• Double helix -- twisted ladder shape of DNA, like spiral staircase
... one has 2nd strand filled in with matching nucleotides • Gene expression -- going from DNA to RNA to protein which results in phenotype, how the genotype determines the phenotype • Template -- model/pattern/stencil that makes copying easy and exact • Nucleotide -- basic unit of DNA, phosphate + suga ...
... one has 2nd strand filled in with matching nucleotides • Gene expression -- going from DNA to RNA to protein which results in phenotype, how the genotype determines the phenotype • Template -- model/pattern/stencil that makes copying easy and exact • Nucleotide -- basic unit of DNA, phosphate + suga ...
Variation, DNA and Protein Synthesis
... Describe the molecular involvement of DNA, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA and amino acids in the process of protein synthesis ...
... Describe the molecular involvement of DNA, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA and amino acids in the process of protein synthesis ...
The presentation
... Genetic determinants of variation in expression levels may contribute to complex traits - phenotype is not just determined by coding regions Biochemical features associated with cis-regulatory modules are being determined genome-wide for a range of cell types. These can be used to predict CRMs, but ...
... Genetic determinants of variation in expression levels may contribute to complex traits - phenotype is not just determined by coding regions Biochemical features associated with cis-regulatory modules are being determined genome-wide for a range of cell types. These can be used to predict CRMs, but ...
Ch 13 Genetic Engineering
... • Scientists can synthesize a DNA strand and connect it to a circular DNA molecule known as a plasmid… which can be found naturally in bacteria. This bacteria can then be injected into a plant, and will insert its DNA into the plant. • If transformation is successful, the recombinant DNA is integra ...
... • Scientists can synthesize a DNA strand and connect it to a circular DNA molecule known as a plasmid… which can be found naturally in bacteria. This bacteria can then be injected into a plant, and will insert its DNA into the plant. • If transformation is successful, the recombinant DNA is integra ...
GENETIC ENGINEERING QUESTIONS
... 1. A scientist wants to mass produce a recombinant form of a protein for human use. He should first a. Purify the protein b. Clone the gene for the protein c. Perform PCR on the protein d. Grow bacteria to make the protein 2. People show restriction fragment length polymorphism because a. They have ...
... 1. A scientist wants to mass produce a recombinant form of a protein for human use. He should first a. Purify the protein b. Clone the gene for the protein c. Perform PCR on the protein d. Grow bacteria to make the protein 2. People show restriction fragment length polymorphism because a. They have ...
Mutations
... genes, which means genes can be Removed, put together, and recombined: 1. Cut out the desired DNA of the gene 2. Combine that DNA with that of the recipient 3. Insert it into the new organism ...
... genes, which means genes can be Removed, put together, and recombined: 1. Cut out the desired DNA of the gene 2. Combine that DNA with that of the recipient 3. Insert it into the new organism ...
evaluation of a one-step dna extraction method for “touch”
... Due to advances in DNA typing technologies, it is possible to generate a DNA profile from touched objects or trace amounts of biological material (< 100pg). Therefore, it is important to ensure that sample collection and DNA purification methods recover the maximal amount of DNA from each sample. Th ...
... Due to advances in DNA typing technologies, it is possible to generate a DNA profile from touched objects or trace amounts of biological material (< 100pg). Therefore, it is important to ensure that sample collection and DNA purification methods recover the maximal amount of DNA from each sample. Th ...
Lecture, Gene Expression
... We call this next part Gene Expression, or the production of a phenotype given information from the genotype (“gene” = segments of DNA) and it can be ...
... We call this next part Gene Expression, or the production of a phenotype given information from the genotype (“gene” = segments of DNA) and it can be ...
DNA and genetic information
... DNA and genetic information • DNA carries plans for the primary structure of nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and proteins. • DNA of single cell has capacity over 1 million pages of text (900 copies of our textbook!) • however, only about 1% of DNA ever gets translated into proteins- equivalent to about 1 l ...
... DNA and genetic information • DNA carries plans for the primary structure of nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and proteins. • DNA of single cell has capacity over 1 million pages of text (900 copies of our textbook!) • however, only about 1% of DNA ever gets translated into proteins- equivalent to about 1 l ...
Study Guide Ch
... 17. Why is DNA called the “code of life” or the “genetic code”? (Hint: What does it code for that is so important?) ...
... 17. Why is DNA called the “code of life” or the “genetic code”? (Hint: What does it code for that is so important?) ...
Ch 11 homework
... A) fact that each individual of a species has a unique set of genes. B) fact that individuals of the same species have different phenotypes. C) process by which genetic information flows from genes to proteins. D) fact that certain genes are visible as dark stripes on a chromosome. E) flow of inform ...
... A) fact that each individual of a species has a unique set of genes. B) fact that individuals of the same species have different phenotypes. C) process by which genetic information flows from genes to proteins. D) fact that certain genes are visible as dark stripes on a chromosome. E) flow of inform ...
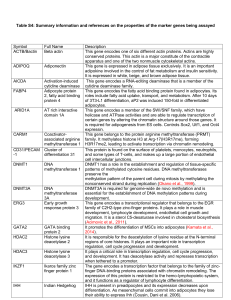
Table S4: Summary information and references on the properties of
... This gene belongs to the protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) family. It methylates histone H3 at Arg-17(H3R17me), forming H3R17me2, leading to activate transcription via chromatin remodeling. This protein is found on the surface of platelets, monocytes, neutrophils, and some types of T-cells, ...
... This gene belongs to the protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) family. It methylates histone H3 at Arg-17(H3R17me), forming H3R17me2, leading to activate transcription via chromatin remodeling. This protein is found on the surface of platelets, monocytes, neutrophils, and some types of T-cells, ...
File
... 6. Compare and contrast mitosis vs. meiosis Mitosis: one cell division, daughter cells identical to parent cell, used for growth/repair Meiosis: Two divisions, daughters have ½ DNA from parent, used to make gametes 7. Describe the difference between sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes. Draw ...
... 6. Compare and contrast mitosis vs. meiosis Mitosis: one cell division, daughter cells identical to parent cell, used for growth/repair Meiosis: Two divisions, daughters have ½ DNA from parent, used to make gametes 7. Describe the difference between sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes. Draw ...
• Double helix -- twisted ladder shape of DNA, like spiral staircase
... one has 2nd strand filled in with matching nucleotides • Gene expression -- going from DNA to RNA to protein which results in phenotype, how the genotype determines the phenotype • Template -- model/pattern/stencil that makes copying easy and exact • Nucleotide -- basic unit of DNA, phosphate + suga ...
... one has 2nd strand filled in with matching nucleotides • Gene expression -- going from DNA to RNA to protein which results in phenotype, how the genotype determines the phenotype • Template -- model/pattern/stencil that makes copying easy and exact • Nucleotide -- basic unit of DNA, phosphate + suga ...
File - sitdownandlogon
... • http://physicsworld.com/cws/ article/news/2013/jan/23/digi tal-files-stored-and-retrievedusing-dna-memory ...
... • http://physicsworld.com/cws/ article/news/2013/jan/23/digi tal-files-stored-and-retrievedusing-dna-memory ...
Poster
... Our enzyme, yHst2, belongs to an important family of enzymes called sirtuins. yHst2 is the yeast homologue of human Sir two 2. All Sir2 deacetylases have amino acid sequences that are very similar in all organisms from bacteria to humans. They all remove acetyl groups from acetyllysine sidechains on ...
... Our enzyme, yHst2, belongs to an important family of enzymes called sirtuins. yHst2 is the yeast homologue of human Sir two 2. All Sir2 deacetylases have amino acid sequences that are very similar in all organisms from bacteria to humans. They all remove acetyl groups from acetyllysine sidechains on ...
7th Grade Life Science: Genetics Unit Essential Question: How does
... 7th Grade Life Science: Genetics Key Learning: DNA determines traits and traits are inherited. Unit Essential Question: How does DNA determine traits and how are traits inherited? ...
... 7th Grade Life Science: Genetics Key Learning: DNA determines traits and traits are inherited. Unit Essential Question: How does DNA determine traits and how are traits inherited? ...
Dr. Ronita Nag Chaudhuri
... both spontaneous and environmentally induced damages at the molecular level. Defects in DNA damage repair in mammalian cells may lead to increased cancer frequency, neurological abnormalities as well as growth and developmental defects, among others. Organization of DNA into nucleosomes and the high ...
... both spontaneous and environmentally induced damages at the molecular level. Defects in DNA damage repair in mammalian cells may lead to increased cancer frequency, neurological abnormalities as well as growth and developmental defects, among others. Organization of DNA into nucleosomes and the high ...
Name: Block: ______ How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism: the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with 6 genes on it. You job is to analyz ...
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism: the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with 6 genes on it. You job is to analyz ...
Human Genetics and Genetic Technology Test Review Jeopardy
... What is to identify all human genes and sequence all the DNA bases? ...
... What is to identify all human genes and sequence all the DNA bases? ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.