Nucleic Acids Notes
... DNA flexibility depends on its sequence! • It is very important to be able to predict this dependence (still not fully solved problem). • What’s more flexible: AAAAA TTTTTT Or: GGGGGG CCCCCC A-T linked by 2 H-bonds, but G-C by 3. Less room to wiggle, so less flexible. ...
... DNA flexibility depends on its sequence! • It is very important to be able to predict this dependence (still not fully solved problem). • What’s more flexible: AAAAA TTTTTT Or: GGGGGG CCCCCC A-T linked by 2 H-bonds, but G-C by 3. Less room to wiggle, so less flexible. ...
E. Coli - mrkeay
... circular chromosome, along with many small, circular pieces of DNA called plasmids • Plasmids carry genes which confer antibiotic resistance, as well as resistance to toxic heavy metals and industrial chemicals • We can use plasmids for biotechnology, since bacteria are able to express foreign ...
... circular chromosome, along with many small, circular pieces of DNA called plasmids • Plasmids carry genes which confer antibiotic resistance, as well as resistance to toxic heavy metals and industrial chemicals • We can use plasmids for biotechnology, since bacteria are able to express foreign ...
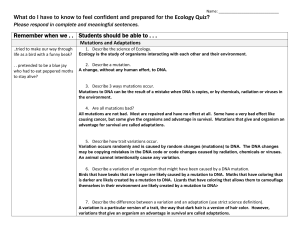
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... 11. Describe the reason why the light and dark peppered moth populations changed over time. The Industrial Revolution increased the amount of black soot on trees where moths rest and gather food. Before the soot, light colored moths were camouflaged by the lichen on the trees and didn’t get eaten as ...
... 11. Describe the reason why the light and dark peppered moth populations changed over time. The Industrial Revolution increased the amount of black soot on trees where moths rest and gather food. Before the soot, light colored moths were camouflaged by the lichen on the trees and didn’t get eaten as ...
DNA
... observation that diploid (somatic cells) sets of chromosomes have twice as much DNA as the haploid sets in gametes of the same organism. ...
... observation that diploid (somatic cells) sets of chromosomes have twice as much DNA as the haploid sets in gametes of the same organism. ...
DNA - SchoolRack
... • Chromosomal mutations occur in all organisms, but are most common in plants. • Few chromosomal mutations are passed to offspring, because the zygote with the chromosomal mutations usually dies. • In cases where the zygote lives, the mature organism with a chromosomal mutation is often ...
... • Chromosomal mutations occur in all organisms, but are most common in plants. • Few chromosomal mutations are passed to offspring, because the zygote with the chromosomal mutations usually dies. • In cases where the zygote lives, the mature organism with a chromosomal mutation is often ...
24 Applied genetics
... 1 A strain of barley (A) has a high yield of seeds but a long stem which is subject to ‘lodging’ (a flattening of areas of the crop). Another strain (B) has a short, sturdy stem but a lower yield. The genotype of variety A is HHss (high yield, long stem) and the genotype of B is hhSS (low yield, sho ...
... 1 A strain of barley (A) has a high yield of seeds but a long stem which is subject to ‘lodging’ (a flattening of areas of the crop). Another strain (B) has a short, sturdy stem but a lower yield. The genotype of variety A is HHss (high yield, long stem) and the genotype of B is hhSS (low yield, sho ...
2001
... 30. A biochemist replaces the DNA binding domain of the yeastGal4 protein with the DNA binding domain from the LexA repressor protein andfinds that the engineered protein no longer regulates transcription of the GAL genes in yeast. Draw a diagram of the different functional domains you would expect ...
... 30. A biochemist replaces the DNA binding domain of the yeastGal4 protein with the DNA binding domain from the LexA repressor protein andfinds that the engineered protein no longer regulates transcription of the GAL genes in yeast. Draw a diagram of the different functional domains you would expect ...
Topic 12 DNA Technology
... sure that they have a baby that is disease free, PGD can reduce the odds 1. in vitro fertilization occurs (IVF) 2. Morula is formed and one of the cells is selected for diagnosis 3. PCR amplifies the region of DNA where the suspected allele may be 4. DNA probe determines if the alleles are present o ...
... sure that they have a baby that is disease free, PGD can reduce the odds 1. in vitro fertilization occurs (IVF) 2. Morula is formed and one of the cells is selected for diagnosis 3. PCR amplifies the region of DNA where the suspected allele may be 4. DNA probe determines if the alleles are present o ...
HOW TO GET A CEA DNA TEST DONE
... UK MEMBERS - To submit a test to OptiGen using Animal DNA Diagnostics Ltd - ISDS / Animal DNA Diagnostics Ltd / OptiGen OptiGen have agreed to cover the costs of the DNA extraction, therefore Animal DNA Diagnostics Ltd will charge members only £10 (including VAT) to cover storing half of the DNA sam ...
... UK MEMBERS - To submit a test to OptiGen using Animal DNA Diagnostics Ltd - ISDS / Animal DNA Diagnostics Ltd / OptiGen OptiGen have agreed to cover the costs of the DNA extraction, therefore Animal DNA Diagnostics Ltd will charge members only £10 (including VAT) to cover storing half of the DNA sam ...
Techniques in Mouse
... take up the DNA, very inefficient need to identify cells that took up the DNA with reporter such as drug resistance • 3) Electroporation – a high voltage pulse “pushes” DNA into cells • 4) Retroviral vectors – a more natural way or getting genes into cells ...
... take up the DNA, very inefficient need to identify cells that took up the DNA with reporter such as drug resistance • 3) Electroporation – a high voltage pulse “pushes” DNA into cells • 4) Retroviral vectors – a more natural way or getting genes into cells ...
Advanced Genetics Unit 2: DNA Structure and Processes Quiz Bowl
... sequence repeats] 20. This area of the DNA molecule in chromosomes is made up of long repeating stretches such as alpha satellites. [centromeres] 21. It would seem that “protein-coding genes” only make up about _______% of the DNA in our cells? [1-2%] 22. RNA type responsible for shuttling amino aci ...
... sequence repeats] 20. This area of the DNA molecule in chromosomes is made up of long repeating stretches such as alpha satellites. [centromeres] 21. It would seem that “protein-coding genes” only make up about _______% of the DNA in our cells? [1-2%] 22. RNA type responsible for shuttling amino aci ...
Glossary for Ancient DNA and Human Evolution
... shared evolutionary history from a common ancestor. Homoplasy: Similarity in DNA sequence or phenotype that has evolved independently. Phylogeny: Historical relationships of species or loci. Polymorphism: An allelic difference observed in more than 1% of the population studied. Allele Frequency: The ...
... shared evolutionary history from a common ancestor. Homoplasy: Similarity in DNA sequence or phenotype that has evolved independently. Phylogeny: Historical relationships of species or loci. Polymorphism: An allelic difference observed in more than 1% of the population studied. Allele Frequency: The ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering
... nucleus of an adult, donor egg is removed This empty egg is fused with another adult somatic cell’s NUCLEUS (diploid, 2N) The cell is stimulated with electric shock to divide normally by mitosis and the zygote is implanted into a surrogate mother The baby is born of the surrogate and has the E ...
... nucleus of an adult, donor egg is removed This empty egg is fused with another adult somatic cell’s NUCLEUS (diploid, 2N) The cell is stimulated with electric shock to divide normally by mitosis and the zygote is implanted into a surrogate mother The baby is born of the surrogate and has the E ...
Biodosimetry - Arkansas State University
... • Molecular biomarkers for ionizing radiation exposure (gene expression changes, blood proteins) can be measured in real time using such diagnostic detection technologies as miniaturized nucleic acid sequences and antigen-based biosensors – Certain genes are turned off or on by acute radiation expos ...
... • Molecular biomarkers for ionizing radiation exposure (gene expression changes, blood proteins) can be measured in real time using such diagnostic detection technologies as miniaturized nucleic acid sequences and antigen-based biosensors – Certain genes are turned off or on by acute radiation expos ...
Answers to Exam Practice Questions 1. Mitosis produces two
... activities that can be useful to the organism in different or changing environments. 20. Gene mutations are a result of a change in a single or a few nucleotides whereas a chromosomal mutation changes the number or structure of the chromosomes and can affect one or many genes. 21. DNA can be used to ...
... activities that can be useful to the organism in different or changing environments. 20. Gene mutations are a result of a change in a single or a few nucleotides whereas a chromosomal mutation changes the number or structure of the chromosomes and can affect one or many genes. 21. DNA can be used to ...
Hot Seat - Protein Synthesis
... Your skin cells have different characteristics than your muscle cells, because __________. A. your skin cells have the genes needed to form skin whereas your muscle cells have the genes needed to form muscles B. your skin cells activate only those genes needed to make skin whereas your muscle cells ...
... Your skin cells have different characteristics than your muscle cells, because __________. A. your skin cells have the genes needed to form skin whereas your muscle cells have the genes needed to form muscles B. your skin cells activate only those genes needed to make skin whereas your muscle cells ...
STAAR Review 4
... 12. After performing amniocentesis, which analysis is most often used to determine the chromosomal condition of a developing fetus? a. blood type b. DNA sequence c. genetic marker d. karyotype ...
... 12. After performing amniocentesis, which analysis is most often used to determine the chromosomal condition of a developing fetus? a. blood type b. DNA sequence c. genetic marker d. karyotype ...
Day 58 - upwardsapbio
... new DNA strand is created from the parent strand. There are many enzymes and proteins that aid in this complex process. After the many enzymes have created this new, semiconservative strand of DNA, it must then be proofread and repaired. The final, completed strand of DNA has about 1 in 10 billion n ...
... new DNA strand is created from the parent strand. There are many enzymes and proteins that aid in this complex process. After the many enzymes have created this new, semiconservative strand of DNA, it must then be proofread and repaired. The final, completed strand of DNA has about 1 in 10 billion n ...
View a technical slide presentation
... • Target trait/gene to a specific genetic locus • Insert multiple traits/genes at one locus • More efficient generation of desired GMO events • Target DNA to location of current de-regulated event or ‘safe’ locus • GMO events with no disruption of native gene function ...
... • Target trait/gene to a specific genetic locus • Insert multiple traits/genes at one locus • More efficient generation of desired GMO events • Target DNA to location of current de-regulated event or ‘safe’ locus • GMO events with no disruption of native gene function ...
Inheriting Characteristics
... • Genes are made up of short lengths of DNA • DNA stands for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid • In the 1950’s Watson and Crick were the first to come up with the structure of DNA • On each chromosome of the pair there can be different version of the same gene, i.e. blue or brown eyes • The variations are kn ...
... • Genes are made up of short lengths of DNA • DNA stands for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid • In the 1950’s Watson and Crick were the first to come up with the structure of DNA • On each chromosome of the pair there can be different version of the same gene, i.e. blue or brown eyes • The variations are kn ...
Gene Technology Quest – Study Guide KEY What is a genome? A
... 3. The fused cell begins to grow and divide to an embryo and is implanted into a female vector to carry the clone. 16. What is the goal of the Human Genome Project? The goal of the Human Genome Project is to create maps showing where genes are located on human chromosomes. 17. What results from a va ...
... 3. The fused cell begins to grow and divide to an embryo and is implanted into a female vector to carry the clone. 16. What is the goal of the Human Genome Project? The goal of the Human Genome Project is to create maps showing where genes are located on human chromosomes. 17. What results from a va ...