slides
... Genes = books Almost every cell in an organism contains the same libraries and the same sets of books. • Books represent all the information (DNA) that every cell in the body needs so it can grow and carry out its various functions. ...
... Genes = books Almost every cell in an organism contains the same libraries and the same sets of books. • Books represent all the information (DNA) that every cell in the body needs so it can grow and carry out its various functions. ...
The subject of the offer are unique sequences of single
... or immobilization of His‐Tagged proteins. ...
... or immobilization of His‐Tagged proteins. ...
Document
... 2. ___reverse transcriptase__ is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. 3. Knockout mice are created by replacing a normal gene segment with a modified segment within embryonic _stem cells_______, then using the latter to create a chimeric embryo. 4. __transformation____ is a method of DNA transfer in bac ...
... 2. ___reverse transcriptase__ is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. 3. Knockout mice are created by replacing a normal gene segment with a modified segment within embryonic _stem cells_______, then using the latter to create a chimeric embryo. 4. __transformation____ is a method of DNA transfer in bac ...
Re-closing linearized plasmids
... Identify correct clones by PCR or restriction digest. The appropriate screening method should distinguish between the desired plasmid and the parental plasmid. If using PCR, see the PCR protocols page for “Insert verification with Vent.” Analyze the PCR products or restriction digests on a 1% agaros ...
... Identify correct clones by PCR or restriction digest. The appropriate screening method should distinguish between the desired plasmid and the parental plasmid. If using PCR, see the PCR protocols page for “Insert verification with Vent.” Analyze the PCR products or restriction digests on a 1% agaros ...
Genetic Engineering
... 1.Create recombinant bacteria with desired gene. 2. Allow the bacteria to “infect" the plant cells. ...
... 1.Create recombinant bacteria with desired gene. 2. Allow the bacteria to “infect" the plant cells. ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... Basic ingredients needed for DNA Recombination: A. Know the gene of interest and the species carrying that gene B. Need a species that can rapidly replicate its DNA and divide C. Need a species containing many restriction sites on its DNA D. Need restriction enzymes—these enzymes are able to cut dou ...
... Basic ingredients needed for DNA Recombination: A. Know the gene of interest and the species carrying that gene B. Need a species that can rapidly replicate its DNA and divide C. Need a species containing many restriction sites on its DNA D. Need restriction enzymes—these enzymes are able to cut dou ...
Name
... D. differences in a base between two individuals 26. Bioinformatics would not have been possible without A. microscopes. B. genes. C. computers. D. genomics. 27. In humans, single-base differences A. occur at about 3 million sites. B. occur rarely in the sex chromosomes. C. seldom occur in normal DN ...
... D. differences in a base between two individuals 26. Bioinformatics would not have been possible without A. microscopes. B. genes. C. computers. D. genomics. 27. In humans, single-base differences A. occur at about 3 million sites. B. occur rarely in the sex chromosomes. C. seldom occur in normal DN ...
DNA stucture - worldofbiology09
... Sections of DNA are known to code for the manufacture of proteins. These sections are called genes. ...
... Sections of DNA are known to code for the manufacture of proteins. These sections are called genes. ...
Antibodies - blobs.org
... are different in different antibodies. The Fc region is the fragment crystallisable region, which is the bit which connects to normal human immune cells, so that lymphocytes can connect to the antibody and recognise that it has found an invader. ...
... are different in different antibodies. The Fc region is the fragment crystallisable region, which is the bit which connects to normal human immune cells, so that lymphocytes can connect to the antibody and recognise that it has found an invader. ...
the original file
... 1. What is the evolutionary purpose of having both an innate and adaptive immune system that function as they do in humans? 2. Name 3 different types of barriers (mechanical, chemical, and microbial) that protect us from pathogens and list the key features for each category. 3. A dendritic cell phag ...
... 1. What is the evolutionary purpose of having both an innate and adaptive immune system that function as they do in humans? 2. Name 3 different types of barriers (mechanical, chemical, and microbial) that protect us from pathogens and list the key features for each category. 3. A dendritic cell phag ...
Biology Vocabulary 8, test on Thursday, 1/19/17
... twisted-ladder shape of DNA, formed by two nucleotide strands twisted around each other ability of an organism to control which genes are transcribed in response to the environment selective breeding of closely related organisms to produce desired traits and eliminate undesired traits, resulting in ...
... twisted-ladder shape of DNA, formed by two nucleotide strands twisted around each other ability of an organism to control which genes are transcribed in response to the environment selective breeding of closely related organisms to produce desired traits and eliminate undesired traits, resulting in ...
Organization of Eukaryotic DNA Dr: Hussein abdelaziz
... b) A genetic finger-print or a gene map for each individual can be done through which we can predict susceptibility or resistance to various diseases ...
... b) A genetic finger-print or a gene map for each individual can be done through which we can predict susceptibility or resistance to various diseases ...
Replication Animation Lab
... http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/DNA_structure.html. Click on DNA Structure 1. What is the shape of DNA called? 2. What is the backbone of DNA? 3. What forms the core of the double helix? 4. What is a pyrimadine? 5. What is a purine? 6. Explain why DNA is considered a polar mo ...
... http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/DNA_structure.html. Click on DNA Structure 1. What is the shape of DNA called? 2. What is the backbone of DNA? 3. What forms the core of the double helix? 4. What is a pyrimadine? 5. What is a purine? 6. Explain why DNA is considered a polar mo ...
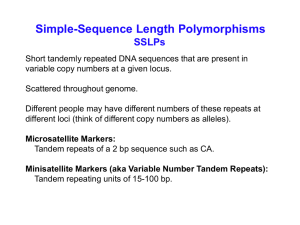
Using microsatellites as molecular markers
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
Immunology
... Two types of MHC antigens: MHC class I found on all body cells MHC class II found on antigen present cells Antigen Presentation Ingestion of the antigen Digestion of antigen into peptide fragments Fusion of vesicles (peptide fragments with MHC-II molecules) Binding of peptide fragments to MHC-II mol ...
... Two types of MHC antigens: MHC class I found on all body cells MHC class II found on antigen present cells Antigen Presentation Ingestion of the antigen Digestion of antigen into peptide fragments Fusion of vesicles (peptide fragments with MHC-II molecules) Binding of peptide fragments to MHC-II mol ...
Teaching Notes
... 3. A simple way to determine whether the DNA model that you made is right handed or left handed is the pretend to wrap your fingers around the DNA molecule, allowing your fingers to follow the DNA backbone. If you can wrap your right hand around the DNA helix, it is right handed and if you wrap the ...
... 3. A simple way to determine whether the DNA model that you made is right handed or left handed is the pretend to wrap your fingers around the DNA molecule, allowing your fingers to follow the DNA backbone. If you can wrap your right hand around the DNA helix, it is right handed and if you wrap the ...
From Mendel to Human Genome
... In the early __________, proceeded to study __________. The ratio of G:C was __________ and the ratio of T:A was __________, with evidence that the long molecule might be wound up in a _______________. Discovered crystallography structured data for DNA. ...
... In the early __________, proceeded to study __________. The ratio of G:C was __________ and the ratio of T:A was __________, with evidence that the long molecule might be wound up in a _______________. Discovered crystallography structured data for DNA. ...
Document
... •CaCl2 method (Mandal and Higa, 1970) •RbCl2 Method (Hanahan, 1983) •Other protocols ...
... •CaCl2 method (Mandal and Higa, 1970) •RbCl2 Method (Hanahan, 1983) •Other protocols ...
35-4 Reading Guide
... HIV and AIDS 9. What does AIDS stand for? 10. What is the term that describes diseases that attack people with a weakened immune system? 11. List four body fluids that can transmit AIDS. A. B. C. D. 12. What behaviors prevent people from being infected with HIV? ...
... HIV and AIDS 9. What does AIDS stand for? 10. What is the term that describes diseases that attack people with a weakened immune system? 11. List four body fluids that can transmit AIDS. A. B. C. D. 12. What behaviors prevent people from being infected with HIV? ...
GSLC Protein Synthesis Computer Activity (word)
... Go back to Old Tour of Basic Genetics. Click on What is a Gene. 1. Genes are made of _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. One stand of DNA contains _____________________________genes. 3. Approximately how many different genes do humans have? __________ ...
... Go back to Old Tour of Basic Genetics. Click on What is a Gene. 1. Genes are made of _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. One stand of DNA contains _____________________________genes. 3. Approximately how many different genes do humans have? __________ ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.