RSV Brochure_final.pmd
... for writing the original manuscript. Thanks to Kathy Brooks, RN, PhD, CIC, Diane Jones, MSN, CIC, and Kim Strelczyk, MSN, CCRN, CIC for reviewing the brochure. Copyright © 2005 by The Assocation for Professionals in Infection Control and ...
... for writing the original manuscript. Thanks to Kathy Brooks, RN, PhD, CIC, Diane Jones, MSN, CIC, and Kim Strelczyk, MSN, CCRN, CIC for reviewing the brochure. Copyright © 2005 by The Assocation for Professionals in Infection Control and ...
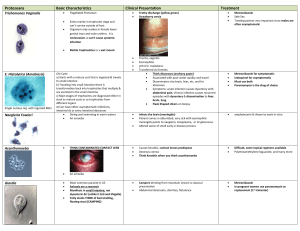
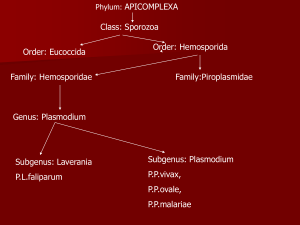
Protozoans
... Filariform larvae penetrate skin and initiate infection, or can have autoinfection from larvae in intestines If immunosuppressed, then preexisting infection can become ...
... Filariform larvae penetrate skin and initiate infection, or can have autoinfection from larvae in intestines If immunosuppressed, then preexisting infection can become ...
九十九學年度 生醫系微生物學期末考 姓名: 學號: 謝絹珠教授:40% I
... E) They are produced by gram-positive bacteria. _____5. Endotoxins are A) Associated with gram-positive bacteria. B) Specific in their method of action. C) Part of the gram-negative cell wall. D) Excreted from the cell. E) A-B toxins. _____6. Patients developed inflammation a few hours following eye ...
... E) They are produced by gram-positive bacteria. _____5. Endotoxins are A) Associated with gram-positive bacteria. B) Specific in their method of action. C) Part of the gram-negative cell wall. D) Excreted from the cell. E) A-B toxins. _____6. Patients developed inflammation a few hours following eye ...
Bloodborne Pathogens Training - University of Michigan
... • Infection of the liver which may lead to liver disease, liver cancer and possibly death. It is the leading occupational disease in the United States. • 12,000 cases of HBV were identified annually (up to the year 1992). Numbers have decreased to approximately 800 cases annually since the introduct ...
... • Infection of the liver which may lead to liver disease, liver cancer and possibly death. It is the leading occupational disease in the United States. • 12,000 cases of HBV were identified annually (up to the year 1992). Numbers have decreased to approximately 800 cases annually since the introduct ...
diagnosis of hiv infection the laboratory
... SEROLOGICAL ASSAYS Depends on rise of antibody levels to detectable range. 2- 8 weeks of acquiring the infection( not useful for early infections) IgM- Gag proteins. IgG- p 24 antigen and the gp120…. gp 41 Persistently undetectable antibodies more than 3 months – rare. ...
... SEROLOGICAL ASSAYS Depends on rise of antibody levels to detectable range. 2- 8 weeks of acquiring the infection( not useful for early infections) IgM- Gag proteins. IgG- p 24 antigen and the gp120…. gp 41 Persistently undetectable antibodies more than 3 months – rare. ...
Medical Microbiology Syllabus (2010)
... knowledge: 1. Lectures will cover the main learning objectives for each section, and are supplemented with: (1) Quizzes, or review questions (2) Discussion on clinical cases and correlations with news of emerging diseases (3) Clinical diagnostic exercises 2. Small Groups: During each section of the ...
... knowledge: 1. Lectures will cover the main learning objectives for each section, and are supplemented with: (1) Quizzes, or review questions (2) Discussion on clinical cases and correlations with news of emerging diseases (3) Clinical diagnostic exercises 2. Small Groups: During each section of the ...
african swine fever
... o fomites include, premises, vehicles, implements, clothes Within tick vector: transstadial, transovarial, and sexual transmission occur ...
... o fomites include, premises, vehicles, implements, clothes Within tick vector: transstadial, transovarial, and sexual transmission occur ...
Hepatitis B FAQ document - National Institute for Communicable
... How is HBV transmitted? Hepatitis B virus is spread when the blood, semen, or other body fluid infected with the Hepatitis B virus enters the body of a person who is not infected. Neonates may become infected with the virus during the birth process (spread from an infected mother to her baby during ...
... How is HBV transmitted? Hepatitis B virus is spread when the blood, semen, or other body fluid infected with the Hepatitis B virus enters the body of a person who is not infected. Neonates may become infected with the virus during the birth process (spread from an infected mother to her baby during ...
Infection
... Shortening of duration of diarrhea from 3 days to 2.6 days, reduction of stool frequency on day 2 by factor 0.8 and so on ...
... Shortening of duration of diarrhea from 3 days to 2.6 days, reduction of stool frequency on day 2 by factor 0.8 and so on ...
MRSA & Bloodborne Pathogens
... **Pathogenic microorganisms that can potentially cause disease **Universal Precautions ...
... **Pathogenic microorganisms that can potentially cause disease **Universal Precautions ...
Pathogenesis of infectious disease
... (e) hemolysins: damage RBC. (f) lecithinase: damage extensive area of tissue. ...
... (e) hemolysins: damage RBC. (f) lecithinase: damage extensive area of tissue. ...
ϕX174 Program of T4 lytic cycle
... ϕX174 • + strand ssDNA genome, 5386 nt with 10 genes • Icosahedral capsid, attaches to LPS • Genome contains overlapping genes: some regions of polycistronic mRNA can be translated in >1 reading frame ...
... ϕX174 • + strand ssDNA genome, 5386 nt with 10 genes • Icosahedral capsid, attaches to LPS • Genome contains overlapping genes: some regions of polycistronic mRNA can be translated in >1 reading frame ...
Administrative Office St. Joseph`s Hospital Site, L301
... 7% (3). Perinatal and sexual transmission is inefficient (1 to 3%) with the former occurring more frequently in individuals with an HIV infection (3). Most people with an acute HCV infection are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms (fatigue, nausea, jaundice) but are unable to clear the virus and are ...
... 7% (3). Perinatal and sexual transmission is inefficient (1 to 3%) with the former occurring more frequently in individuals with an HIV infection (3). Most people with an acute HCV infection are asymptomatic or have mild symptoms (fatigue, nausea, jaundice) but are unable to clear the virus and are ...
TORCH Infections
... infection in pregnancy • Infection rate higher with infxn in 3rd trimester • Fetal death higher with infxn in 1st trimester ...
... infection in pregnancy • Infection rate higher with infxn in 3rd trimester • Fetal death higher with infxn in 1st trimester ...
Rickettsia prowazekii
... trunk and spreading centrifugally, but usually sparing the palms and soles. Not recognized in 30-70% of cases Conjunctival injection and conjunctivitis common Primary symptoms often accompanied by dry mouth, nausea and vomiting, and constipation Patient may appear toxic, with apathy, delirium, cough ...
... trunk and spreading centrifugally, but usually sparing the palms and soles. Not recognized in 30-70% of cases Conjunctival injection and conjunctivitis common Primary symptoms often accompanied by dry mouth, nausea and vomiting, and constipation Patient may appear toxic, with apathy, delirium, cough ...
Unit 13: Sexually Transmitted Diseases
... • Hepatitis = inflammation of the liver • There are six variations of the virus that causes it (A,B,C,D,E and G) • Initial symptoms are similar to the flu, may progress to nausea, vomiting, dark urine, abdominal pain, jaundice (yellow skin) • Chronic hepatitis can cause cirrhosis of the liver, liver ...
... • Hepatitis = inflammation of the liver • There are six variations of the virus that causes it (A,B,C,D,E and G) • Initial symptoms are similar to the flu, may progress to nausea, vomiting, dark urine, abdominal pain, jaundice (yellow skin) • Chronic hepatitis can cause cirrhosis of the liver, liver ...
Vocabulary List
... VIRUS – Smallest microorganism which needs a host to supply food and an environment in which to multiply. There are no specific medications to treat viruses. Viruses can multiply rapidly and are easily transmitted by blood and body secretions. VRE (Vancomycin Resistant Enterococcus): a form of intes ...
... VIRUS – Smallest microorganism which needs a host to supply food and an environment in which to multiply. There are no specific medications to treat viruses. Viruses can multiply rapidly and are easily transmitted by blood and body secretions. VRE (Vancomycin Resistant Enterococcus): a form of intes ...
AISouth Milady Chapter 5
... certain foods, chemicals, or other normally harmless substances. 17. Harmless microorganisms that may perform useful functions and are safe to come in contact with since they do not cause disease or harm. 19. The invasion of body tissues by diseasecausing pathogens. 21. The presence, or the reasonab ...
... certain foods, chemicals, or other normally harmless substances. 17. Harmless microorganisms that may perform useful functions and are safe to come in contact with since they do not cause disease or harm. 19. The invasion of body tissues by diseasecausing pathogens. 21. The presence, or the reasonab ...
toxoplasmosis new
... temperature, sporulation occurs 2 to 21 days after the oocyte is excreted in the feces ) ...
... temperature, sporulation occurs 2 to 21 days after the oocyte is excreted in the feces ) ...
Virus
... What type of gene is mutated to give rise to a tumor? What are two ways that viruses can introduce such mutations? Are most tumors caused this way? In animals, viruses attach to specific receptors on host cells. There are no such receptors in plants. How, then, do viruses infect plants? ...
... What type of gene is mutated to give rise to a tumor? What are two ways that viruses can introduce such mutations? Are most tumors caused this way? In animals, viruses attach to specific receptors on host cells. There are no such receptors in plants. How, then, do viruses infect plants? ...
The Immune System
... Created by transferring antibodies made from one organism into another organism 1. Person bitten by a dog or bat 2. Often acquired before birth may be given antibodies taken from people who have been • As the fetus develops, it receives vaccinated against rabies. antibodies from its mother Why? Rab ...
... Created by transferring antibodies made from one organism into another organism 1. Person bitten by a dog or bat 2. Often acquired before birth may be given antibodies taken from people who have been • As the fetus develops, it receives vaccinated against rabies. antibodies from its mother Why? Rab ...
The Salvation Army Bridge Programme
... 1. good hygiene practices, including hand washing 2. the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) as barriers (Eg. gloves and masks) 3. the appropriate handling and disposal of clinical waste, including sharps 4. hygienic cleaning and care of buildings, furniture and equipment Staff must use stand ...
... 1. good hygiene practices, including hand washing 2. the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) as barriers (Eg. gloves and masks) 3. the appropriate handling and disposal of clinical waste, including sharps 4. hygienic cleaning and care of buildings, furniture and equipment Staff must use stand ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... protozoa or fungi getting into or onto the body[1].Occupation at times poses certain exposurerisks, such as Salmonella species,Vivrio species and Escherichia coli in poultry ,seafood, and beef processing industries. Veterinarian and other working with animals are at increased risk of various zoonosi ...
... protozoa or fungi getting into or onto the body[1].Occupation at times poses certain exposurerisks, such as Salmonella species,Vivrio species and Escherichia coli in poultry ,seafood, and beef processing industries. Veterinarian and other working with animals are at increased risk of various zoonosi ...
Glossary - WHO Western Pacific Region
... Antigen: Any foreign substance, usually a protein that stimulates the body's immune system to produce antibodies. (The name antigen reflects its role in stimulating an immune response antibody generating.) Antiviral: Drug that is used to prevent or cure a disease caused by a virus, by interfering wi ...
... Antigen: Any foreign substance, usually a protein that stimulates the body's immune system to produce antibodies. (The name antigen reflects its role in stimulating an immune response antibody generating.) Antiviral: Drug that is used to prevent or cure a disease caused by a virus, by interfering wi ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.