Small-Subunit Ribosomal RNA Sequence from
... after divergence of the ancestors of these two flagellate organisms. Extrachromosomal rRNA genes may therefore be the ancestral eukaryotic condition rather than a lineagespecific peculiarity. The positioning of the NaegZeria branch node so close to that of Euglena and Trypanosoma suggests a flagella ...
... after divergence of the ancestors of these two flagellate organisms. Extrachromosomal rRNA genes may therefore be the ancestral eukaryotic condition rather than a lineagespecific peculiarity. The positioning of the NaegZeria branch node so close to that of Euglena and Trypanosoma suggests a flagella ...
RNA Polymerase - California Lutheran University
... • Single primary transcript can be spliced into different mRNAs by the inclusion of different sets of exons • 15% of known human genetic disorders are due to altered splicing • 35 to 59% of human genes exhibit some form of ...
... • Single primary transcript can be spliced into different mRNAs by the inclusion of different sets of exons • 15% of known human genetic disorders are due to altered splicing • 35 to 59% of human genes exhibit some form of ...
Document
... genes, or messenger RNAs, which are the RNAs that get translated into proteins. Also, most snRNA (splicing) and microRNAs (RNAi). This is the most studied type, and due to the high level of control required over transcription a range of transcription factors are required for its binding to promoters ...
... genes, or messenger RNAs, which are the RNAs that get translated into proteins. Also, most snRNA (splicing) and microRNAs (RNAi). This is the most studied type, and due to the high level of control required over transcription a range of transcription factors are required for its binding to promoters ...
Chapter 11: Gene Expression PPT
... issues associated with gene technologies: genetic engineering, cloning, transgenic organism production, stem cell research, and DNA fingerprinting. ...
... issues associated with gene technologies: genetic engineering, cloning, transgenic organism production, stem cell research, and DNA fingerprinting. ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods
... Responder: none of the probe-sets/genes showed an expression above the 60th percentile of that population; in case all 3 target genes (14 probe-sets) were used, less than 3 probe-sets had expression intensity above the 60th percentile of the population studied. ...
... Responder: none of the probe-sets/genes showed an expression above the 60th percentile of that population; in case all 3 target genes (14 probe-sets) were used, less than 3 probe-sets had expression intensity above the 60th percentile of the population studied. ...
Astrovirus Replication: An Overview
... capsid biology. This approach has recently been used by two different research groups, leading to similar conclusions.27,35 Consistently, all significant matches for VP34 sequence from different HAstV serotypes and other animal astroviruses correspond to coat proteins from simple, icosahedrally symm ...
... capsid biology. This approach has recently been used by two different research groups, leading to similar conclusions.27,35 Consistently, all significant matches for VP34 sequence from different HAstV serotypes and other animal astroviruses correspond to coat proteins from simple, icosahedrally symm ...
Aminoacylated tmRNA from Escherichia coli interacts with
... unpubl+ results)+ What about the other tRNA specific proteins involved in translation? E. coli tmRNA is found associated with 70S ribosomes in vivo, at about one molecule per 10 ribosomes (Ushida et al+, 1994; Komine et al+, 1996)+ How tmRNA enters the ribosomal A-site remains unknown+ It could eith ...
... unpubl+ results)+ What about the other tRNA specific proteins involved in translation? E. coli tmRNA is found associated with 70S ribosomes in vivo, at about one molecule per 10 ribosomes (Ushida et al+, 1994; Komine et al+, 1996)+ How tmRNA enters the ribosomal A-site remains unknown+ It could eith ...
pdf
... a. The concentration of charged tRNAs is a measure of the amount of Trp available for protein synthesis. If most tRNAtrp is charged, there is an abundance of Trp, and the cell does not need to make more. b. Low [Trp-tRNAtrp] allows read-through transcription through the attenuator, so that trpEDCBA ...
... a. The concentration of charged tRNAs is a measure of the amount of Trp available for protein synthesis. If most tRNAtrp is charged, there is an abundance of Trp, and the cell does not need to make more. b. Low [Trp-tRNAtrp] allows read-through transcription through the attenuator, so that trpEDCBA ...
5 min Insect DNA/RNA Preservation and Extraction Kit
... Biofactories’ 5 min Insect DNA/RNA Preservation and Extraction Kit provides the fastest method for the storage/preservation and isolation/purification of total DNA/RNA from insect samples. The kit is specially designed for preservation and extraction of cellular and viral DNA/RNA from insect such as ...
... Biofactories’ 5 min Insect DNA/RNA Preservation and Extraction Kit provides the fastest method for the storage/preservation and isolation/purification of total DNA/RNA from insect samples. The kit is specially designed for preservation and extraction of cellular and viral DNA/RNA from insect such as ...
MOL WS 2016 Handout T3 Metabolism RNA world
... The hepatitis delta virus (HDV) ribozyme is a non-coding RNA found in the hepatitis delta virus that is necessary for viral replication and is thought to be the only catalytic RNA known to be required for viability of a human pathogen. The ribozyme acts to process the RNA transcripts to unit lengths ...
... The hepatitis delta virus (HDV) ribozyme is a non-coding RNA found in the hepatitis delta virus that is necessary for viral replication and is thought to be the only catalytic RNA known to be required for viability of a human pathogen. The ribozyme acts to process the RNA transcripts to unit lengths ...
RNA Polymerases
... regulation of their transcription. Some promoters such as the U6 small nuclear RNA (U6 snRNA ) and small RNA genes from the Epstein-Barr virus use only regulatory sequences upstream from their transcription start sites. The coding region of the U6 snRNA has a characteristic A box. However, this sequ ...
... regulation of their transcription. Some promoters such as the U6 small nuclear RNA (U6 snRNA ) and small RNA genes from the Epstein-Barr virus use only regulatory sequences upstream from their transcription start sites. The coding region of the U6 snRNA has a characteristic A box. However, this sequ ...
A lophotrochozoan-specific nuclear hormone receptor
... physiological processes in metazoans, with sexual development being among the most renowned. In mammals, androgen (Wang et al., 2009), progesterone (Chappell et al., 1997), and estrogen receptors (Walker and Korach, 2004) all have well-established roles in both male and female sex organ development ...
... physiological processes in metazoans, with sexual development being among the most renowned. In mammals, androgen (Wang et al., 2009), progesterone (Chappell et al., 1997), and estrogen receptors (Walker and Korach, 2004) all have well-established roles in both male and female sex organ development ...
Chapter 10
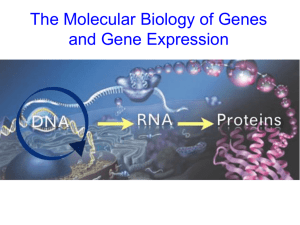
... • The flow of genetic information is from DNA to RNA to protein. • In transcription (DNA → RNA), the mRNA is synthesized on a DNA template. • In eukaryotic cells, transcription occurs in the nucleus, and the messenger RNA is processed before it travels to the cytoplasm. • In prokaryotes, transcripti ...
... • The flow of genetic information is from DNA to RNA to protein. • In transcription (DNA → RNA), the mRNA is synthesized on a DNA template. • In eukaryotic cells, transcription occurs in the nucleus, and the messenger RNA is processed before it travels to the cytoplasm. • In prokaryotes, transcripti ...
Lec 16 - RNA and IT`s Structure
... With the discovery of the molecular structure of the DNA double helix in 1953, researchers turned to the structure of ribonucleic acid (RNA) as the next critical puzzle to be solved on the road to understanding the molecular basis of life. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a type of molecule that consists o ...
... With the discovery of the molecular structure of the DNA double helix in 1953, researchers turned to the structure of ribonucleic acid (RNA) as the next critical puzzle to be solved on the road to understanding the molecular basis of life. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a type of molecule that consists o ...
Slide 1
... gene expression in response to environmental conditions In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences in cell types RNA molecules play many roles in regulating gene expression in eukaryotes ...
... gene expression in response to environmental conditions In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences in cell types RNA molecules play many roles in regulating gene expression in eukaryotes ...
Gibberellin Regulates Mitochondrial Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
... OsPDK1 expression was up-regulated by GA3 at the transcript level and was repressed in PDK1 RNAi transgenic rice. To examine whether mtPDH activity was directly affected by GA3 or by expression of PDK1 RNAi, a series of mtPDH assays were performed. Two-week-old rice seedlings were treated with 5 µM ...
... OsPDK1 expression was up-regulated by GA3 at the transcript level and was repressed in PDK1 RNAi transgenic rice. To examine whether mtPDH activity was directly affected by GA3 or by expression of PDK1 RNAi, a series of mtPDH assays were performed. Two-week-old rice seedlings were treated with 5 µM ...
Chapter 14
... The amino acid sequence of the recognition helix makes contacts with particular bases in the operator sequence that it recognizes. ...
... The amino acid sequence of the recognition helix makes contacts with particular bases in the operator sequence that it recognizes. ...
MicroRNAs act sequentially and asymmetrically to
... Christian Frokjaer-Jensen, Shawn Lockery and Oliver Hobert ...
... Christian Frokjaer-Jensen, Shawn Lockery and Oliver Hobert ...
3 - HCC Learning Web
... • At a point about 10 to 35 nucleotides past this sequence, the pre-mRNA is cut from the enzyme. • The completed single-stranded RNA transcript is released and the RNA polymerase will detach from the DNA ...
... • At a point about 10 to 35 nucleotides past this sequence, the pre-mRNA is cut from the enzyme. • The completed single-stranded RNA transcript is released and the RNA polymerase will detach from the DNA ...
Chapter 6: Gene Expression
... mRNA Modifications in Eukaryotes: Part I In prokaryotes, transcription and translation can occur simultaneously. In eukaryotes, mRNA must undergo modifications before it crosses the nuclear membrane to the cytoplasm. Once the modified mRNA enters the cytoplasm, it can undergo translation. There are ...
... mRNA Modifications in Eukaryotes: Part I In prokaryotes, transcription and translation can occur simultaneously. In eukaryotes, mRNA must undergo modifications before it crosses the nuclear membrane to the cytoplasm. Once the modified mRNA enters the cytoplasm, it can undergo translation. There are ...
MicroRNA Involvement in Breast Cancer Multidrug Resistance
... Multidrug resistance (MDR) has been frequently associated with elevated expression of one or more ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporters such as three well-known drug efflux proteins: P-glycoprotein (MDR-1), multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP-1), and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP ...
... Multidrug resistance (MDR) has been frequently associated with elevated expression of one or more ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporters such as three well-known drug efflux proteins: P-glycoprotein (MDR-1), multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP-1), and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP ...
Global MicroRNA Amplification Kit
... Micro RNAs are 19-24 nucleotide long single stranded RNAs that regulate the expression of target genes by interacting with complementary sites in the 3’ UTR of the target mRNAs and inhibiting translation. MiRNAs are a conserved group of noncoding RNAs with very important regulatory roles. Mature miR ...
... Micro RNAs are 19-24 nucleotide long single stranded RNAs that regulate the expression of target genes by interacting with complementary sites in the 3’ UTR of the target mRNAs and inhibiting translation. MiRNAs are a conserved group of noncoding RNAs with very important regulatory roles. Mature miR ...
MicroRNAs as Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors
... regulated by a single microRNA, which implies that over one third of protein-coding genes in humans are regulated by microRNAs. Thus, the microRNA milieu can modulate levels of protein expression by dampening the translation of thousands of mRNAs. Indeed, microRNA-mediated gene regulation is now con ...
... regulated by a single microRNA, which implies that over one third of protein-coding genes in humans are regulated by microRNAs. Thus, the microRNA milieu can modulate levels of protein expression by dampening the translation of thousands of mRNAs. Indeed, microRNA-mediated gene regulation is now con ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.