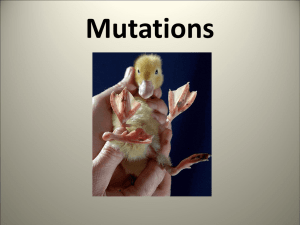
Protein Synthesis Review Guide
... a) Draw a line down through the sequence after every three bases b) Three bases on the mRNA = 1 amino acid. We call these three bases a CODON. c) Use the first letter of the codons to determine what row across you need in the table. d) Use the second letter of the codons to determine what column dow ...
... a) Draw a line down through the sequence after every three bases b) Three bases on the mRNA = 1 amino acid. We call these three bases a CODON. c) Use the first letter of the codons to determine what row across you need in the table. d) Use the second letter of the codons to determine what column dow ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... Mutations are any change in the genetic code: 1. DNA may not replicate properly and the incorrect base attached 2. There may be a mistake in transcription 3. There may be a mistake in translation ...
... Mutations are any change in the genetic code: 1. DNA may not replicate properly and the incorrect base attached 2. There may be a mistake in transcription 3. There may be a mistake in translation ...
Lecture 1, Part I
... chromosomal structural integrity and regulating when, where, and in what quantity proteins are made (regulatory regions). • The terms exon and intron refer to coding (translated into a protein) and non-coding DNA, respectively. ...
... chromosomal structural integrity and regulating when, where, and in what quantity proteins are made (regulatory regions). • The terms exon and intron refer to coding (translated into a protein) and non-coding DNA, respectively. ...
DNA unit Summary
... DNA is an example of a complex biological polymer called a nucleic acid. Nucleic acids are made up of smaller subunits called nucleotides. The components of a DNA nucleotide are deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. In DNA, there are four possible nitrogen bases – adenine (A), guanine ...
... DNA is an example of a complex biological polymer called a nucleic acid. Nucleic acids are made up of smaller subunits called nucleotides. The components of a DNA nucleotide are deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. In DNA, there are four possible nitrogen bases – adenine (A), guanine ...
TEAM CONTACTS – Clinician Investigator Teams Team/PIs Title of
... Abstract: Canada, like most developed nations, is in the midst of an obesity epidemic: one in four adults is currently classified as obese, with this number expected to increase to one in three in the next two decades. In London Ontario, 45% of births are by overweight or obese mothers, posing s ...
... Abstract: Canada, like most developed nations, is in the midst of an obesity epidemic: one in four adults is currently classified as obese, with this number expected to increase to one in three in the next two decades. In London Ontario, 45% of births are by overweight or obese mothers, posing s ...
DNA Methylation
... DNA Methylation • DNA methylation, the addition of methyl groups to certain bases in DNA, is associated with reduced transcription in some species • DNA methylation can cause long-term inactivation of genes in cellular differentiation • In genomic imprinting, methylation regulates expression of eit ...
... DNA Methylation • DNA methylation, the addition of methyl groups to certain bases in DNA, is associated with reduced transcription in some species • DNA methylation can cause long-term inactivation of genes in cellular differentiation • In genomic imprinting, methylation regulates expression of eit ...
DNA paper 1 - DavidHein-CESRC-page
... basic types of RNA which are; mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. mRNA is the messenger of genetic information. It carries the information from the DNA is the nucleus to the cytosol. tRNA is transfer RNA. It is about 80 RNA nucleotides. It folds into a hairpin shape and binds to an amino acid to deliver to the ri ...
... basic types of RNA which are; mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. mRNA is the messenger of genetic information. It carries the information from the DNA is the nucleus to the cytosol. tRNA is transfer RNA. It is about 80 RNA nucleotides. It folds into a hairpin shape and binds to an amino acid to deliver to the ri ...
Mutation - TeacherWeb
... wrapped around histone protein which are tightly packed and organized •Chromatin makes up chromosomes 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) in humans ...
... wrapped around histone protein which are tightly packed and organized •Chromatin makes up chromosomes 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) in humans ...
Mutations
... Types of mutations (either germ or somatic): 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. -Example: Down Syndrome Edwards Syndrome ...
... Types of mutations (either germ or somatic): 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. -Example: Down Syndrome Edwards Syndrome ...
Genetics BOE approved April 15, 2010 Learner Objective: Cells go
... A. Sexual identity is guided by genes, hormones, feelings, and experiences. B. Genes on the sex chromosomes (sex-linked) have unique inheritance patterns. C. Some genes-autosomal as well as X- or Y- linked- are expressed in one sex but not the other, or may be inherited as a dominant trait in one bu ...
... A. Sexual identity is guided by genes, hormones, feelings, and experiences. B. Genes on the sex chromosomes (sex-linked) have unique inheritance patterns. C. Some genes-autosomal as well as X- or Y- linked- are expressed in one sex but not the other, or may be inherited as a dominant trait in one bu ...
Test Review on DNA Structure, DNA Replication
... Understand that DNA is a double helix composed of two strands of nucleotides and be able to describe this shape. Know the three parts of a nucleotide. Understand that the nitrogen base is the part of the nucleotide that forms the genetic code, and be able to name the four possible nitrogen bases in ...
... Understand that DNA is a double helix composed of two strands of nucleotides and be able to describe this shape. Know the three parts of a nucleotide. Understand that the nitrogen base is the part of the nucleotide that forms the genetic code, and be able to name the four possible nitrogen bases in ...
1. What are the 3 parts of DNA nucleotide?
... 2. How is DNA different from RNA? DNA: 2 strands, deoxyribose sugar, contains thymine; RNA: 1 strand, ribose sugar, contains uracil instead of thymine. 3. What scientists: First determined the structure of DNA? Watson and Crick X-rayed DNA, giving necessary clues to its structure? Rosalind Franklin ...
... 2. How is DNA different from RNA? DNA: 2 strands, deoxyribose sugar, contains thymine; RNA: 1 strand, ribose sugar, contains uracil instead of thymine. 3. What scientists: First determined the structure of DNA? Watson and Crick X-rayed DNA, giving necessary clues to its structure? Rosalind Franklin ...
Chapter 11 Vocabulary and Objectives
... explain that organisms have systems to fight diseases Lesson 1: How are Molecules of Life Involved in Heredity? I. Objectives: Describe the structure of nucleotides; Explain the structure of a DNA molecule; Explain complementary pairing. II. Vocabulary: sugarphosphate backbone cytosine ( ...
... explain that organisms have systems to fight diseases Lesson 1: How are Molecules of Life Involved in Heredity? I. Objectives: Describe the structure of nucleotides; Explain the structure of a DNA molecule; Explain complementary pairing. II. Vocabulary: sugarphosphate backbone cytosine ( ...
DNA Replication: Seeing Double
... Let’s Make a Model 0 At your table you have many pieces of the DNA ...
... Let’s Make a Model 0 At your table you have many pieces of the DNA ...
DNA - morescience
... DNA polymerase III - main DNA building enzyme Primase - lays down RNA primer on lagging strand DNA polymerase I - editing, repair & primer removal ** Ligase - “glues” Okazaki fragments together on lagging strand ...
... DNA polymerase III - main DNA building enzyme Primase - lays down RNA primer on lagging strand DNA polymerase I - editing, repair & primer removal ** Ligase - “glues” Okazaki fragments together on lagging strand ...
Study guide unit 3
... ______________ location of DNA in human cells ______________ number of cells in a human body ______________ length of DNA in a single cell ______________ a strand of DNA, human cells have 46 ______________ building blocks of the DNA polymer ______________ number of bases in a human genome (a single ...
... ______________ location of DNA in human cells ______________ number of cells in a human body ______________ length of DNA in a single cell ______________ a strand of DNA, human cells have 46 ______________ building blocks of the DNA polymer ______________ number of bases in a human genome (a single ...
DNA RNA structure
... DNA is in the nucleus. RNA is made in the nucleus but travels to the cytoplasm • RNA is made in the nucleoli but can travel out to the cytoplasm ...
... DNA is in the nucleus. RNA is made in the nucleus but travels to the cytoplasm • RNA is made in the nucleoli but can travel out to the cytoplasm ...
Genetic Engineering - Needham Public Schools
... • Breed only those plants or animals with desirable traits ...
... • Breed only those plants or animals with desirable traits ...
NOTES: 12.1 - History of DNA (powerpoint)
... disease-causing ability to the harmless strain ● Griffith called this TRANSFORMATION – One strain of bacteria (harmless) had changed into the other (harmful, or disease-causing) ● Some factor was transferred from the heat killed cells to the live cells – This factor might contain a GENE with informa ...
... disease-causing ability to the harmless strain ● Griffith called this TRANSFORMATION – One strain of bacteria (harmless) had changed into the other (harmful, or disease-causing) ● Some factor was transferred from the heat killed cells to the live cells – This factor might contain a GENE with informa ...
From DNA to Protein
... 1. Introduction: Dartmouth scientist, part of what I study is DNA – 2 minutes ...
... 1. Introduction: Dartmouth scientist, part of what I study is DNA – 2 minutes ...
12.1 - DNA History / Discovery
... disease-causing ability to the harmless strain ● Griffith called this TRANSFORMATION – One strain of bacteria (harmless) had changed into the other (harmful, or disease-causing) ● Some factor was transferred from the heat killed cells to the live cells – This factor might contain a GENE with informa ...
... disease-causing ability to the harmless strain ● Griffith called this TRANSFORMATION – One strain of bacteria (harmless) had changed into the other (harmful, or disease-causing) ● Some factor was transferred from the heat killed cells to the live cells – This factor might contain a GENE with informa ...
Heredity and Genes
... one of the pairs of homologous chromosomes. dominant: the allele that, if present, is ALWAYS expressed. Example: TT or Tt recessive: the allele that is expressed only if it is not in the presence of the dominant allele i.e. if the individual is homozygous for the recessive allele. Example: tt ...
... one of the pairs of homologous chromosomes. dominant: the allele that, if present, is ALWAYS expressed. Example: TT or Tt recessive: the allele that is expressed only if it is not in the presence of the dominant allele i.e. if the individual is homozygous for the recessive allele. Example: tt ...