Objective A - TuHS Physics Homepage
... 2. What important thing that they were observing at the time could Bohr’s atom predict? 3. Why do atoms make bright line spectra, and how is this related to the Bohr Orbits? Objective L: Bohr and de Broglie Problems: Chapter 27: 63c,e(150 eV, 0.13 nm) Questions: 1. How did de Broglie’s matter waves ...
... 2. What important thing that they were observing at the time could Bohr’s atom predict? 3. Why do atoms make bright line spectra, and how is this related to the Bohr Orbits? Objective L: Bohr and de Broglie Problems: Chapter 27: 63c,e(150 eV, 0.13 nm) Questions: 1. How did de Broglie’s matter waves ...
View PDF
... Indeed, the physical state of a particle and its composition and heterogeneity can be resolved with a degree of spatial resolution by single particle analytical methodology [1-3]. In this work we have investigated chemical and microstructure evolution of unique particles composed of inorganic salts ...
... Indeed, the physical state of a particle and its composition and heterogeneity can be resolved with a degree of spatial resolution by single particle analytical methodology [1-3]. In this work we have investigated chemical and microstructure evolution of unique particles composed of inorganic salts ...
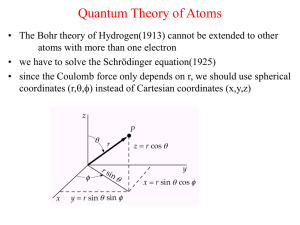
Quantum Theory of Atoms
... m= -l,(-l+1),…0,1,2,…,l => 2l+1 values of m for a given l • n is the principal quantum number and is associated with the distance r of an electron from the nucleus • l is the orbital quantum number and the angular momentum of the electron is given by L=[l(l+1)]1/2 ħ • m is the magnetic quantum numbe ...
... m= -l,(-l+1),…0,1,2,…,l => 2l+1 values of m for a given l • n is the principal quantum number and is associated with the distance r of an electron from the nucleus • l is the orbital quantum number and the angular momentum of the electron is given by L=[l(l+1)]1/2 ħ • m is the magnetic quantum numbe ...
Quantum Interference of Molecules
... history. Is light a wave or is it made up of particles? The earliest theory on the nature of light goes back to the corpuscular theory of Newton in 1704. Though Christian Huygens had proposed the wave theory of light in 1690, Newton's corpuscular theory, according to which light is composed of tiny ...
... history. Is light a wave or is it made up of particles? The earliest theory on the nature of light goes back to the corpuscular theory of Newton in 1704. Though Christian Huygens had proposed the wave theory of light in 1690, Newton's corpuscular theory, according to which light is composed of tiny ...
The Wave
... • In 1900 Max Planck proposed that light energy comes in packets (quanta) spread at random on a wave front called PHOTONS. • He even doubted his idea since: It went against wave theory by saying that electromagnetic waves don't transmit energy continuously but in small packets. ...
... • In 1900 Max Planck proposed that light energy comes in packets (quanta) spread at random on a wave front called PHOTONS. • He even doubted his idea since: It went against wave theory by saying that electromagnetic waves don't transmit energy continuously but in small packets. ...
Atomic Structure
... • Quantum Mechanics – deBroglie, Schrodinger, Heisenberg • Electrons not just particles – also act as waves • Find electrons in orbitals – know probable location of electron but not exact at any given time (Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle) • Schrodinger assigned quantum numbers to describe properti ...
... • Quantum Mechanics – deBroglie, Schrodinger, Heisenberg • Electrons not just particles – also act as waves • Find electrons in orbitals – know probable location of electron but not exact at any given time (Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle) • Schrodinger assigned quantum numbers to describe properti ...
Heisenberg`s uncertainty principle
... quantum mechanics shows that certain pairs of physical properties, like position and speed, cannot both be known to arbitrary precision: the more precisely one property is known, the less precisely the other can be known. This statement is known as the uncertainty principle. The uncertainty principl ...
... quantum mechanics shows that certain pairs of physical properties, like position and speed, cannot both be known to arbitrary precision: the more precisely one property is known, the less precisely the other can be known. This statement is known as the uncertainty principle. The uncertainty principl ...
The Wave Nature of Matter - Waterford Public Schools
... • Instead, mathematical solutions to the wave functions give 3dimensional shapes (orbitals) within which electrons can usually be found ...
... • Instead, mathematical solutions to the wave functions give 3dimensional shapes (orbitals) within which electrons can usually be found ...
The Michelson Interferometer
... glass screen. At the screen, the two beams are superposed and one can observe the interference between them. ...
... glass screen. At the screen, the two beams are superposed and one can observe the interference between them. ...
De Broglie Waves, Uncertainty, and Atoms
... Black side is hotter:gas molecules bounce off it with more momentum than on shiny side-this is a bigger effect than the photon momentum ...
... Black side is hotter:gas molecules bounce off it with more momentum than on shiny side-this is a bigger effect than the photon momentum ...
PPT
... • | Ψ (x,t)| 2 V is the probability that an electron would be found in the little volume V near point x at time t, if an experiment is done that could locate it that accurately. • Because |Ψ2| gives a probability density, when we have a large ensemble it tells us the rate at which electrons arrive ...
... • | Ψ (x,t)| 2 V is the probability that an electron would be found in the little volume V near point x at time t, if an experiment is done that could locate it that accurately. • Because |Ψ2| gives a probability density, when we have a large ensemble it tells us the rate at which electrons arrive ...
Quantum1
... Newtonian Mechanics, however, we know that a large number of events will behave in a statistically predictable way. probability for an electron to be found between x and x+dx ...
... Newtonian Mechanics, however, we know that a large number of events will behave in a statistically predictable way. probability for an electron to be found between x and x+dx ...
Chapter 27: Summary
... uncertainty principle is important for objects around the size of an atom or less. If Planck’s constant was a great deal larger, such as 1 J s, the uncertainty principle (and the de Broglie wavelength) would be relevant for all objects we deal with on an everyday basis. The world would be a much str ...
... uncertainty principle is important for objects around the size of an atom or less. If Planck’s constant was a great deal larger, such as 1 J s, the uncertainty principle (and the de Broglie wavelength) would be relevant for all objects we deal with on an everyday basis. The world would be a much str ...
Theoretical Physics T2 Quantum Mechanics
... the foundation of quantum mechanics. A metal surface emits electrons when illuminated by ultraviolet light. The importance of this discovery lies within the inability of classical physics to describe the effect in its full extent based on three observations. 1. ) The kinetic energy of the emitted el ...
... the foundation of quantum mechanics. A metal surface emits electrons when illuminated by ultraviolet light. The importance of this discovery lies within the inability of classical physics to describe the effect in its full extent based on three observations. 1. ) The kinetic energy of the emitted el ...
- Snistnote
... numbers are required to specify completely each energy state. since for a particle inside the box, ‘ Ψ ’ cannot be zero, no quantum number can be zero. 2.The energy ‘ E ’ depends on the sum of the squares of the quantum numbers n1,n2 and n3 and no on their individual values. 3.Several combinations o ...
... numbers are required to specify completely each energy state. since for a particle inside the box, ‘ Ψ ’ cannot be zero, no quantum number can be zero. 2.The energy ‘ E ’ depends on the sum of the squares of the quantum numbers n1,n2 and n3 and no on their individual values. 3.Several combinations o ...