BIOL 222 - philipdarrenjones.com
... A) The tRNA that was in the A site moves into the P site. B) The tRNA that was in the P site moves into the A site. C) The tRNA that was in the A site moves to the E site and is released. D) The tRNA that was in the A site departs from the ribosome via a tunnel. ...
... A) The tRNA that was in the A site moves into the P site. B) The tRNA that was in the P site moves into the A site. C) The tRNA that was in the A site moves to the E site and is released. D) The tRNA that was in the A site departs from the ribosome via a tunnel. ...
Complete the following chart using your genetic code chart worksheet:
... 8. An agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a(n) a. Zygote b. Inversion c. Mutagen ...
... 8. An agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a(n) a. Zygote b. Inversion c. Mutagen ...
DNA Bank Acquisitions Policy
... biodiversity, the aim of the DNA Bank is to house samples in plant and fungal groups studied by Garden scientists, as well as other taxa from the diverse geographic regions in which our staff works. The DNA Bank will accept existing collections from other institutions and individuals provided that t ...
... biodiversity, the aim of the DNA Bank is to house samples in plant and fungal groups studied by Garden scientists, as well as other taxa from the diverse geographic regions in which our staff works. The DNA Bank will accept existing collections from other institutions and individuals provided that t ...
Lecture Notes - Course Notes
... The primary transcript (pre-mRNA) is modified in the nucleus in a process known as post-transcriptional processing, involving cleavages of some sequences and additions of others. The fully processed, mature mRNA, is then transported to the cytoplasm, where translation takes place. It is the 3’ to 5’ ...
... The primary transcript (pre-mRNA) is modified in the nucleus in a process known as post-transcriptional processing, involving cleavages of some sequences and additions of others. The fully processed, mature mRNA, is then transported to the cytoplasm, where translation takes place. It is the 3’ to 5’ ...
Prenatal Care and Life Cycle PP
... During prenatal visits, the female will have a complete physical that includes blood tests and a pelvic exam. The obstetrician or nurse-midwife will monitor the ...
... During prenatal visits, the female will have a complete physical that includes blood tests and a pelvic exam. The obstetrician or nurse-midwife will monitor the ...
DNA notes - Chapel Hill
... • Other proteins, such as enzymes, control chemical reactions that perform key life functions—breaking down glucose molecules in cellular respiration, digesting food, or making spindle fibers during mitosis. ...
... • Other proteins, such as enzymes, control chemical reactions that perform key life functions—breaking down glucose molecules in cellular respiration, digesting food, or making spindle fibers during mitosis. ...
Ethanol precipitation of DNA with salts
... The purpose of adding salts is to neutralize the charge on the sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA. Ethanol’s task is a little more complex than "removing" the water. For a precipitation, you're interested in forming ion pairs between the polyanion (DNA) and the cation (Na+, Mg++, etc). In dilute aq ...
... The purpose of adding salts is to neutralize the charge on the sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA. Ethanol’s task is a little more complex than "removing" the water. For a precipitation, you're interested in forming ion pairs between the polyanion (DNA) and the cation (Na+, Mg++, etc). In dilute aq ...
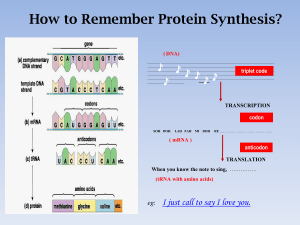
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
Keystone Review Module B
... 2. Compare asexual reproduction to sexual reproduction. In your comparison, be sure to include: Which type of reproduction results in offspring that are usually genetically identical to the previous generation and explain why this occurs. One other was these methods of reproduction differ ______ ...
... 2. Compare asexual reproduction to sexual reproduction. In your comparison, be sure to include: Which type of reproduction results in offspring that are usually genetically identical to the previous generation and explain why this occurs. One other was these methods of reproduction differ ______ ...
STSE Power point
... Capable of examining from either the entire genome, several areas of the genome, or one specific area of the genome It can examine the genetic information for one individual , or many individuals for one or many SNP’s Useful for making a connection between the presence of an SNP and a disease. It ca ...
... Capable of examining from either the entire genome, several areas of the genome, or one specific area of the genome It can examine the genetic information for one individual , or many individuals for one or many SNP’s Useful for making a connection between the presence of an SNP and a disease. It ca ...
PCR-technique Applications
... • synthesis of DNA from the primers • incubate a certain time 3) Repeat the process: ...
... • synthesis of DNA from the primers • incubate a certain time 3) Repeat the process: ...
Document
... How to clone the gene you want? Create a “Library”: •Clone enough fragments of foreign donor DNA to represent the entire genome of the organism of interest. • Each clone will represent a portion of the genome. • Libraries may use plasmid vectors and host bacteria, or they may use a bacteriophage ve ...
... How to clone the gene you want? Create a “Library”: •Clone enough fragments of foreign donor DNA to represent the entire genome of the organism of interest. • Each clone will represent a portion of the genome. • Libraries may use plasmid vectors and host bacteria, or they may use a bacteriophage ve ...
Integrated Programme Sec 2 SBGE, LSS Biology Module Topic
... One Small compared to size of DNA, varies with size of gene Short term Nucleus and cytoplasm ...
... One Small compared to size of DNA, varies with size of gene Short term Nucleus and cytoplasm ...
Alternative Approaches to Molecular Biology
... Since each strand of the starting DNA is used as a template for one copy of the replicated DNA (semiconservative replication) one copy will be shorter than the other. After many, many rounds of replication, cells with dramatically shorter ends can result. ...
... Since each strand of the starting DNA is used as a template for one copy of the replicated DNA (semiconservative replication) one copy will be shorter than the other. After many, many rounds of replication, cells with dramatically shorter ends can result. ...
Human karyotype preparation
... Polar body of eggs examined for presence of defective gene - if present in polar body, then the gene in the egg is normal and egg is used. If the polar body chromosomes are normal, the egg carries the defective gene and is discarded. Eggs that pass screening can be used for IVF to eliminate transmis ...
... Polar body of eggs examined for presence of defective gene - if present in polar body, then the gene in the egg is normal and egg is used. If the polar body chromosomes are normal, the egg carries the defective gene and is discarded. Eggs that pass screening can be used for IVF to eliminate transmis ...
Red line Introduction
... – 19 students used Red Line to visualize next-gen RNA-Seq data to investigate presence/absence variation (PAV) in maize – 12 hours effort, each student group annotated 100 kb and then imported next-gen RNA-Seq data from 5 different tissues in 30 maize inbred lines for a gene that they had previously ...
... – 19 students used Red Line to visualize next-gen RNA-Seq data to investigate presence/absence variation (PAV) in maize – 12 hours effort, each student group annotated 100 kb and then imported next-gen RNA-Seq data from 5 different tissues in 30 maize inbred lines for a gene that they had previously ...
NAME: NWAIWU ROSEMARY DEPT: BIOCHEMISTRY COURSE
... an entire gene or several neighboring genes. The deleted DNA may alter the function of the resulting protein(s) DUPLICATION- A duplication consists of a piece of DNA that is abnormally copied one or more times. This type of mutation may alter the function of the resulting protein. FRAMESHIFT MUTATI ...
... an entire gene or several neighboring genes. The deleted DNA may alter the function of the resulting protein(s) DUPLICATION- A duplication consists of a piece of DNA that is abnormally copied one or more times. This type of mutation may alter the function of the resulting protein. FRAMESHIFT MUTATI ...
Chapter 14
... A point mutation is a change of a single nucleotide in a sequence from one kind of base to another. (substitution) A mutation is silent when it has no effect on a gene’s function. ...
... A point mutation is a change of a single nucleotide in a sequence from one kind of base to another. (substitution) A mutation is silent when it has no effect on a gene’s function. ...
Chapter 15 Study Guide
... Complete each statement by underlining the correct term or phrase in the brackets. 1. Cohen and Boyer revolutionized genetics by producing recombinant [DNA / RNA]. 2. In Cohen and Boyer’s 1973 experiment, genetically engineered [bacterial / human] cells produced frog rRNA. 3. Moving genes from one o ...
... Complete each statement by underlining the correct term or phrase in the brackets. 1. Cohen and Boyer revolutionized genetics by producing recombinant [DNA / RNA]. 2. In Cohen and Boyer’s 1973 experiment, genetically engineered [bacterial / human] cells produced frog rRNA. 3. Moving genes from one o ...
Quick Vocabulary Lesson 1 Lesson 2 dominant trait
... the offspring’s phenotype is a blend of the parents’ phenotypes ...
... the offspring’s phenotype is a blend of the parents’ phenotypes ...
Information Townes-Brocks Syndrome Molecular genetic testing of
... autosomal-dominantly inherited disease, characterized by a combination of malformations of the thumbs (thumbs with three bones (triphalangeal thumbs) or doubled thumbs (preaxial polydactyly)) with those of the external ears and of the anus (imperforate anus, anal stenosis, anal anteposition). Other ...
... autosomal-dominantly inherited disease, characterized by a combination of malformations of the thumbs (thumbs with three bones (triphalangeal thumbs) or doubled thumbs (preaxial polydactyly)) with those of the external ears and of the anus (imperforate anus, anal stenosis, anal anteposition). Other ...
DNA and Genealogy
... one of the DNA macromolecules found in the cell nucleus. Humans have 46 chromosomes. See also X and Y. ...
... one of the DNA macromolecules found in the cell nucleus. Humans have 46 chromosomes. See also X and Y. ...