Applied Immunology - European Centre for Disease Prevention and
... Large molecules, is anything that obtain the formation of a specific immune response (Anomy) Ag determinants (epitopes) are the particular chemical groups on a molecule that are antigenic Antibody(Ab)/immunoglobulin (Ig). A special group of soluble proteins that are produced in response to foreign a ...
... Large molecules, is anything that obtain the formation of a specific immune response (Anomy) Ag determinants (epitopes) are the particular chemical groups on a molecule that are antigenic Antibody(Ab)/immunoglobulin (Ig). A special group of soluble proteins that are produced in response to foreign a ...
Viktor`s Notes * Infections of Nervous System
... CSF is indicated in any patient (after exclusion of intracranial mass). brain biopsy (→ immunostaining techniques, electron microscopy, injection into susceptible animals and tissue culture cell lines) is still standard of diagnosis in some specific CNS infections. CBC with differential is nonspecif ...
... CSF is indicated in any patient (after exclusion of intracranial mass). brain biopsy (→ immunostaining techniques, electron microscopy, injection into susceptible animals and tissue culture cell lines) is still standard of diagnosis in some specific CNS infections. CBC with differential is nonspecif ...
Expansion of in vitro potency testing: Case Study with Serovar Hardjo
... Split Hardjo into types • Hardjo-bovis isolated around the world • Hardjo type prajitno UK, Africa and ...
... Split Hardjo into types • Hardjo-bovis isolated around the world • Hardjo type prajitno UK, Africa and ...
Infectious Disease Policy
... consult with appropriate health care professionals to determine whether continuing to provide professional services represents a material risk to the client. If a dental faculty member, student or staff member learns that continuing to provide professional services represents a material risk to clie ...
... consult with appropriate health care professionals to determine whether continuing to provide professional services represents a material risk to the client. If a dental faculty member, student or staff member learns that continuing to provide professional services represents a material risk to clie ...
Universal Precautions - Natomas Unified School District
... have ISG (Immune Serum Globulin) within two weeks of contact. In the school setting, food handlers and other persons working in the cafeteria should be instructed to wash hands carefully before working. Plastic gloves should be worn when handling foods such as salads and sandwiches. Hepatitis B and ...
... have ISG (Immune Serum Globulin) within two weeks of contact. In the school setting, food handlers and other persons working in the cafeteria should be instructed to wash hands carefully before working. Plastic gloves should be worn when handling foods such as salads and sandwiches. Hepatitis B and ...
Concepts of Infectious Diseases
... presentations of illness – witness the first presentations of AIDS, West Nile virus or Legionnaire’s Disease. Most infections are, however, subclinical and are detected only when serologic or other sensitive assays become available for recognition of past exposure. This concept is often referred to ...
... presentations of illness – witness the first presentations of AIDS, West Nile virus or Legionnaire’s Disease. Most infections are, however, subclinical and are detected only when serologic or other sensitive assays become available for recognition of past exposure. This concept is often referred to ...
Viral vaccines
... Gene coding for immunizing proteins of the influenza virus, herpes simplex virus, and rabies virus have been synthesized in bacteria. A recombinant hepatitis B virus vaccine contains viral protein synthesized in yeast cells or mammalian cell lines. ...
... Gene coding for immunizing proteins of the influenza virus, herpes simplex virus, and rabies virus have been synthesized in bacteria. A recombinant hepatitis B virus vaccine contains viral protein synthesized in yeast cells or mammalian cell lines. ...
Identification of Infectious Disease Processes
... Tumor Necrosis Factorcause protein catabolism in host w/ loss of muscle mass Lymphotoxin: promotes inflammation; stimulates neutrophils Granulocyte and Monocyte Stimulating Factors - reproduction ...
... Tumor Necrosis Factorcause protein catabolism in host w/ loss of muscle mass Lymphotoxin: promotes inflammation; stimulates neutrophils Granulocyte and Monocyte Stimulating Factors - reproduction ...
CS12 Herpes Simplex Virus_Presentation
... infection was caused by HSV-1 or HSV-2? (cont…) • There is some difference between the cytopathic effect caused by HSV-1 and HSV-2 in the cell culture. HSV-1 produces CPE throughout the cells’ monolayer, whereas HSV-2 CPE tend to be focal. • Although HSV-1 and HSV-2 have many antigens in common, the ...
... infection was caused by HSV-1 or HSV-2? (cont…) • There is some difference between the cytopathic effect caused by HSV-1 and HSV-2 in the cell culture. HSV-1 produces CPE throughout the cells’ monolayer, whereas HSV-2 CPE tend to be focal. • Although HSV-1 and HSV-2 have many antigens in common, the ...
Concepts of Infectious Diseases
... presentations of illness – witness the first presentations of AIDS, West Nile virus or Legionnaire’s Disease. Most infections are, however, subclinical and are detected only when serologic or other sensitive assays become available for recognition of past exposure. This concept is often referred to ...
... presentations of illness – witness the first presentations of AIDS, West Nile virus or Legionnaire’s Disease. Most infections are, however, subclinical and are detected only when serologic or other sensitive assays become available for recognition of past exposure. This concept is often referred to ...
Programme - Wilton Park
... universal access to ARV therapy, diagnosis and treatment of HIV co-infections must become a priority in resource-limited settings. Despite many challenges, encouraging progress continues in the development of screening tools and effective drug therapies for viral hepatitis co-infections, and in maki ...
... universal access to ARV therapy, diagnosis and treatment of HIV co-infections must become a priority in resource-limited settings. Despite many challenges, encouraging progress continues in the development of screening tools and effective drug therapies for viral hepatitis co-infections, and in maki ...
tsukamurella
... accommodate a group of chemically unique organisms characterized by a series of very long chain (68– 76 carbons), highly unsaturated mycolic acids, meso-diaminopimelic acid and arabinogalactan, common to the genus Corynebacterium. The type species is T. paurometabola, and the following additional sp ...
... accommodate a group of chemically unique organisms characterized by a series of very long chain (68– 76 carbons), highly unsaturated mycolic acids, meso-diaminopimelic acid and arabinogalactan, common to the genus Corynebacterium. The type species is T. paurometabola, and the following additional sp ...
HIV (AIDS) - Austin Community College
... and access to free condoms and clean needles. In Thailand the Ministry of Public Health has attempted to inspire 100 percent condom use in brothels. It provides condoms and advocates safer sex practices through the media. [9] ...
... and access to free condoms and clean needles. In Thailand the Ministry of Public Health has attempted to inspire 100 percent condom use in brothels. It provides condoms and advocates safer sex practices through the media. [9] ...
Vargas, Sarah
... mononucleosis, which is often referred to as “mono” or “the kissing disease”. Infectious mononucleosis is a common illness that is often seen in teens and young adults that by the age of forty 90% of adults have developed an immunity to. This kissing disease is transmittable through saliva, mucous f ...
... mononucleosis, which is often referred to as “mono” or “the kissing disease”. Infectious mononucleosis is a common illness that is often seen in teens and young adults that by the age of forty 90% of adults have developed an immunity to. This kissing disease is transmittable through saliva, mucous f ...
conceptsID_Lowy
... presentations of illness – witness the first presentations of AIDS, West Nile virus or Legionnaire’s Disease. Most infections are, however, subclinical and are detected only when serologic or other sensitive assays become available for recognition of past exposure. This concept is often referred to ...
... presentations of illness – witness the first presentations of AIDS, West Nile virus or Legionnaire’s Disease. Most infections are, however, subclinical and are detected only when serologic or other sensitive assays become available for recognition of past exposure. This concept is often referred to ...
Concepts of Infectious Diseases
... presentations of illness – witness the first presentations of AIDS, West Nile virus or Legionnaire’s Disease. Most infections are, however, subclinical and are detected only when serologic or other sensitive assays become available for recognition of past exposure. This concept is often referred to ...
... presentations of illness – witness the first presentations of AIDS, West Nile virus or Legionnaire’s Disease. Most infections are, however, subclinical and are detected only when serologic or other sensitive assays become available for recognition of past exposure. This concept is often referred to ...
Slide 1
... Inactivated or killed disease agents Less effective but safer, need boosters Subunit vaccines – use only subunits of antigens Toxoid vaccines - against toxins made by bacteria ...
... Inactivated or killed disease agents Less effective but safer, need boosters Subunit vaccines – use only subunits of antigens Toxoid vaccines - against toxins made by bacteria ...
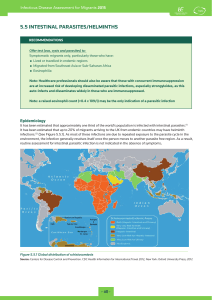
5.5 INTESTINAL PARASITES/HELMINTHS
... = Migrated from Southeast Asia or Sub-Saharan Africa = Eosinophilia ...
... = Migrated from Southeast Asia or Sub-Saharan Africa = Eosinophilia ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... Bloodborne Pathogens are microorganisms that may be present in human blood and other body fluids and can cause diseases such as hepatitis B & C and HIV. It pays to know as much as you can about Bloodborne Pathogens and what steps you can take to avoid exposure. It is estimated that 1 out of 250 peop ...
... Bloodborne Pathogens are microorganisms that may be present in human blood and other body fluids and can cause diseases such as hepatitis B & C and HIV. It pays to know as much as you can about Bloodborne Pathogens and what steps you can take to avoid exposure. It is estimated that 1 out of 250 peop ...
Progressive Right-Sided Hemiparesis in a Man
... Only select cell types express the specific polysialic acid receptor for the JC virus. In the central nervous system, this receptor is found on astrocytes and oligodendroglial lineages. JC viral entry occurs via clathrin-mediated endocytosis and can also be facilitated by serotonin receptors (subtype ...
... Only select cell types express the specific polysialic acid receptor for the JC virus. In the central nervous system, this receptor is found on astrocytes and oligodendroglial lineages. JC viral entry occurs via clathrin-mediated endocytosis and can also be facilitated by serotonin receptors (subtype ...
Notification of Infectious Disease
... under Act 491 are tuberculosis, meningitis, measles, chicken pox, and influenza. Bloodborne diseases covered under Act 491 are human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis A, hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C, and venereal diseases, including syphilis on gohnorea. Observing some or all of the fo ...
... under Act 491 are tuberculosis, meningitis, measles, chicken pox, and influenza. Bloodborne diseases covered under Act 491 are human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis A, hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C, and venereal diseases, including syphilis on gohnorea. Observing some or all of the fo ...
Fingernail Infection (Paronychia)
... What is the cause? If the cuticle has a large pimple or is draining pus, it is usually infected with the Staphylococcus bacteria. The bacteria usually enters the skin through a break in the skin caused by pulling on or chewing on the cuticle. If the cuticle area is only red and swollen without pus, ...
... What is the cause? If the cuticle has a large pimple or is draining pus, it is usually infected with the Staphylococcus bacteria. The bacteria usually enters the skin through a break in the skin caused by pulling on or chewing on the cuticle. If the cuticle area is only red and swollen without pus, ...
Hepatitis B – Acute Case
... In persons with clinical illness, the onset is usually insidious with anorexia, vague abdominal discomfort, nausea and vomiting, sometimes arthralgias and rash, often progressing to jaundice. Fever may be absent or mild. Severity ranges from inapparent cases detectable only by liver function tests t ...
... In persons with clinical illness, the onset is usually insidious with anorexia, vague abdominal discomfort, nausea and vomiting, sometimes arthralgias and rash, often progressing to jaundice. Fever may be absent or mild. Severity ranges from inapparent cases detectable only by liver function tests t ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.