary causes of juvenile salmonid death in the Klamath River. • 54% infected in 2008, compared to 10% in other rivers in the West. ...
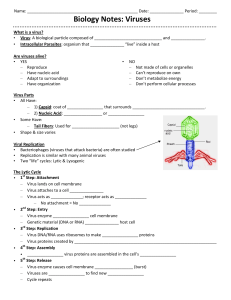
Biology Notes: Viruses
... - Are virus proteins built to make new viruses? ______________________________________ - Is a provirus created? _____________________ - Does a virus connect with the host cell’s receptors? ______________________________ 7. Which two objects make up a provirus? 8. Which virus “life” cycle is cons ...
... - Are virus proteins built to make new viruses? ______________________________________ - Is a provirus created? _____________________ - Does a virus connect with the host cell’s receptors? ______________________________ 7. Which two objects make up a provirus? 8. Which virus “life” cycle is cons ...
viruses
... 2. Vaccines are the best way to protect against viruses a) A vaccine is a dead or weakened version of a virus that is injected into a person to stimulate the immune system. b) Vaccines provide protection only if they are used before an infection begins. ...
... 2. Vaccines are the best way to protect against viruses a) A vaccine is a dead or weakened version of a virus that is injected into a person to stimulate the immune system. b) Vaccines provide protection only if they are used before an infection begins. ...
The Characterization of Myeloid Cell Subsets in Innate and Adaptive
... subsets is still unclear. Furthermore, innate immune responses are not defined well compared to adaptive immune response against Listeria. In particular, immunity in secondary lymphoid organ such as lymph node (LN), there are much more complicated network among immune cells. Therefore I focused on t ...
... subsets is still unclear. Furthermore, innate immune responses are not defined well compared to adaptive immune response against Listeria. In particular, immunity in secondary lymphoid organ such as lymph node (LN), there are much more complicated network among immune cells. Therefore I focused on t ...
Viruses
... living things. • They only respond when they make contact with a suitable host • All types of cells are attacked by viruses – most viruses are specific to one cell type. • Do not have ribosomes, mitochondria or other cytoplasmic organelles cannot carry out metabolisms on their own • Must invade hos ...
... living things. • They only respond when they make contact with a suitable host • All types of cells are attacked by viruses – most viruses are specific to one cell type. • Do not have ribosomes, mitochondria or other cytoplasmic organelles cannot carry out metabolisms on their own • Must invade hos ...
EBV Disease Post-Renal Transplant and PTLD
... • CMV post-transplant infection: evidence of CMV replication regardless of symptoms. • CMV post-transplant disease: evidence of CMV infection with attributable symptoms. Can be further characterized as either a viral syndrome with fever and/or malaise, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia or as tissue invas ...
... • CMV post-transplant infection: evidence of CMV replication regardless of symptoms. • CMV post-transplant disease: evidence of CMV infection with attributable symptoms. Can be further characterized as either a viral syndrome with fever and/or malaise, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia or as tissue invas ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 7. Differentiate inoculative from contaminative mode of infection. 8. Distinguish hepatitis A from Hepatitis B. 9. What are the symptoms of cholera? 10. What is hCG? PART – B Answer any FOUR questions. ...
... 7. Differentiate inoculative from contaminative mode of infection. 8. Distinguish hepatitis A from Hepatitis B. 9. What are the symptoms of cholera? 10. What is hCG? PART – B Answer any FOUR questions. ...
briefing document - Santia Consulting
... bodily fluids of infected animals. It then spreads through human-to-human contact through broken skin or mucous via the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected people. It can also be spread by indirect contact with environments contaminated with such fluids. Health-care workers ...
... bodily fluids of infected animals. It then spreads through human-to-human contact through broken skin or mucous via the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected people. It can also be spread by indirect contact with environments contaminated with such fluids. Health-care workers ...
Blood Borne Pathogens and Other Potentially Infectious
... and the provision of appropriate post-exposure evaluation, prophylaxis and follow-ups for those employees who experience an exposure incident. Endnotes: ”Bloodborne Pathogens” means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and infectious materials that can cause disease in humans. T ...
... and the provision of appropriate post-exposure evaluation, prophylaxis and follow-ups for those employees who experience an exposure incident. Endnotes: ”Bloodborne Pathogens” means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and infectious materials that can cause disease in humans. T ...
Viruses - Mr Murphy`s Science Blog
... Viruses can only multiply inside living cells, therefore they are then obligate parasites Viruses cause diseases in humans, animals and plants Different kinds of viruses have different shapes They can only be seen with an electron microscope ...
... Viruses can only multiply inside living cells, therefore they are then obligate parasites Viruses cause diseases in humans, animals and plants Different kinds of viruses have different shapes They can only be seen with an electron microscope ...
Viruses
... • Reduced risk of perinatal transmission with prenatal zidovudine (AZT) • The most common routes of transmission in the US are sexual contact, IV drug use, and vertical passage from infected mothers to offspring. • Since 1985, transmission by blood transfusion has been rare due to good testing of bl ...
... • Reduced risk of perinatal transmission with prenatal zidovudine (AZT) • The most common routes of transmission in the US are sexual contact, IV drug use, and vertical passage from infected mothers to offspring. • Since 1985, transmission by blood transfusion has been rare due to good testing of bl ...
Ekaterina Dadachova, Ph.D.
... energy the same way as an electron and has the same range in water. It then combines with an electron in annihilation reaction, in which its mass and that of electron are converted into the energy of two 511 keV annihilation photons emitted in exact opposite directions (180o apart). An alpha particl ...
... energy the same way as an electron and has the same range in water. It then combines with an electron in annihilation reaction, in which its mass and that of electron are converted into the energy of two 511 keV annihilation photons emitted in exact opposite directions (180o apart). An alpha particl ...
Epidemic Typhus - AAP Red Book - American Academy of Pediatrics
... Charles-Jules-Henri Nicolle (1866-1936), a physician, microbiologist, novelist, philosopher, and historian. From 1903 until his death in 1936, he was director of the Institut Pasteur in Tunis, Tunisia. Nicolle's many accomplishments include the discovery that epidemic typhus is transmitted by body l ...
... Charles-Jules-Henri Nicolle (1866-1936), a physician, microbiologist, novelist, philosopher, and historian. From 1903 until his death in 1936, he was director of the Institut Pasteur in Tunis, Tunisia. Nicolle's many accomplishments include the discovery that epidemic typhus is transmitted by body l ...
Disorders in Immunity
... Immunity process is a powerful system of _______ Seek out, recognize, and ______ foreign materials to prevent disease BUT, On the other side, overreactivity or underreactivity of immune system can be ...
... Immunity process is a powerful system of _______ Seek out, recognize, and ______ foreign materials to prevent disease BUT, On the other side, overreactivity or underreactivity of immune system can be ...
End of Chapter Questions
... parasite- an organism that lives at the expense of another organism inside of or on the host A virus is an infectious particle that multiplies only within a living cell. 2. Viral infection is usually very specific. Identify the structure of the cell surface that permits only specific viruses to infe ...
... parasite- an organism that lives at the expense of another organism inside of or on the host A virus is an infectious particle that multiplies only within a living cell. 2. Viral infection is usually very specific. Identify the structure of the cell surface that permits only specific viruses to infe ...
Immunogeno: Protective mechanism for Rift Valley fever in the
... immunisation of susceptible domestic animals in endemic countries does not protect animals against the clinical disease but prevents the propagation of virus to human population through reduction of the amplification degree in host animals. The humoral immunity is sufficient for protection for anima ...
... immunisation of susceptible domestic animals in endemic countries does not protect animals against the clinical disease but prevents the propagation of virus to human population through reduction of the amplification degree in host animals. The humoral immunity is sufficient for protection for anima ...
Evaluation of Combination Regimens in GT1
... • Improved response to interferon based treatment • Faster progression to cirrhosis in HIV infection • Treatment effect less significant with HCV direct acting antivirals • Potential role in treatment decisions in acute HCV infection Barreiro P et al. J Infect Dis. 2011;203:1629-1636 DL Ge et al. Na ...
... • Improved response to interferon based treatment • Faster progression to cirrhosis in HIV infection • Treatment effect less significant with HCV direct acting antivirals • Potential role in treatment decisions in acute HCV infection Barreiro P et al. J Infect Dis. 2011;203:1629-1636 DL Ge et al. Na ...
Infection Control Study Guide
... In California in 2000 in the pedicure salons there was an infection in over a 100 salons called Mycobacterium Fortuitum Furunculosis Cocci rarely show self-movement Flagella is a bacteria with hair like extensions to help it move about Mitosis is the process by which bacteria divide Spores during th ...
... In California in 2000 in the pedicure salons there was an infection in over a 100 salons called Mycobacterium Fortuitum Furunculosis Cocci rarely show self-movement Flagella is a bacteria with hair like extensions to help it move about Mitosis is the process by which bacteria divide Spores during th ...
msdoc - Rexano
... [email protected] Sent from the Internet (Details) Dear Sir, This is in response to your inquiry of June 29, 2007, to the Centers for Disease Control and Promotion, regarding transmission of disease from nonhuman primates. Our veterinary officer advises the following: There have been several docum ...
... [email protected] Sent from the Internet (Details) Dear Sir, This is in response to your inquiry of June 29, 2007, to the Centers for Disease Control and Promotion, regarding transmission of disease from nonhuman primates. Our veterinary officer advises the following: There have been several docum ...
Mike Shaw - Institute for People and Technology
... traditional methods such as culture/isolation or visualization of antigens/antibodies: Allows more laboratories to detect pathogens and thus increases the amount of surveillance data. Allows surveillance of more pathogens. Makes true Molecular Epidemiology possible. ...
... traditional methods such as culture/isolation or visualization of antigens/antibodies: Allows more laboratories to detect pathogens and thus increases the amount of surveillance data. Allows surveillance of more pathogens. Makes true Molecular Epidemiology possible. ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.