6CDE Transcription and Translation
... 1. Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from DNA (in the nucleus in eukaryotic cells); this is gene expression. For transcription to occur, the DNA helix unzips itself, and the antisense strand of the DNA is transcribed into mRNA. 2. Translation is the process of synthesizing proteins fr ...
... 1. Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from DNA (in the nucleus in eukaryotic cells); this is gene expression. For transcription to occur, the DNA helix unzips itself, and the antisense strand of the DNA is transcribed into mRNA. 2. Translation is the process of synthesizing proteins fr ...
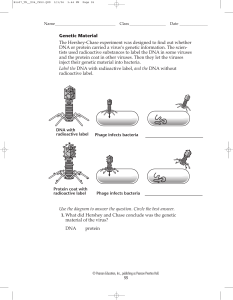
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
CHEM523 Test 3
... 2) (4 points) List two proteins or enzymes, other than DNA polymerase III, that are found at the replication fork in E. coli; describe each of their functions with a single, coherent and complete sentence (that means nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs in an intelligent and relevant arrangement). ...
... 2) (4 points) List two proteins or enzymes, other than DNA polymerase III, that are found at the replication fork in E. coli; describe each of their functions with a single, coherent and complete sentence (that means nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs in an intelligent and relevant arrangement). ...
4 chapter_test_b 4 chapter_test_b
... 1. DNA is composed of subunits known as ______________________. 2. Chargaff’s rules state that the amount of ______________________ in DNA is always equal to the amount of guanine. 3. When scientists transfer genes from one organism to another, it is called ______________________. 4. When sequences ...
... 1. DNA is composed of subunits known as ______________________. 2. Chargaff’s rules state that the amount of ______________________ in DNA is always equal to the amount of guanine. 3. When scientists transfer genes from one organism to another, it is called ______________________. 4. When sequences ...
BIOL/GEN 313_Exam 1 Review_013116
... 20. What is telomerase? How is DNA replication by telomerase different than DNA replication by DNA polymerase? ...
... 20. What is telomerase? How is DNA replication by telomerase different than DNA replication by DNA polymerase? ...
File - Cowan Science
... another • occurs naturally in nature (identical twins) • may be used for cloning stem cells, reviving endangered or extinct species, reproducing a deceased pet or child. How is a clone made? • An early stage embryo is split into cells before those cells have differentiated, the cells are then grown ...
... another • occurs naturally in nature (identical twins) • may be used for cloning stem cells, reviving endangered or extinct species, reproducing a deceased pet or child. How is a clone made? • An early stage embryo is split into cells before those cells have differentiated, the cells are then grown ...
242413_Fx_DNA_Fingerprinting_Lab
... Using the Hardy-Weinberg equation provided, what is the probability of a Hispanic individual being heterozygous for D8S1179 for alleles 9 and 13? ...
... Using the Hardy-Weinberg equation provided, what is the probability of a Hispanic individual being heterozygous for D8S1179 for alleles 9 and 13? ...
DNA: The Genetic Material
... genetic material of phages – small viruses that infect bacteria -- and ...
... genetic material of phages – small viruses that infect bacteria -- and ...
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... Which of the following statements is true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
... Which of the following statements is true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
Slide 1 - Brookwood High School
... Result when chromosomes do not separate correctly during meiosis Most common error = nondisjunction – chromosomes do not separately properly and results in abnormal number of chromosomes in gametes Ex. Down syndrome = Trisomy 21, have 3 copies of chromosome 21 ...
... Result when chromosomes do not separate correctly during meiosis Most common error = nondisjunction – chromosomes do not separately properly and results in abnormal number of chromosomes in gametes Ex. Down syndrome = Trisomy 21, have 3 copies of chromosome 21 ...
DNA quantification
... • Concentration and quality of a sample of DNA or RNA are measured with a UV spectrophotometer. • Since nitrogenous bases absorb UV light, the more concentrated the DNA solution, the more UV light it will absorb. • A solution containing 50 µg per ml of double strand DNA has an absorbancy (optical de ...
... • Concentration and quality of a sample of DNA or RNA are measured with a UV spectrophotometer. • Since nitrogenous bases absorb UV light, the more concentrated the DNA solution, the more UV light it will absorb. • A solution containing 50 µg per ml of double strand DNA has an absorbancy (optical de ...
I - cloudfront.net
... Take the tour of DNA by clicking on “What is DNA?” and answer the questions below: 1. In what organelle (CELL PART) would I find your DNA (YOUR INSTRUCTIONS)? _________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? __________________________ 3. The DNA molecule comes in the form of a ___________ladder and sci ...
... Take the tour of DNA by clicking on “What is DNA?” and answer the questions below: 1. In what organelle (CELL PART) would I find your DNA (YOUR INSTRUCTIONS)? _________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? __________________________ 3. The DNA molecule comes in the form of a ___________ladder and sci ...
GENETIC ENGINEERING QUESTIONS
... b. The amount of DNA produced by PCR doubled with each cycle c. The DNA copies produced by PCR were not accurate copies of the DNA d. The rate at which PCR produced accurate copies fell in later cycles 8. Based on the graph, which of the following might have happened between cycles 12 and 13? a. PCR ...
... b. The amount of DNA produced by PCR doubled with each cycle c. The DNA copies produced by PCR were not accurate copies of the DNA d. The rate at which PCR produced accurate copies fell in later cycles 8. Based on the graph, which of the following might have happened between cycles 12 and 13? a. PCR ...
Molecular Genetics
... • 1. Polymers of nucleotides are produced by dehydration synthesis of nucleotides in a 5’ to 3’ direction • 2. this represents a single strand of DNA • 3. If another nucleotide were to join this existing strand-to where would it attach? Which end? ...
... • 1. Polymers of nucleotides are produced by dehydration synthesis of nucleotides in a 5’ to 3’ direction • 2. this represents a single strand of DNA • 3. If another nucleotide were to join this existing strand-to where would it attach? Which end? ...
Molecular Genetics
... • 1. Polymers of nucleotides are produced by dehydration synthesis of nucleotides in a 5’ to 3’ direction • 2. this represents a single strand of DNA • 3. If another nucleotide were to join this existing strand-to where would it attach? Which end? ...
... • 1. Polymers of nucleotides are produced by dehydration synthesis of nucleotides in a 5’ to 3’ direction • 2. this represents a single strand of DNA • 3. If another nucleotide were to join this existing strand-to where would it attach? Which end? ...
Chapter 9 DNA: The Genetic Material
... RNA polymerase binds to genes promoter (sequence that signals process to start.) DNA strands unwind and separate. Complementary RNA nucleotides are added to make mRNA strand. Codon - sequence of 3 nucleotides on mRNA; stands for one amino acid in a protein. 2. Translation – tRNA (transfer RN ...
... RNA polymerase binds to genes promoter (sequence that signals process to start.) DNA strands unwind and separate. Complementary RNA nucleotides are added to make mRNA strand. Codon - sequence of 3 nucleotides on mRNA; stands for one amino acid in a protein. 2. Translation – tRNA (transfer RN ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.