DNA
... 1. RNA is composed on one strand of nucleotides rather than two strands 2. RNA nucleotides contain the five carbon sugar RIBOSE rather than the sugar deoxyribose. 3. RNA nucleotides have the nitrogen base called URACIL (U) instead of thymine. Although no thymine bases are found in RNA, the other bas ...
... 1. RNA is composed on one strand of nucleotides rather than two strands 2. RNA nucleotides contain the five carbon sugar RIBOSE rather than the sugar deoxyribose. 3. RNA nucleotides have the nitrogen base called URACIL (U) instead of thymine. Although no thymine bases are found in RNA, the other bas ...
Document
... lengths (usually several million bp in length.) • These are the “elephants” in the race through the agarose and cant enter the gel matrix when they are this big. • Restriction enzymes made possible the cutting of DNA into smaller fragments together with their separation and visualization by agarose ...
... lengths (usually several million bp in length.) • These are the “elephants” in the race through the agarose and cant enter the gel matrix when they are this big. • Restriction enzymes made possible the cutting of DNA into smaller fragments together with their separation and visualization by agarose ...
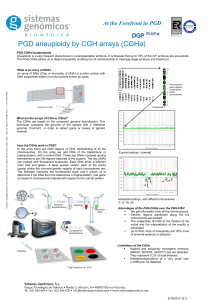
At the Forefront in PGD
... Fundamentals of combined chromosomal PGD Couples with one member carrying a balanced chromosomal rearrangement (translocation or inversion) have an increased risk of generating abnormal embryos as a result of segregation of the balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many case ...
... Fundamentals of combined chromosomal PGD Couples with one member carrying a balanced chromosomal rearrangement (translocation or inversion) have an increased risk of generating abnormal embryos as a result of segregation of the balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many case ...
The Human Genome Chapter 14
... Scientists begin answering the question about what makes us human by seeing the human cell with a microscope, starting with the chromosomes. The cell biologists photograph the cells in mitosis to analyze the chromes. A picture of chromosomes arranged in pairs is known as a karyotype. Two of the 46 c ...
... Scientists begin answering the question about what makes us human by seeing the human cell with a microscope, starting with the chromosomes. The cell biologists photograph the cells in mitosis to analyze the chromes. A picture of chromosomes arranged in pairs is known as a karyotype. Two of the 46 c ...
CHAPTER 4 Study Guide
... 10. What must occur for a girl to be colorblind? a. Each parent must be colorblind. b. Each parent must have the dominant allele for colorblindness. c. Each parent must have the recessive allele for colorblindness. d. Each parent must have two codominant alleles for colorblindness. 11. How does a ge ...
... 10. What must occur for a girl to be colorblind? a. Each parent must be colorblind. b. Each parent must have the dominant allele for colorblindness. c. Each parent must have the recessive allele for colorblindness. d. Each parent must have two codominant alleles for colorblindness. 11. How does a ge ...
Practical II - Faculty Websites
... strongly recommend that you study these thoroughly. It might be helpful to refer to these study guides while looking at the demos. Practical II General Review Guide Practical II Tests Study Photos for Practical II Review the lab manual, lab handouts, quizzes and the lab reports, especially the ...
... strongly recommend that you study these thoroughly. It might be helpful to refer to these study guides while looking at the demos. Practical II General Review Guide Practical II Tests Study Photos for Practical II Review the lab manual, lab handouts, quizzes and the lab reports, especially the ...
bio12_sm_07_2
... 6. DNA Replication and Transcription DNA replication Both DNA transcription - produces 2 semi-create new -produces a conserved double complementary nucleic single strand of stranded DNA molecules acid strands mRNA -uses DNA polymerase -read DNA code -use RNA polymerase 7. Answers may vary. Sample an ...
... 6. DNA Replication and Transcription DNA replication Both DNA transcription - produces 2 semi-create new -produces a conserved double complementary nucleic single strand of stranded DNA molecules acid strands mRNA -uses DNA polymerase -read DNA code -use RNA polymerase 7. Answers may vary. Sample an ...
Alief ISD Biology STAAR EOC Review Reporting Category 2
... Proteins have a role in shaping the traits of organisms. I.e. they may form structures in cells, act as catalyst in reactions (enzymes), transmits signals throughout the body (hormones) or help an organism fight invaders (antibodies) Changes in DNA- mutations Mutation- A change to the structure or o ...
... Proteins have a role in shaping the traits of organisms. I.e. they may form structures in cells, act as catalyst in reactions (enzymes), transmits signals throughout the body (hormones) or help an organism fight invaders (antibodies) Changes in DNA- mutations Mutation- A change to the structure or o ...
File - Gander biology
... Proteins have a role in shaping the traits of organisms. I.e. they may form structures in cells, act as catalyst in reactions (enzymes), transmits signals throughout the body (hormones) or help an organism fight invaders (antibodies) Changes in DNA- mutations Mutation- A change to the structure or o ...
... Proteins have a role in shaping the traits of organisms. I.e. they may form structures in cells, act as catalyst in reactions (enzymes), transmits signals throughout the body (hormones) or help an organism fight invaders (antibodies) Changes in DNA- mutations Mutation- A change to the structure or o ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... Now RNA polymerase binds to the operator and brings about transcription of the genes that code for enzymes necessary to lactose metabolism. Structural genes code for enzymes of a metabolic pathway that are transcribed as a unit. A regulator gene codes for a repressor that can bind to the operator a ...
... Now RNA polymerase binds to the operator and brings about transcription of the genes that code for enzymes necessary to lactose metabolism. Structural genes code for enzymes of a metabolic pathway that are transcribed as a unit. A regulator gene codes for a repressor that can bind to the operator a ...
Selective propagation of the clones
... studied using a variety of different techniques such as Restriction enzyme analysis, DNA sequencing, in vitro expression studies. Molecular Hybridization: The DNA fragment is not amplified but rather studied as it is found in a complex mixture of DNA fragments. The restriction analysis can be perf ...
... studied using a variety of different techniques such as Restriction enzyme analysis, DNA sequencing, in vitro expression studies. Molecular Hybridization: The DNA fragment is not amplified but rather studied as it is found in a complex mixture of DNA fragments. The restriction analysis can be perf ...
Topic 7: Mendelian and Human Genetics
... Most chromosome conditions are referred to by category of aneuploidy followed by the number of the affected chromosome. For example, trisomy 13 means that three copies of chromosome 13 are present. POINT ABNORMALITIES Sometimes mutations occur on a much smaller scale that cause genetic disorders. Be ...
... Most chromosome conditions are referred to by category of aneuploidy followed by the number of the affected chromosome. For example, trisomy 13 means that three copies of chromosome 13 are present. POINT ABNORMALITIES Sometimes mutations occur on a much smaller scale that cause genetic disorders. Be ...
Chapter 2 Human Genetics Overview The purpose of this chapter is
... In a heterozygote (two alleles at a given locus are different), an allele is dominant when it masks the effect of the other allele at a given locus. ...
... In a heterozygote (two alleles at a given locus are different), an allele is dominant when it masks the effect of the other allele at a given locus. ...
Topic 7: Mendelian and Human Genetics Uncover Inheritance
... Most chromosome conditions are referred to by category of aneuploidy followed by the number of the affected chromosome. For example, trisomy 13 means that three copies of chromosome 13 are present. POINT ABNORMALITIES Sometimes mutations occur on a much smaller scale that cause genetic disorders. Be ...
... Most chromosome conditions are referred to by category of aneuploidy followed by the number of the affected chromosome. For example, trisomy 13 means that three copies of chromosome 13 are present. POINT ABNORMALITIES Sometimes mutations occur on a much smaller scale that cause genetic disorders. Be ...
Chapter 6 Genes and Gene Technology Section 1 We now know
... DNA molecules. 9. James ________________ and Francis _______________ modeled DNA and determined the shape must be a _________________ _________________. 10. Describe and draw a double helix DNA molecule. 11. Draw the DNA molecule with at least 10 base pairs correctly matched (your drawing on this po ...
... DNA molecules. 9. James ________________ and Francis _______________ modeled DNA and determined the shape must be a _________________ _________________. 10. Describe and draw a double helix DNA molecule. 11. Draw the DNA molecule with at least 10 base pairs correctly matched (your drawing on this po ...
Topic 7 - Genetics
... Most chromosome conditions are referred to by category of aneuploidy followed by the number of the affected chromosome. For example, trisomy 13 means that three copies of chromosome 13 are present. POINT ABNORMALITIES Sometimes mutations occur on a much smaller scale that cause genetic disorders. Be ...
... Most chromosome conditions are referred to by category of aneuploidy followed by the number of the affected chromosome. For example, trisomy 13 means that three copies of chromosome 13 are present. POINT ABNORMALITIES Sometimes mutations occur on a much smaller scale that cause genetic disorders. Be ...
Lecture 10
... • Genetic markers are employed in genealogical DNA testing for genetic genealogy to determine genetic distance between individuals or populations. • With the aid of genetic markers, researchers were able to provide conclusive evidence that the cancerous tumor cell evolved into a transmissible parasi ...
... • Genetic markers are employed in genealogical DNA testing for genetic genealogy to determine genetic distance between individuals or populations. • With the aid of genetic markers, researchers were able to provide conclusive evidence that the cancerous tumor cell evolved into a transmissible parasi ...
Document
... Learning Targets Please write at the top of your notes: Explain the difference between autosomal and sexlinked genes and how sex-linked genes produce different inheritance patterns in males and females. ...
... Learning Targets Please write at the top of your notes: Explain the difference between autosomal and sexlinked genes and how sex-linked genes produce different inheritance patterns in males and females. ...
Chapter 9 Eukaryotic Cells and Multicellular Organisms
... • Different molecules have different mutation rates – higher rate, better for studying closely related species – lower rate, better for studying distantly related species • Ribosomal RNA is used to study distantly related species – many conservative regions because the shape is so important – lower ...
... • Different molecules have different mutation rates – higher rate, better for studying closely related species – lower rate, better for studying distantly related species • Ribosomal RNA is used to study distantly related species – many conservative regions because the shape is so important – lower ...
DNA packing - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... One gene of an insertion sequence codes for transposase, which catalyzes the transposon’s movement. The inverted repeats, about 20 to 40 nucleotide pairs long, are backward, upside-down versions of each oth. In transposition, transposase molecules bind to the inverted repeats & catalyze the cutting ...
... One gene of an insertion sequence codes for transposase, which catalyzes the transposon’s movement. The inverted repeats, about 20 to 40 nucleotide pairs long, are backward, upside-down versions of each oth. In transposition, transposase molecules bind to the inverted repeats & catalyze the cutting ...
Designing Molecular Machines·
... double-helical ON A by creating a sho rr piece of DN A that would form a local third stcand at that one site. In other words, cou ld this rhreestranded structure- the details of which are still imperfectly understood, and whose biological use, if any, remains unknown-be used for a new function: sequ ...
... double-helical ON A by creating a sho rr piece of DN A that would form a local third stcand at that one site. In other words, cou ld this rhreestranded structure- the details of which are still imperfectly understood, and whose biological use, if any, remains unknown-be used for a new function: sequ ...