Genotyping of Mice to Study Role of Krüppel
... The β-globin locus contains CACCC binding sites in the promoters of the β-like genes, which could serve as targets for KLF2 binding ...
... The β-globin locus contains CACCC binding sites in the promoters of the β-like genes, which could serve as targets for KLF2 binding ...
Gene Expression
... of mRNA are removed (introns). • Exons are spliced together. – Males and females have the same set of genes, the fact that they are spliced differently accounts for the difference in gender. – Splicing and DNA rearrangement account for millions of different antibodies from the same genes. ...
... of mRNA are removed (introns). • Exons are spliced together. – Males and females have the same set of genes, the fact that they are spliced differently accounts for the difference in gender. – Splicing and DNA rearrangement account for millions of different antibodies from the same genes. ...
Encoding Contingency in Multicellular Organisms
... organisms to a relatively few highly adaptive options despite the vagaries of history, so that „„the evolutionary routes are many, but the destinations are limited.‟‟ Evolution is broadly repeatable, and multiple replays would reveal striking similarities in important features, with contingency most ...
... organisms to a relatively few highly adaptive options despite the vagaries of history, so that „„the evolutionary routes are many, but the destinations are limited.‟‟ Evolution is broadly repeatable, and multiple replays would reveal striking similarities in important features, with contingency most ...
MicroRNA Involvement in Breast Cancer Multidrug Resistance
... with elevated expression of one or more ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporters such as three well-known drug efflux proteins: P-glycoprotein (MDR-1), multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP-1), and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). However, the regulation of these transporters remains c ...
... with elevated expression of one or more ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporters such as three well-known drug efflux proteins: P-glycoprotein (MDR-1), multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP-1), and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). However, the regulation of these transporters remains c ...
Answers section 4
... 6. general transcription factors (includes TAT binding protein – TBP, which binds to the TATA box and recruits the rest of the GTFs) and sequence specific transcription factors 7. introns 8. liver because it has the sequence-specific transcription factors that bind to the upstream portion of the pr ...
... 6. general transcription factors (includes TAT binding protein – TBP, which binds to the TATA box and recruits the rest of the GTFs) and sequence specific transcription factors 7. introns 8. liver because it has the sequence-specific transcription factors that bind to the upstream portion of the pr ...
View PDF - OMICS Group
... of the 5S rRNA allows TFIIIA to return to the nucleus, where it can activate the expression of additional 5S rRNA. As 5S rRNA transcripts are produced, TFIIIA progressively becomes sequestered in the cytoplasm thus leading to reduced transcription of the 5S rRNA gene. TF also regulate genes post-tra ...
... of the 5S rRNA allows TFIIIA to return to the nucleus, where it can activate the expression of additional 5S rRNA. As 5S rRNA transcripts are produced, TFIIIA progressively becomes sequestered in the cytoplasm thus leading to reduced transcription of the 5S rRNA gene. TF also regulate genes post-tra ...
Nucleic Acids: Revisiting the Central Dogma
... is degraded by miRNA RISC complexes. The molecular hallmarks of lin-4, the founding member of the microRNA family. Sequence complementarity between lin-4 (red) and the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of lin-14 mRNA (blue). lin-4 is partially complementary to 7 sites in the lin-14 3' UTR; its binding to ...
... is degraded by miRNA RISC complexes. The molecular hallmarks of lin-4, the founding member of the microRNA family. Sequence complementarity between lin-4 (red) and the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of lin-14 mRNA (blue). lin-4 is partially complementary to 7 sites in the lin-14 3' UTR; its binding to ...
Silence is green - Biochemical Society Transactions
... of strong ago1 alleles. New data now show that these alleles significantly elevate a number of different miRNA targets [43]. Functionally, this places AGO1 in plant RISC, but another interpretation is that AGO1 has a role in directing miRNA traffic. One line of evidence for this idea is that the sta ...
... of strong ago1 alleles. New data now show that these alleles significantly elevate a number of different miRNA targets [43]. Functionally, this places AGO1 in plant RISC, but another interpretation is that AGO1 has a role in directing miRNA traffic. One line of evidence for this idea is that the sta ...
Messenger RNA profiling: a prototype method to supplant
... used in a sexual assault sexual abuse of a young child by a person living in the same residence as the victim in which the suspect’s DNA is found on the child’s clothing or bed linen ...
... used in a sexual assault sexual abuse of a young child by a person living in the same residence as the victim in which the suspect’s DNA is found on the child’s clothing or bed linen ...
Figure S2.
... Figure S2. NELF-E potentiates expression of the slp1[PESE]-lacZ reporter. Fluorescent double in situ hybridization was used to compare the expression of a reporter gene containing a slp1 cis-regulatory element extending from 3.9 to 1.8 kb upstream of the slp1 promoter fused to a 129 bp slp1 basal pr ...
... Figure S2. NELF-E potentiates expression of the slp1[PESE]-lacZ reporter. Fluorescent double in situ hybridization was used to compare the expression of a reporter gene containing a slp1 cis-regulatory element extending from 3.9 to 1.8 kb upstream of the slp1 promoter fused to a 129 bp slp1 basal pr ...
Lecture 1
... of the appearance of functional gene products. The functional gene product can be RNA, protein but mostly it is the regulation of the expression of the protein coding genes (gene switching). 3. Gene Expression is regulated at different levels: z Chemical & structural modification of DNA or chromatin ...
... of the appearance of functional gene products. The functional gene product can be RNA, protein but mostly it is the regulation of the expression of the protein coding genes (gene switching). 3. Gene Expression is regulated at different levels: z Chemical & structural modification of DNA or chromatin ...
microRNA Mimic and Inhibitor Functional Analysis
... as described in Section III. The candidate MRE is cloned into the 3'-UTR of the reporter plasmid. Binding of an miRNA or miRNA mimic to the MRE will result in reduced level of the reporter protein, while binding of an inhibitor to the miRNA will increase the reporter protein level. When a biological ...
... as described in Section III. The candidate MRE is cloned into the 3'-UTR of the reporter plasmid. Binding of an miRNA or miRNA mimic to the MRE will result in reduced level of the reporter protein, while binding of an inhibitor to the miRNA will increase the reporter protein level. When a biological ...
Input: window.results files (output of Stage 4).
... This pipeline is intended to process and quantify small RNA-seq reads mapping to (1) established miRNAs, and (2) potential novel miRNAs. miRNAs are small noncoding RNAs that are involved in the post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA. The 5’-end of miRNAs contains the “seed” region, which plays a si ...
... This pipeline is intended to process and quantify small RNA-seq reads mapping to (1) established miRNAs, and (2) potential novel miRNAs. miRNAs are small noncoding RNAs that are involved in the post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA. The 5’-end of miRNAs contains the “seed” region, which plays a si ...
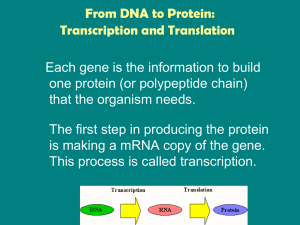
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... • Only a gene is copied, not the whole chromosome. • RNA nucleotides are added instead of DNA nucleotides. – Uracil is paired with adenine instead of thymine. • Transcription occurs on an ongoing basis as proteins needed, replication only occurs prior ...
... • Only a gene is copied, not the whole chromosome. • RNA nucleotides are added instead of DNA nucleotides. – Uracil is paired with adenine instead of thymine. • Transcription occurs on an ongoing basis as proteins needed, replication only occurs prior ...
Chapter 18 notes
... with RNA pol to initiate transcription. d} repressors may block RNA pol or prevent other transcription factors from interacting with RNA pol. e} repressors may affect chromatin structure via recruitment of histone modifiers f} seems to be a common method for silencing genes ...
... with RNA pol to initiate transcription. d} repressors may block RNA pol or prevent other transcription factors from interacting with RNA pol. e} repressors may affect chromatin structure via recruitment of histone modifiers f} seems to be a common method for silencing genes ...
5 CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Types of Ribonucleic
... Discovery of miRNAs Genes and Their Roles in Various Organisms ...
... Discovery of miRNAs Genes and Their Roles in Various Organisms ...
siRNA therapy delivery etc.pptx
... siRNA Design • Initial use of longer dsRNA lead to a non‐specific Type I interferon response (widespread changes in protein expressionapoptosis) • Dr. Thomas Tuschl’s lab discovered that RNAi is mediated by 21 and 22 nt RNAs • Also discovered the important characteristics needed by the R ...
... siRNA Design • Initial use of longer dsRNA lead to a non‐specific Type I interferon response (widespread changes in protein expressionapoptosis) • Dr. Thomas Tuschl’s lab discovered that RNAi is mediated by 21 and 22 nt RNAs • Also discovered the important characteristics needed by the R ...
Lecture 4 – Gene Expression Control and Regulation
... RNA cannot pass through a nuclear pore unless bound to certain proteins. Transport protein binding affects where the transcript will be delivered in the cell. ...
... RNA cannot pass through a nuclear pore unless bound to certain proteins. Transport protein binding affects where the transcript will be delivered in the cell. ...
Transcription – Part II
... 8. Regulation of gene expression in eukaryotes is considered much more complex than in prokaryotes. Why do you think that is? 9. What is the role of enhancers and silencers in transcriptional regulation? 10. Describe the three different DNA binding motifs associated with transcription factors. 11. U ...
... 8. Regulation of gene expression in eukaryotes is considered much more complex than in prokaryotes. Why do you think that is? 9. What is the role of enhancers and silencers in transcriptional regulation? 10. Describe the three different DNA binding motifs associated with transcription factors. 11. U ...
Gene Regulation - Eukaryotic Cells
... Epigenetics • Epigenetics refers to processes that influence gene expression or function without changing the underlying DNA sequence. 1. Acetylation 2. Methylation ...
... Epigenetics • Epigenetics refers to processes that influence gene expression or function without changing the underlying DNA sequence. 1. Acetylation 2. Methylation ...
Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis
... • Protein synthesis is carried out in three distinct stages: transcription; translation; and protein folding ...
... • Protein synthesis is carried out in three distinct stages: transcription; translation; and protein folding ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... rRNA: structural component of ribosome, along with a protein it forms the ribosome which provides the construction site for polypeptide assembly snRNA: small nuclear RNA involved in modification of mRNA molecules The purpose of TRANSCRIPTION: produce a copy of a small section of DNA. Similar in euka ...
... rRNA: structural component of ribosome, along with a protein it forms the ribosome which provides the construction site for polypeptide assembly snRNA: small nuclear RNA involved in modification of mRNA molecules The purpose of TRANSCRIPTION: produce a copy of a small section of DNA. Similar in euka ...
MicroRNA
A micro RNA (abbreviated miRNA) is a small non-coding RNA molecule (containing about 22 nucleotides) found in plants, animals, and some viruses, which functions in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression.Encoded by eukaryotic nuclear DNA in plants and animals and by viral DNA in certain viruses whose genome is based on DNA, miRNAs function via base-pairing with complementary sequences within mRNA molecules. As a result, these mRNA molecules are silenced by one or more of the following processes: 1) cleavage of the mRNA strand into two pieces, 2) destabilization of the mRNA through shortening of its poly(A) tail, and 3) less efficient translation of the mRNA into proteins by ribosomes. miRNAs resemble the small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. The human genome may encode over 1000 miRNAs, which are abundant in many mammalian cell types and appear to target about 60% of the genes of humans and other mammals.miRNAs are well conserved in both plants and animals, and are thought to be a vital and evolutionarily ancient component of genetic regulation. While core components of the microRNA pathway are conserved between plants and animals, miRNA repertoires in the two kingdoms appear to have emerged independently with different primary modes of action. Plant miRNAs usually have near-perfect pairing with their mRNA targets, which induces gene repression through cleavage of the target transcripts. In contrast, animal miRNAs are able to recognize their target mRNAs by using as little as 6–8 nucleotides (the seed region) at the 5' end of the miRNA, which is not enough pairing to induce cleavage of the target mRNAs. Combinatorial regulation is a feature of miRNA regulation in animals. A given miRNA may have hundreds of different mRNA targets, and a given target might be regulated by multiple miRNAs.The first miRNA was discovered in the early 1990s. However, miRNAs were not recognized as a distinct class of biological regulators until the early 2000s. Since then, miRNA research has revealed different sets of miRNAs expressed in different cell types and tissuesand has revealed multiple roles for miRNAs in plant and animal development and in many other biological processes. Aberrant expression of miRNAs has been implicated in numerous disease states, and miRNA-based therapies are under investigation.Estimates of the average number of unique messenger RNAs that are targets for repression by a typical microRNA vary, depending on the method used to make the estimate, but several approaches show that mammalian miRNAs can have many unique targets. For example, an analysis of the miRNAs highly conserved in vertebrate animals shows that each of these miRNAs has, on average, roughly 400 conserved targets. Likewise, experiments show that a single miRNA can reduce the stability of hundreds of unique messenger RNAs, and other experiments show that a single miRNA may repress the production of hundreds of proteins, but that this repression often is relatively mild (less than 2-fold).