Study Guide for Exam 3
... 15. Give the function of DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase. 16. Explain the implications of the DNA code being common to all organisms. 17. Explain how DNA from one organism is used in another organism. 18. Identify potential medical treatments based on DNA technology. 19.Chapter 9 20. Name the purp ...
... 15. Give the function of DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase. 16. Explain the implications of the DNA code being common to all organisms. 17. Explain how DNA from one organism is used in another organism. 18. Identify potential medical treatments based on DNA technology. 19.Chapter 9 20. Name the purp ...
Genetics Packet 2017
... to another cellular organism. This cell is typically a bacterial plasmid. This cell will then divide and the DNA will be reproduced in this new cell. Scientists studying a particular gene often use bacterial plasmids to generate multiple copies of the same gene. Scientists then use this “recombinant ...
... to another cellular organism. This cell is typically a bacterial plasmid. This cell will then divide and the DNA will be reproduced in this new cell. Scientists studying a particular gene often use bacterial plasmids to generate multiple copies of the same gene. Scientists then use this “recombinant ...
Mutation and Genetic Variation - Cal State LA
... For every gene, there are many different alleles - alleles are versions of the same gene that differ in their DNA base sequence ...
... For every gene, there are many different alleles - alleles are versions of the same gene that differ in their DNA base sequence ...
cells
... the nucleus called chromosomes • He called the process of cell division mitosis • Wilhelm Roux (1883) and August Weisman (shortly after) suggested that chromosomes carried the genetic material ...
... the nucleus called chromosomes • He called the process of cell division mitosis • Wilhelm Roux (1883) and August Weisman (shortly after) suggested that chromosomes carried the genetic material ...
PS 4 answers
... One of the most common applications of using recombinant DNA techniques like PCR, restriction enzyme digests, and agarose gels is to test samples of human cells such as blood cells to identify people for forensic analysis or paternity testing. This problem is designed to show you how this type of an ...
... One of the most common applications of using recombinant DNA techniques like PCR, restriction enzyme digests, and agarose gels is to test samples of human cells such as blood cells to identify people for forensic analysis or paternity testing. This problem is designed to show you how this type of an ...
Sequencing a genome and Basic Sequence Alignment
... The figure shows to sequences of nucleic acids. Some have the same base (nucleic acid ) and so there is a match at this position between the strands. This is represented by a vertical line and a blue highlight. Others do not match and have no vertical line and blue highlight: these are unmatched pai ...
... The figure shows to sequences of nucleic acids. Some have the same base (nucleic acid ) and so there is a match at this position between the strands. This is represented by a vertical line and a blue highlight. Others do not match and have no vertical line and blue highlight: these are unmatched pai ...
No Slide Title
... randomly add yeast sequences to a selectable marker and transform only cells which took up plasmid containing marker and origin grew call eukaryotic origins ARS ...
... randomly add yeast sequences to a selectable marker and transform only cells which took up plasmid containing marker and origin grew call eukaryotic origins ARS ...
GenomeCompress: A Novel Algorithm for DNA
... sux tree in the 1st pass. In the encoding phase, the repetitions are coded with guaranteed gain; otherwise, two-bit per base encoding will be used. This is similar to the codeword encoding condition in Biocompress-2 except that the order-2 arithmetic coding is not used in Cfact. E. Rivals et al. [16 ...
... sux tree in the 1st pass. In the encoding phase, the repetitions are coded with guaranteed gain; otherwise, two-bit per base encoding will be used. This is similar to the codeword encoding condition in Biocompress-2 except that the order-2 arithmetic coding is not used in Cfact. E. Rivals et al. [16 ...
Manipulating Genomes
... The Human Genome provides a context for exploring whole chromosomes and relating their structure to their DNA sequences, using resources from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. The GeneBoy tool on this site allows students to perform their own analysis of sections of sequence so they can understand how ...
... The Human Genome provides a context for exploring whole chromosomes and relating their structure to their DNA sequences, using resources from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. The GeneBoy tool on this site allows students to perform their own analysis of sections of sequence so they can understand how ...
Microbial Genetics - University of Montana
... Mobilizable plasmids • Donor cell has mobilizable and selftransmissible plasmids • Coupling protein of selftransmissible plasmids signals cell contact made • mob relaxase initiates transfer of mobilizable plasmid DNA strand • Mobilized plasmid replicated in recipient cell • Self-transmissible plasm ...
... Mobilizable plasmids • Donor cell has mobilizable and selftransmissible plasmids • Coupling protein of selftransmissible plasmids signals cell contact made • mob relaxase initiates transfer of mobilizable plasmid DNA strand • Mobilized plasmid replicated in recipient cell • Self-transmissible plasm ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Nucleotide Structure
... o The two strands are antiparallel (opposite in direction). o The two strands are complementary. A always pairs with T (two hydrogen bonds), and G always pairs with C (three hydrogen bonds). Thus, the base sequence on one strand defines the base sequence on the other strand. o Because of the specifi ...
... o The two strands are antiparallel (opposite in direction). o The two strands are complementary. A always pairs with T (two hydrogen bonds), and G always pairs with C (three hydrogen bonds). Thus, the base sequence on one strand defines the base sequence on the other strand. o Because of the specifi ...
Local DNA stretching mimics the distortion caused by - ENS-phys
... JUMNA also allows helical symmetry to be imposed by simply grouping together helically equivalent variables. In this case, it is possible to further reduce the cost of energy calculations and to avoid end-effects by optimizing the energy of one symmetry repeating unit within a regular polymeric envi ...
... JUMNA also allows helical symmetry to be imposed by simply grouping together helically equivalent variables. In this case, it is possible to further reduce the cost of energy calculations and to avoid end-effects by optimizing the energy of one symmetry repeating unit within a regular polymeric envi ...
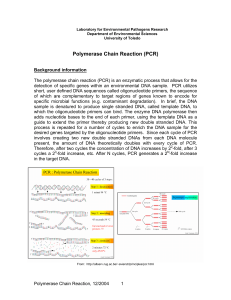
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - Department of Environmental
... 200µM. It is very important to have equal concentrations of each dNTP (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP), as inaccuracy in the concentration of even a single dNTP dramatically increases the misincorporation level. Taq DNA polymerase This DNA polymerase is isolated from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus, which l ...
... 200µM. It is very important to have equal concentrations of each dNTP (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP), as inaccuracy in the concentration of even a single dNTP dramatically increases the misincorporation level. Taq DNA polymerase This DNA polymerase is isolated from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus, which l ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein.
... similar ways, they do have differences in cellular machinery and in details of the processes. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases differ from those of prokaryotes and require transcription factors. They differ in how transcription is terminated. Their ribosomes also are different. ...
... similar ways, they do have differences in cellular machinery and in details of the processes. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases differ from those of prokaryotes and require transcription factors. They differ in how transcription is terminated. Their ribosomes also are different. ...
03-131 Genes, Drugs, and Diseases Exam 2 – F2015 Name:____________________
... Choice C: What is herd immunity and why is it important for protection of the population? Choice A: Because the virus changes each year due to mixing of the RNA chromosomes in the virus by infection of the same cell by two different flu viruses. The virus produced from this cell will have a mixture ...
... Choice C: What is herd immunity and why is it important for protection of the population? Choice A: Because the virus changes each year due to mixing of the RNA chromosomes in the virus by infection of the same cell by two different flu viruses. The virus produced from this cell will have a mixture ...
Meiosis
... and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.9-10.5 Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms. Identify the basic structure and function of nucleic ...
... and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.9-10.5 Analyze the structure of the relationships among concepts in a text, including relationships among key terms. Identify the basic structure and function of nucleic ...
Punnett Square Practice
... a) What percentage of offspring would be expected to have short whiskers from the cross of two longwhiskered seals, one that is homozygous dominant and one that is heterozygous? ______ b) If one parent seal is pure long-whiskered and the other is short-whiskered, what percent of offspring would have ...
... a) What percentage of offspring would be expected to have short whiskers from the cross of two longwhiskered seals, one that is homozygous dominant and one that is heterozygous? ______ b) If one parent seal is pure long-whiskered and the other is short-whiskered, what percent of offspring would have ...
REVIEW SHEET FOR EVOLUTION UNIT
... 7. Be able to summarize Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection (page 386 in textbook ). 8. Be able to provide definition and example for adaptive radiation, convergent evolution and coevolution (handout Arise of a New Species and read pp. 436-437. 9. Natural Selection can affect the distributions of p ...
... 7. Be able to summarize Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection (page 386 in textbook ). 8. Be able to provide definition and example for adaptive radiation, convergent evolution and coevolution (handout Arise of a New Species and read pp. 436-437. 9. Natural Selection can affect the distributions of p ...
A History of Genetics and Genomics
... Therefore, his groundbreaking research went largely unnoticed. It was not until 1900 that others, who had performed similar experiments to his, arrived at the same conclusions. Their publications cited his work, leading to a rediscovery of the Mendelian principles. Quickly following the rediscovery, ...
... Therefore, his groundbreaking research went largely unnoticed. It was not until 1900 that others, who had performed similar experiments to his, arrived at the same conclusions. Their publications cited his work, leading to a rediscovery of the Mendelian principles. Quickly following the rediscovery, ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.