Lesson 1 DNA and proteins
... • Polypeptides are chains of amino acid residues joined by peptide bonds. • There are 20 different aa and their sequence determines the structure and function of the protein. • The sequence of bases in a DNA molecule determines the sequence of aa. • A gene is a length of DNA that codes for one (or m ...
... • Polypeptides are chains of amino acid residues joined by peptide bonds. • There are 20 different aa and their sequence determines the structure and function of the protein. • The sequence of bases in a DNA molecule determines the sequence of aa. • A gene is a length of DNA that codes for one (or m ...
Science - edl.io
... c) 3rd sentence = Explain HOW your evidence works d) 4th sentence = Summarize answer -OR- Second piece of evidence A) When cells make proteins, why do they make a copy of mRNA to send out of the nucleus to the ribosome? Why don’t they just send a piece of the original DNA, to make sure there can’t b ...
... c) 3rd sentence = Explain HOW your evidence works d) 4th sentence = Summarize answer -OR- Second piece of evidence A) When cells make proteins, why do they make a copy of mRNA to send out of the nucleus to the ribosome? Why don’t they just send a piece of the original DNA, to make sure there can’t b ...
Word Picture Definition Gene mRNA Base Uracil Ribosome tRNA
... c) 3rd sentence = Explain HOW your evidence works d) 4th sentence = Summarize answer -OR- Second piece of evidence A) When cells make proteins, why do they make a copy of mRNA to send out of the nucleus to the ribosome? Why don’t they just send a piece of the original DNA, to make sure there can’t b ...
... c) 3rd sentence = Explain HOW your evidence works d) 4th sentence = Summarize answer -OR- Second piece of evidence A) When cells make proteins, why do they make a copy of mRNA to send out of the nucleus to the ribosome? Why don’t they just send a piece of the original DNA, to make sure there can’t b ...
DNA Typing
... Falls at rate of one degree per hour Obesity and warm environment slows cooling • None of the above are totally reliable and can be manipulated ...
... Falls at rate of one degree per hour Obesity and warm environment slows cooling • None of the above are totally reliable and can be manipulated ...
Document
... wound around proteins (called histones) residing in the nucleus of the cell. Genes are sections of DNA that code for a specific protein that determines a particular characteristic. ...
... wound around proteins (called histones) residing in the nucleus of the cell. Genes are sections of DNA that code for a specific protein that determines a particular characteristic. ...
Slide 1 - Brookwood High School
... the sex chromosomes Y chromosome much smaller than X so many genes only found on X Males express all X-linked alleles since they have only one X chromosome – even recessives Ex. Color blindness, hemophilia ...
... the sex chromosomes Y chromosome much smaller than X so many genes only found on X Males express all X-linked alleles since they have only one X chromosome – even recessives Ex. Color blindness, hemophilia ...
What Processes Produce RNA from DNA and Protein from mRNA
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
DNA Technology Notes
... hair, or skin, is needed. For example, the amount of DNA found at the root of one hair is usually sufficient ...
... hair, or skin, is needed. For example, the amount of DNA found at the root of one hair is usually sufficient ...
Heterochromatin-2015
... Pol IV is recruited to chromatin and transcribes ssRNA which is converted to dsRNA by RDR2 siRNA is produced by DCL3 and loaded onto AGO4 Pol V transcribes a scaffold RNA that base pairs with AGP4-bound siRNA DNA is unwound and DRM2 is recruited and methylates DNA Histones are modified to reinforce ...
... Pol IV is recruited to chromatin and transcribes ssRNA which is converted to dsRNA by RDR2 siRNA is produced by DCL3 and loaded onto AGO4 Pol V transcribes a scaffold RNA that base pairs with AGP4-bound siRNA DNA is unwound and DRM2 is recruited and methylates DNA Histones are modified to reinforce ...
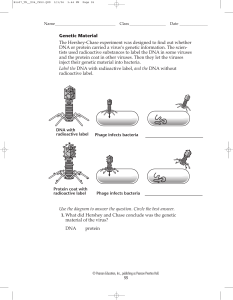
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... DNA or protein carried a virus’s genetic information. The scientists used radioactive substances to label the DNA in some viruses and the protein coat in other viruses. Then they let the viruses inject their genetic material into bacteria. Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without ra ...
... DNA or protein carried a virus’s genetic information. The scientists used radioactive substances to label the DNA in some viruses and the protein coat in other viruses. Then they let the viruses inject their genetic material into bacteria. Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without ra ...
Gene Section CBFb (subunit b of core binding factor)
... CBF binds to a core motif of the DNA (herein the name); CBFb by itself does not contain any known DNA binding motif or any transcriptional activation domain; CBFa binds to DNA; CBFb increases CBFa's affinity to DNA by 5 to 10 fold; CBF is a transcription factor which regulates the expression of myel ...
... CBF binds to a core motif of the DNA (herein the name); CBFb by itself does not contain any known DNA binding motif or any transcriptional activation domain; CBFa binds to DNA; CBFb increases CBFa's affinity to DNA by 5 to 10 fold; CBF is a transcription factor which regulates the expression of myel ...
Genetic Engineering
... The simple addition, deletion, or manipulation of a single trait in an organism to create a desired change. ...
... The simple addition, deletion, or manipulation of a single trait in an organism to create a desired change. ...
Document
... daughter cells in the process of mitosis (12.4, 12.5) 2. DNA replication is part of the cell cycle (12.6) 3. Sister chromatids experience cohesion from the time of their creation 4. Steps in sorting sister chromatids (steps of mitosis) (12.6, 12.7, 12.9, 12.10) 5. Because of DNA replication and mito ...
... daughter cells in the process of mitosis (12.4, 12.5) 2. DNA replication is part of the cell cycle (12.6) 3. Sister chromatids experience cohesion from the time of their creation 4. Steps in sorting sister chromatids (steps of mitosis) (12.6, 12.7, 12.9, 12.10) 5. Because of DNA replication and mito ...
File - NCEA Level 3 Biology
... STR — short tandem repeats. Short sequences (2–8 base pairs) able to repeat up to 100 times. Humans have many microsatellites and the number of repeats varies between people. This is used to gene profile people using PCR ...
... STR — short tandem repeats. Short sequences (2–8 base pairs) able to repeat up to 100 times. Humans have many microsatellites and the number of repeats varies between people. This is used to gene profile people using PCR ...
NUCLEOTIDES AND NUCLEIC ACIDS 2
... • Factors that are responsible for denaturation of DNA includes: ↑temperature, ↓pH. • Because there are 3 bonds between G and C but only 2 between A and T, DNA that contains high concentration of A and T will denaturate at a lower temperature than G and C rich DNA. ...
... • Factors that are responsible for denaturation of DNA includes: ↑temperature, ↓pH. • Because there are 3 bonds between G and C but only 2 between A and T, DNA that contains high concentration of A and T will denaturate at a lower temperature than G and C rich DNA. ...
Unit 4 Resources - Schoolwires.net
... 5. Few chromosome mutations are passed on to the next generation because a. the zygote usually dies. b. the mature organism is sterile. c. the mature organism is often incapable of producing offspring. d. all of the above. ...
... 5. Few chromosome mutations are passed on to the next generation because a. the zygote usually dies. b. the mature organism is sterile. c. the mature organism is often incapable of producing offspring. d. all of the above. ...
PowerPoint Genetic Technology Notes
... No individual is exactly like any other genetically—except for ___________ twins, who share the same genome. Chromosomes contain many regions with ___________ DNA sequences that do not code for proteins. These vary from person to person. DNA fingerprinting can be used to ___________ individuals by a ...
... No individual is exactly like any other genetically—except for ___________ twins, who share the same genome. Chromosomes contain many regions with ___________ DNA sequences that do not code for proteins. These vary from person to person. DNA fingerprinting can be used to ___________ individuals by a ...
What do Genes Look Like - Effingham County Schools
... Ex: German Shepard x German Shepard = German Shepard VII. _______________________________ – Desired genes are removed from one organism and added or recombined into another organism. This forms a transgenic organism with recombinant DNA A. This is used to make proteins not normally made by the cel ...
... Ex: German Shepard x German Shepard = German Shepard VII. _______________________________ – Desired genes are removed from one organism and added or recombined into another organism. This forms a transgenic organism with recombinant DNA A. This is used to make proteins not normally made by the cel ...
Learning Targets - Unit 9 DNA, RNA, Proteins, Mutation
... explain the principal function of DNA describe the structure of DNA diagram and label the 3 parts of a nucleotide explain the role of complementary base pairing in the replication of DNA summarize the main features of DNA replication explain the primary functions of each type of RNA compare the stru ...
... explain the principal function of DNA describe the structure of DNA diagram and label the 3 parts of a nucleotide explain the role of complementary base pairing in the replication of DNA summarize the main features of DNA replication explain the primary functions of each type of RNA compare the stru ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... experiment. Four pairs of PCR primers were used to amplify DNA isolated from one man's somatic cells, and from 21 single sperm that he donated for this study. Each primer pair amplifies a different region of the human genome, referred to as genes A, B, C and D. Each of these amplified regions was th ...
... experiment. Four pairs of PCR primers were used to amplify DNA isolated from one man's somatic cells, and from 21 single sperm that he donated for this study. Each primer pair amplifies a different region of the human genome, referred to as genes A, B, C and D. Each of these amplified regions was th ...
Section 1.1 Name:
... Review of Old Information: Recall that the DNA is the hereditary information for all living things. In this molecule is the code for all of our traits. However, one important question remains… how do we get from the genetic code from DNA in the nucleus, to the production of our phenotypes (or what w ...
... Review of Old Information: Recall that the DNA is the hereditary information for all living things. In this molecule is the code for all of our traits. However, one important question remains… how do we get from the genetic code from DNA in the nucleus, to the production of our phenotypes (or what w ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.