Big Questions
... Genetics and Heredity Unit Part One: Meiosis Big Questions: Where do my chromosomes come from? What happens during meiosis? Word Wall: ...
... Genetics and Heredity Unit Part One: Meiosis Big Questions: Where do my chromosomes come from? What happens during meiosis? Word Wall: ...
Genetically Modified Food
... vector into a host cell (transformation) and Cloning the DNA Step 1) Adding the plasmid vector into a flask containing culture of a host cell Step 2) Generating temporary pores on the surface of the host cell Step 3) Allowing the plasmid vector to enter the host cell Step 4) Placing the host ...
... vector into a host cell (transformation) and Cloning the DNA Step 1) Adding the plasmid vector into a flask containing culture of a host cell Step 2) Generating temporary pores on the surface of the host cell Step 3) Allowing the plasmid vector to enter the host cell Step 4) Placing the host ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... 20. The parts of DNA that provide the code for proteins are the – a. sugars b. nitrogenous bases ...
... 20. The parts of DNA that provide the code for proteins are the – a. sugars b. nitrogenous bases ...
Inherited traits are traits that you get from your parents
... Inherited traits are traits that you get from your parents that are influenced by your genes. Environmental traits are influenced by your environment (you can learn them or control them). 2) List 3 examples of inherited traits. Explain why these traits are inherited traits. Natural hair color, natur ...
... Inherited traits are traits that you get from your parents that are influenced by your genes. Environmental traits are influenced by your environment (you can learn them or control them). 2) List 3 examples of inherited traits. Explain why these traits are inherited traits. Natural hair color, natur ...
chapter11
... 12. Complementary base paring of adenine and thymine and guanine and cytosine are the basis of Chargaff ‘s rule, which is A = T and C = T in DNA. ...
... 12. Complementary base paring of adenine and thymine and guanine and cytosine are the basis of Chargaff ‘s rule, which is A = T and C = T in DNA. ...
BL220
... Construct a simple restriction enzyme map Carry out an experiment in gene transmission using Drosophila as a test organism Perform simple population problems using the Hardy-Weinberg equation EXAMS: There will be four hourly exams worth 15% each. These will be a combination of problems, essays and o ...
... Construct a simple restriction enzyme map Carry out an experiment in gene transmission using Drosophila as a test organism Perform simple population problems using the Hardy-Weinberg equation EXAMS: There will be four hourly exams worth 15% each. These will be a combination of problems, essays and o ...
Chapter 12 - Biotechnology
... Viruses • Viruses are the vectors of choice for animal cells. • They can accept larger amounts of DNA than plasmids. • When the virus reproduces within the animal cell, it also reproduces the foreign gene that it carries. The gene is therefore cloned. • The DNA of some retroviruses becomes integrate ...
... Viruses • Viruses are the vectors of choice for animal cells. • They can accept larger amounts of DNA than plasmids. • When the virus reproduces within the animal cell, it also reproduces the foreign gene that it carries. The gene is therefore cloned. • The DNA of some retroviruses becomes integrate ...
Chapter 20~ DNA Technology & Genomics
... CGACTAGCATGATCGATCAGCTACATGCTAGCACACYC GTACATCGATCCTGACATCGACCTGCTCGTACATGCTA ...
... CGACTAGCATGATCGATCAGCTACATGCTAGCACACYC GTACATCGATCCTGACATCGACCTGCTCGTACATGCTA ...
Biotechnology Part 1
... Plasmid: Small circular loop of DNA, outside of the main chromosome Bioinformatics: Use computers to sort through data ...
... Plasmid: Small circular loop of DNA, outside of the main chromosome Bioinformatics: Use computers to sort through data ...
Genetics Quiz – 18 October 2005
... For the next few questions - A) True / B) False 1. Somatic cells include all body cells with the exception of gamete producing cells True 2. Gametes (sperm or egg) are diploid, that is they have half the number of chromosomes of either parent False 3. mitosis occurs in gametes producing four identic ...
... For the next few questions - A) True / B) False 1. Somatic cells include all body cells with the exception of gamete producing cells True 2. Gametes (sperm or egg) are diploid, that is they have half the number of chromosomes of either parent False 3. mitosis occurs in gametes producing four identic ...
NMEICT PROJECT
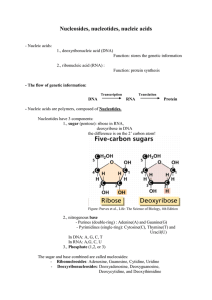
... 1. Who proposed the structure of of nucleic acid? 2. Which are the three covalently bound parts of nucleotides? 3. What are the sugars of nucleic acid? 4. Which are the bases of nucleic acid? 5. How nucleotides polymerize to form nucleotides? 6. What are the features of nucleic acid defined by Watso ...
... 1. Who proposed the structure of of nucleic acid? 2. Which are the three covalently bound parts of nucleotides? 3. What are the sugars of nucleic acid? 4. Which are the bases of nucleic acid? 5. How nucleotides polymerize to form nucleotides? 6. What are the features of nucleic acid defined by Watso ...
Name of structure?
... shared by all organisms? All 20 amino acids are common to all living systems ...
... shared by all organisms? All 20 amino acids are common to all living systems ...
19-7-SA-V1-S1__mcq_a..
... 1. Who proposed the structure of of nucleic acid? 2. Which are the three covalently bound parts of nucleotides? 3. What are the sugars of nucleic acid? 4. Which are the bases of nucleic acid? 5. How nucleotides polymerize to form nucleotides? 6. What are the features of nucleic acid defined by Watso ...
... 1. Who proposed the structure of of nucleic acid? 2. Which are the three covalently bound parts of nucleotides? 3. What are the sugars of nucleic acid? 4. Which are the bases of nucleic acid? 5. How nucleotides polymerize to form nucleotides? 6. What are the features of nucleic acid defined by Watso ...
Chapter 16 Review
... The DNA of somatic cells is constantly bombarded with agents from the environment that could cause mutations. Select the correct statement about mutations and somatic cells. A. Somatic cells are in the various organs of organisms and are shielded from the harmful agents that might cause mutations. ...
... The DNA of somatic cells is constantly bombarded with agents from the environment that could cause mutations. Select the correct statement about mutations and somatic cells. A. Somatic cells are in the various organs of organisms and are shielded from the harmful agents that might cause mutations. ...
Biology EOC Class 4
... “record the number of organisms in the sample area,” “measure the height of the plant,” or “measure the time for seeds to germinate” to earn credit for the responding variable. Students are expected to include at least three conditions of the manipulated/independent variable for both controlled expe ...
... “record the number of organisms in the sample area,” “measure the height of the plant,” or “measure the time for seeds to germinate” to earn credit for the responding variable. Students are expected to include at least three conditions of the manipulated/independent variable for both controlled expe ...
Objective - Central Magnet School
... Bell Work • Why is Taq polymerase used in PCR instead of human polymerase? ...
... Bell Work • Why is Taq polymerase used in PCR instead of human polymerase? ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations Guided Notes
... o There is a different base ______________ (U) takes the place of ___________ (T) The job of mRNA is to take directions for one gene and transport it to a ____________ in the ________________. o This is so a cell can begin assembling _________________, the building blocks of ________________! o It ...
... o There is a different base ______________ (U) takes the place of ___________ (T) The job of mRNA is to take directions for one gene and transport it to a ____________ in the ________________. o This is so a cell can begin assembling _________________, the building blocks of ________________! o It ...
News in DNA/RNA electrophoresis: Midori
... used as a safer alternative to the traditional Ethidium Bromide stain for detecting nucleic acid in agarose gels. It is as sensitive as ethidium bromide and can be used exactly the same way in agarose gel electrophoresis (Figure 1). ...
... used as a safer alternative to the traditional Ethidium Bromide stain for detecting nucleic acid in agarose gels. It is as sensitive as ethidium bromide and can be used exactly the same way in agarose gel electrophoresis (Figure 1). ...
Document
... Chapter 12. Transcriptional Activators in Eucaryotes Chapter 11. General Transcription Factors in Eucaryotes. ...
... Chapter 12. Transcriptional Activators in Eucaryotes Chapter 11. General Transcription Factors in Eucaryotes. ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.























