* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Abundance of the invertebrate polychaete host
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
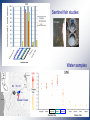
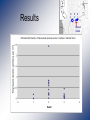
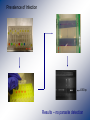
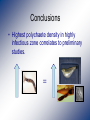
Abundance of the polychaete host of Ceratomyxa shasta and prevalence of infection in the Klamath River. Sue-Jie Koo Mentors: Jerri Bartholomew Sascha Hallett Department of Microbiology Oregon State University Ceratomyxa shasta : The parasite • A myxozoan parasite • Ceratomyxosis – epithelial lining necrotises in salmonids. ~10 μm • Enzootic to the Pacific NW of the United States. – Particularly prevalent in the Klamath River • One of the primary causes of juvenile salmonid death in the Klamath River. • 54% infected in 2008, compared to 10% in other rivers in the West. Life cycle of C. shasta Manayunkia speciosa : The polychaete • Freshwater • Definitive host in the lifecycle of C. shasta • Few studies on its ecology • Spatial distribution • Seasonality • Density • Few studies on its role in the infection dynamics of C. shasta • • • • Prevalence of infection Intensity of infection Seasonality Spatial distribution Working hypothesis • Polychaete densities and infection prevalence with Ceratomyxa shasta directly correlate with disease effects in salmonids. + = Significance • Assist in parasite management options to reduce the impact of the parasite on salmonid populations in the Klamath River. • Reduction in returns affect fishermen and farmers • Contribute data to the information known about M. speciosa. Methodology • The samples were collected as part of a large sampling study in the Klamath River in 2006. R3 R2 R1 Sentinel fish studies Water samples R3 R2 R1 Beaver Creek Polychaete Density Stained Manayunkia speciosa Av. # polychaetes x # squares Field density = Av. field sampling area Results R 3 R 2 R 1 Beaver Creek Prevalence of Infection 630 bp Results – no parasite detection Troubleshooting DNA recovery • Parasite spike was inhibited • Change DNA extraction buffers and dilution • 2006 Polychaete DNA not replicated in PCR • Change extraction buffers, dilution, primers, PCR programs • Diagnostics comparing 2006 and 2009 polychaetes • Crude vs Qiagen purified • Qiagen purified 2006 DNA inconsistent results Conclusions • Highest polychaete density in highly infectious zone correlates to preliminary studies. Potential Future Work • Manayunkia speciosa temporal distribution • M. speciosa prevalence of infection with Ceratomyxa shasta Acknowledgements Sascha Hallett Jerri Bartholomew Gerri Buckles Jill Pridgen Dan Horner Bartholomew Lab Salmon Disease Lab Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife HHMI Kevin Ahern