Chapter 19 - Biology Junction
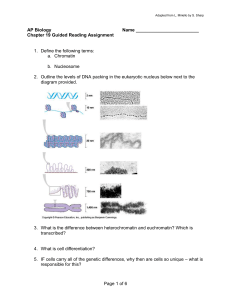
... 4. What is cell differentiation? 5. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? ...
... 4. What is cell differentiation? 5. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? ...
Cloning and Sequencing
... Reading the Sequence • In the tube with the ddTTP, every time it is time to add a T to the new strand, some Ts will be dTTP and some will be ddTTP. • When the ddTTP is added, then extension stops and you have a DNA fragment of a particular length. • The T tube will, therefore, have a series of DNA ...
... Reading the Sequence • In the tube with the ddTTP, every time it is time to add a T to the new strand, some Ts will be dTTP and some will be ddTTP. • When the ddTTP is added, then extension stops and you have a DNA fragment of a particular length. • The T tube will, therefore, have a series of DNA ...
Chapters 10a and 11 PowerPoint
... You have learned that there are stop codons that signal the end of an amino acid chain. Why is it important that a signal to stop translation be part of protein synthesis? In general, sequence the steps involved in protein synthesis from the production of mRNA to the final translation of the DNA cod ...
... You have learned that there are stop codons that signal the end of an amino acid chain. Why is it important that a signal to stop translation be part of protein synthesis? In general, sequence the steps involved in protein synthesis from the production of mRNA to the final translation of the DNA cod ...
Concept Sheet - Fredericksburg City Public Schools
... For example, broccoli is the flower head of a plant. In the wild, the flower head is relatively small and not very compact. To increase volume of edible parts, people selected broccoli plants with larger, denser flower heads and bred them together. They continued this for many generations until we ...
... For example, broccoli is the flower head of a plant. In the wild, the flower head is relatively small and not very compact. To increase volume of edible parts, people selected broccoli plants with larger, denser flower heads and bred them together. They continued this for many generations until we ...
DNA is the hereditary material that transfers info btwn bacterial cells
... Gene Expression & Cancer • Oncogene: Gene that causes cancer • Proto-oncogene = normal gene, regulates cell growth. May mutate into oncogene that may lead to cancer • Tumor-supressor gene (3 types): for protein that prevents uncontrolled cell division, mutation may stop this protein production • Vi ...
... Gene Expression & Cancer • Oncogene: Gene that causes cancer • Proto-oncogene = normal gene, regulates cell growth. May mutate into oncogene that may lead to cancer • Tumor-supressor gene (3 types): for protein that prevents uncontrolled cell division, mutation may stop this protein production • Vi ...
chapt04_lecture
... Extremes in Chromosome # • The record for minimum number of chromosomes belongs to a subspecies of the ant Myrmecia pilosula, in which females have a single pair of chromosomes. This species reproduces by a process called haplodiploidy, in which fertilized eggs (diploid) ...
... Extremes in Chromosome # • The record for minimum number of chromosomes belongs to a subspecies of the ant Myrmecia pilosula, in which females have a single pair of chromosomes. This species reproduces by a process called haplodiploidy, in which fertilized eggs (diploid) ...
Bio 93 2013 Final: 1. Which option best describes transformation in
... D) cannot repair thymine dimers. ...
... D) cannot repair thymine dimers. ...
Prokaryotes
... 10X’s more biomass Wider range of environments Greater diversity Single, circular chromosome Best known as bacteria ...
... 10X’s more biomass Wider range of environments Greater diversity Single, circular chromosome Best known as bacteria ...
Hypothesis: Variations in the rate of DNA replication determine the
... UMR CNRS 6522, Department of Science, Univ. of Rouen, F-76821, France Laboratoire de Génétique Microbienne, INRA, F-78352 Jouy en Josas, France ...
... UMR CNRS 6522, Department of Science, Univ. of Rouen, F-76821, France Laboratoire de Génétique Microbienne, INRA, F-78352 Jouy en Josas, France ...
DETERMINING THE METHOD OF DNA REPLICATION LAB
... After the publication of the structure of DNA, several possible hypotheses were advanced to describe how the DNA replicated. Three hypotheses were considered the most likely candidates to correctly explain replication: conservative, semiconservative, and dispersive. During conservative replication, ...
... After the publication of the structure of DNA, several possible hypotheses were advanced to describe how the DNA replicated. Three hypotheses were considered the most likely candidates to correctly explain replication: conservative, semiconservative, and dispersive. During conservative replication, ...
Slide 1 - Indiana University–Purdue University Indianapolis
... The material of inheritance within the nucleus of a cell is arranged in long strands called chromosomes. On the molecular level the chromosomes are actually nothing more than two long strings of DNA wound together in a spiral-like structure called a double helix. ...
... The material of inheritance within the nucleus of a cell is arranged in long strands called chromosomes. On the molecular level the chromosomes are actually nothing more than two long strings of DNA wound together in a spiral-like structure called a double helix. ...
Chapter 11 and 12 Genetics is the scientific study of heredity
... acids form the completed protein. This process is called translation. Before translation begins, mRNA has to be transcribed from DNA. Then, the newly formed mRNA moves into the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. As each codon of the mRNA moves through the ribosome, the proper amino acid is brough ...
... acids form the completed protein. This process is called translation. Before translation begins, mRNA has to be transcribed from DNA. Then, the newly formed mRNA moves into the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. As each codon of the mRNA moves through the ribosome, the proper amino acid is brough ...
Introduction to Next Generation Sequencing
... Functional Genomics Data Analysis • Map reads to the genome ...
... Functional Genomics Data Analysis • Map reads to the genome ...
Week 5 EOC Review DNA, Mitosis, Meiosis, and Genetics
... C. number of carbon atoms in sugar molecules D. sequence of subunits in DNA ...
... C. number of carbon atoms in sugar molecules D. sequence of subunits in DNA ...
Mendel`s work
... chromosomes out of partially bad ones • But, unfortunately, the opposite is also true • Something must generate an asymmetry because recombination is “costly” ...
... chromosomes out of partially bad ones • But, unfortunately, the opposite is also true • Something must generate an asymmetry because recombination is “costly” ...
Nucleus - Maryville University
... • Law of complimentary base pairing allows building of one DNA strand based on the bases in 2nd strand • Steps of replication process – DNA helicase opens short segment of helix • replication fork is point of separation of 2 strands ...
... • Law of complimentary base pairing allows building of one DNA strand based on the bases in 2nd strand • Steps of replication process – DNA helicase opens short segment of helix • replication fork is point of separation of 2 strands ...
Unit D Review
... scientists study organisms that __________________ quickly Gregor ________________ was the first geneticist information gained from the study of one type of organism can be _________________ to other organisms proves inherited diseases are usually caused by ___________ Traits can be determin ...
... scientists study organisms that __________________ quickly Gregor ________________ was the first geneticist information gained from the study of one type of organism can be _________________ to other organisms proves inherited diseases are usually caused by ___________ Traits can be determin ...
Genetics (4) - HCC Learning Web
... • Law of complimentary base pairing allows building of one DNA strand based on the bases in 2nd strand • Steps of replication process – DNA helicase opens short segment of helix • replication fork is point of separation of 2 strands ...
... • Law of complimentary base pairing allows building of one DNA strand based on the bases in 2nd strand • Steps of replication process – DNA helicase opens short segment of helix • replication fork is point of separation of 2 strands ...
DNA Profiles
... possible using DNA chips (microarrays), which can hold thousands of genes DNA microarray • A series of short nucleotide sequences placed on a solid support (such as glass) that have several different uses ...
... possible using DNA chips (microarrays), which can hold thousands of genes DNA microarray • A series of short nucleotide sequences placed on a solid support (such as glass) that have several different uses ...
Cloning - Cloudfront.net
... Cloning Gene cloning – replication of donor genes in bacterial or other host cells – clone – a group of cells, organisms, or genes that are exact copies of each other – donor gene inserted into a bacterium is copied every time the plasmid containing it replicates – genes can be cloned by growing gen ...
... Cloning Gene cloning – replication of donor genes in bacterial or other host cells – clone – a group of cells, organisms, or genes that are exact copies of each other – donor gene inserted into a bacterium is copied every time the plasmid containing it replicates – genes can be cloned by growing gen ...
Cloning - cloudfront.net
... Cloning Gene cloning – replication of donor genes in bacterial or other host cells – clone – a group of cells, organisms, or genes that are exact copies of each other – donor gene inserted into a bacterium is copied every time the plasmid containing it replicates – genes can be cloned by growing gen ...
... Cloning Gene cloning – replication of donor genes in bacterial or other host cells – clone – a group of cells, organisms, or genes that are exact copies of each other – donor gene inserted into a bacterium is copied every time the plasmid containing it replicates – genes can be cloned by growing gen ...
chapter11
... 1. The enzyme DNA helicase travels along the helix opening it as they move. 2. Helix-destabilizing proteins bind to the single DNA strands preventing reformation of the double helix. 3. Topoisomerases break and rejoin sections of the DNA to relieve strain and prevent knots during replication. 4. DNA ...
... 1. The enzyme DNA helicase travels along the helix opening it as they move. 2. Helix-destabilizing proteins bind to the single DNA strands preventing reformation of the double helix. 3. Topoisomerases break and rejoin sections of the DNA to relieve strain and prevent knots during replication. 4. DNA ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.























