DNA Technology - De Anza College
... What is the name of the technique used to make insulin? Recombinant DNA technology gene A discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA (or RNA, in some viruses) ...
... What is the name of the technique used to make insulin? Recombinant DNA technology gene A discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA (or RNA, in some viruses) ...
Mutated
... • About 1 in every 1,000 nucleotides is different between 2 people • (0.1% difference means 99.9% identical) • We have about 3 billion nucleotides in all, so that means there are about 3 million nucleotide differences between 2 people ...
... • About 1 in every 1,000 nucleotides is different between 2 people • (0.1% difference means 99.9% identical) • We have about 3 billion nucleotides in all, so that means there are about 3 million nucleotide differences between 2 people ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 10
... How do histones contribute to the construction of a eukaryotic chromosome and what happens to them during DNA replication? (p. 216) The small, basic histone proteins interact with the negatively charged DNA sugar-phosphate backboneforming nucleosomes. Histones are important for the tight packaging o ...
... How do histones contribute to the construction of a eukaryotic chromosome and what happens to them during DNA replication? (p. 216) The small, basic histone proteins interact with the negatively charged DNA sugar-phosphate backboneforming nucleosomes. Histones are important for the tight packaging o ...
101 -- 2006
... a) Meiosis and fertilization d) Mitosis and fertilization b) Mutation and translocation e) Differentiation and specialization c) Nondisjunction and pleiotropy __ 65. Meiosis results in the production of: a) Diploid cells with no homologous chromosomes d) Haploid cells with homologous chromosomes b) ...
... a) Meiosis and fertilization d) Mitosis and fertilization b) Mutation and translocation e) Differentiation and specialization c) Nondisjunction and pleiotropy __ 65. Meiosis results in the production of: a) Diploid cells with no homologous chromosomes d) Haploid cells with homologous chromosomes b) ...
HEPATITIS B VIRAL (HBV DNA), QUANTITATIVE
... Linear reporting range of the assay is 20 - 1.7 x 10 8 IU/mL Conversion factor: 1 IU/mL = 5.82 copies / mL Test conducted on Serum / Plasma This test is not intended for use as a screening test for the presence of HBV in blood or blood products or as a diagnostic test to confirm the presence of HBV ...
... Linear reporting range of the assay is 20 - 1.7 x 10 8 IU/mL Conversion factor: 1 IU/mL = 5.82 copies / mL Test conducted on Serum / Plasma This test is not intended for use as a screening test for the presence of HBV in blood or blood products or as a diagnostic test to confirm the presence of HBV ...
Name SIS # 1 Introductory Biochemistry BI 28 Third Midterm
... C) They are part of a bacterial defense system in which foreign DNA is cleaved. D) They cleave and ligate DNA. E) They cleave DNA only at recognition sequences specific to a given restriction enzyme. Circle the correct answer 35) [2] The technique known as two hybrid analysis for detecting interacti ...
... C) They are part of a bacterial defense system in which foreign DNA is cleaved. D) They cleave and ligate DNA. E) They cleave DNA only at recognition sequences specific to a given restriction enzyme. Circle the correct answer 35) [2] The technique known as two hybrid analysis for detecting interacti ...
Teacher quality grant
... FROM GENOME TO GENE GENOME An organism’s complete set of DNA. In eukaryotes, this information can be found in the nucleus of virtually every cell. Eukaryotic cell Nucleus CHROMOSOME One or more unique pieces of DNA—circular in prokaryotes, linear in eukaryotes—that together make up an organism's ge ...
... FROM GENOME TO GENE GENOME An organism’s complete set of DNA. In eukaryotes, this information can be found in the nucleus of virtually every cell. Eukaryotic cell Nucleus CHROMOSOME One or more unique pieces of DNA—circular in prokaryotes, linear in eukaryotes—that together make up an organism's ge ...
MUTATIONS
... Mutations that occur in the body cells cause cell death or cancer, and are not passed on to the next generation. Mutations are usually recessive and are inherited in a Mendelian way. ...
... Mutations that occur in the body cells cause cell death or cancer, and are not passed on to the next generation. Mutations are usually recessive and are inherited in a Mendelian way. ...
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
... FROM GENOME TO GENE GENOME An organism’s complete set of DNA. In eukaryotes, this information can be found in the nucleus of virtually every cell. Eukaryotic cell Nucleus CHROMOSOME One or more unique pieces of DNA—circular in prokaryotes, linear in eukaryotes—that together make up an organism's ge ...
... FROM GENOME TO GENE GENOME An organism’s complete set of DNA. In eukaryotes, this information can be found in the nucleus of virtually every cell. Eukaryotic cell Nucleus CHROMOSOME One or more unique pieces of DNA—circular in prokaryotes, linear in eukaryotes—that together make up an organism's ge ...
Cancer Prone Disease Section Trichothiodystrophy (TTD) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Inheritance: Recessive autosomal. ...
... Inheritance: Recessive autosomal. ...
7. Recombinant DNA Vectors
... plasmids--analyzing small DNA regions, expressing genes in cell viruses--cloning larger regions (lambda virus), gene therapy (adenovirus) artificial chromosome vectors (BACs, PACs, YACs)--cloning chromosomal regions b. Conventional E. coli plasmid cloning vectors typically have: origin of replicatio ...
... plasmids--analyzing small DNA regions, expressing genes in cell viruses--cloning larger regions (lambda virus), gene therapy (adenovirus) artificial chromosome vectors (BACs, PACs, YACs)--cloning chromosomal regions b. Conventional E. coli plasmid cloning vectors typically have: origin of replicatio ...
Acc_Bio_DNA_Webquest
... I learn this stuff? At the end of this internet activity you will be brainstorming with a partner the answer to this question. Good luck on your journey through the web! ...
... I learn this stuff? At the end of this internet activity you will be brainstorming with a partner the answer to this question. Good luck on your journey through the web! ...
43 ppt
... Point mutations can lead to a stop= “nonsense” = shortened protein Mutations do NOT stop transcription ...
... Point mutations can lead to a stop= “nonsense” = shortened protein Mutations do NOT stop transcription ...
7.1 DNA Introduction
... Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944): transforming factor is DNA Erwin Chargaff (1947): Chargaff rules: A = T, C = G Hershey & Chase (1952): confirmation that DNA is genetic material Watson & Crick (1953): determined double helix structure of DNA Meselson & Stahl (1958): semi-conservative replication ...
... Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944): transforming factor is DNA Erwin Chargaff (1947): Chargaff rules: A = T, C = G Hershey & Chase (1952): confirmation that DNA is genetic material Watson & Crick (1953): determined double helix structure of DNA Meselson & Stahl (1958): semi-conservative replication ...
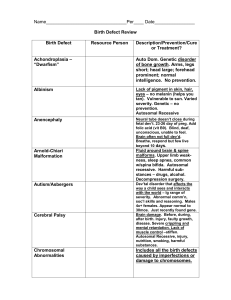
Birth Defects Presentation Review Notes
... Disorder” caused by less or poor quality collagen. Metal rods for strength. “Rodding”. ...
... Disorder” caused by less or poor quality collagen. Metal rods for strength. “Rodding”. ...
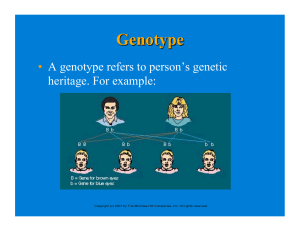
• A genotype refers to person`s genetic heritage. For example:
... Some disorders are entirely hereditary and are passed on according to principles of inheritance - e.g. hemophilia, Huntington’s disease. ...
... Some disorders are entirely hereditary and are passed on according to principles of inheritance - e.g. hemophilia, Huntington’s disease. ...
GOALS OF THE HUMAN GENOME PROJECT
... Chromosomes have 2 arms that are separated by the centromere: – p arm – for petite – q arm – long arm ...
... Chromosomes have 2 arms that are separated by the centromere: – p arm – for petite – q arm – long arm ...
goals of the human genome project
... Chromosomes have 2 arms that are separated by the centromere: – p arm – for petite – q arm – long arm ...
... Chromosomes have 2 arms that are separated by the centromere: – p arm – for petite – q arm – long arm ...
Course: Biology I Honors Course Code: 2000320 Quarter 2
... Dragon Genetics: Students will work in pairs in the lab to produce a dragon from the random mixing of genetic traits. Can be done with any organism and a pre-set of genes for students to combine. Can also be done as a “baby making” project if teachers choose to have students acquire their own genoty ...
... Dragon Genetics: Students will work in pairs in the lab to produce a dragon from the random mixing of genetic traits. Can be done with any organism and a pre-set of genes for students to combine. Can also be done as a “baby making” project if teachers choose to have students acquire their own genoty ...
Genetic Disorder Project
... Genetic disorders can be a challenge to individuals and families living with the condition. However, a variety of disorders have been discovered, allowing for treatment to start right at birth. Your goal of this project is to give a detailed presentation of the disorder to your peers. You will creat ...
... Genetic disorders can be a challenge to individuals and families living with the condition. However, a variety of disorders have been discovered, allowing for treatment to start right at birth. Your goal of this project is to give a detailed presentation of the disorder to your peers. You will creat ...
Lecture 14 – 10/5 – Dr. Wormington
... during each monthly ovulation between the ages of 12–50 •12–50 years may elapse between when an oocyte was 1st formed and when it completes meiosis & is ovulated •Only 400/106 oocytes ever complete meiosis •75-80% of fertilized eggs never develop into a viable embryo Primarily due to nondisjunction ...
... during each monthly ovulation between the ages of 12–50 •12–50 years may elapse between when an oocyte was 1st formed and when it completes meiosis & is ovulated •Only 400/106 oocytes ever complete meiosis •75-80% of fertilized eggs never develop into a viable embryo Primarily due to nondisjunction ...
Answers questions chapter 12
... Mu insertion is mediated by interactions between MuA, a transposase that binds to the terminal repeats of the transposing Mu element; and MuB, an ATP-dependent DNA-binding protein. For Mu insertion to occur, MuB must be bound to the target-site DNA, something that can occur only when MuB is in its A ...
... Mu insertion is mediated by interactions between MuA, a transposase that binds to the terminal repeats of the transposing Mu element; and MuB, an ATP-dependent DNA-binding protein. For Mu insertion to occur, MuB must be bound to the target-site DNA, something that can occur only when MuB is in its A ...