Preferential expression of one P-tubulin gene during
... alleles d and e (Fig. l), indicating that p50l is derived from betA, and to the monomorphic band f, indicating that band f may also be derived from betA. p50l hybridizes less strongly to alleles of other loci. p502 cDNA preferentially hybridizes to betB alleles g and h (Fig. I), indicating that p502 ...
... alleles d and e (Fig. l), indicating that p50l is derived from betA, and to the monomorphic band f, indicating that band f may also be derived from betA. p50l hybridizes less strongly to alleles of other loci. p502 cDNA preferentially hybridizes to betB alleles g and h (Fig. I), indicating that p502 ...
Course Outline
... known to be tobacco mosaic virus. His experiments showed that the crushed leaf extracts from infected tobacco plants are still infectious after filtration. Ivanovski suggested the infection might be caused by a toxin produced by bacteria, but did not pursue the idea. At the time it was thought that ...
... known to be tobacco mosaic virus. His experiments showed that the crushed leaf extracts from infected tobacco plants are still infectious after filtration. Ivanovski suggested the infection might be caused by a toxin produced by bacteria, but did not pursue the idea. At the time it was thought that ...
5 end
... • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus modify premRNA before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm • During RNA processing, both ends of the primary transcript are usually altered • Also, usually some interior parts of the molecule are cut out, and the other parts ...
... • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus modify premRNA before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm • During RNA processing, both ends of the primary transcript are usually altered • Also, usually some interior parts of the molecule are cut out, and the other parts ...
On the Nucleotide Sequence of Yeast Tyrosine Transfer RNA
... there may be an enzyme that converts U to in the lower loop and another enzyme that does the right-hand loop (or the same enzyme might work on both loops). In either case the ~ in the tyrosine anticodon might be an incidental product of an enzyme whose real purpose is to change U to v2 in the wobble ...
... there may be an enzyme that converts U to in the lower loop and another enzyme that does the right-hand loop (or the same enzyme might work on both loops). In either case the ~ in the tyrosine anticodon might be an incidental product of an enzyme whose real purpose is to change U to v2 in the wobble ...
The hepatitis C virus Core protein is a potent nucleic acid chaperone
... Core protein. Here we report that Core protein chaperones the annealing of complementary DNA and RNA sequences and the formation of the most stable duplex by strand exchange. These results show that the HCV Core is a nucleic acid chaperone similar to retroviral NC proteins. We also ®nd that the Core ...
... Core protein. Here we report that Core protein chaperones the annealing of complementary DNA and RNA sequences and the formation of the most stable duplex by strand exchange. These results show that the HCV Core is a nucleic acid chaperone similar to retroviral NC proteins. We also ®nd that the Core ...
An Arabidopsis Minute
... pleiotropic morphological aberrations (e.g. short thoracic bristles), and recessive embryo lethality. Kongsuwan and coworkers (Kongsuwan et al., 1985) first showed that a Minute phenotype was caused by a deletion of a RP gene, and now, at least 11 Minute loci have been assigned to RP genes (Lamberts ...
... pleiotropic morphological aberrations (e.g. short thoracic bristles), and recessive embryo lethality. Kongsuwan and coworkers (Kongsuwan et al., 1985) first showed that a Minute phenotype was caused by a deletion of a RP gene, and now, at least 11 Minute loci have been assigned to RP genes (Lamberts ...
Fatty Acids - Mayo Clinic
... HIV-1 RNA quantitation is performed by PCR using the Roche Amplicor System. Plasma is chemically extracted and the viral RNA is precipitated with isopropanol. A known amount of a standard synthetic RNA molecule is added to each specimen to permit quantitation of HIV RNA by a comparison of resulting ...
... HIV-1 RNA quantitation is performed by PCR using the Roche Amplicor System. Plasma is chemically extracted and the viral RNA is precipitated with isopropanol. A known amount of a standard synthetic RNA molecule is added to each specimen to permit quantitation of HIV RNA by a comparison of resulting ...
Maize Metabolic Network Construction and Transcriptome Analysis
... and/or distributed throughout an organ, and vary across growth and developmental stages. Although our representation of the maize metabolic network mainly focuses on catalytic events performed by a small number of genes encoding enzymes and transporters that are responsible for phenotype and functio ...
... and/or distributed throughout an organ, and vary across growth and developmental stages. Although our representation of the maize metabolic network mainly focuses on catalytic events performed by a small number of genes encoding enzymes and transporters that are responsible for phenotype and functio ...
Summary 121 Summary The Hox genes form a subset of the
... number of genes present in a cluster varies between animal species; the number of clusters in each species also varies. The Hox clusters are thought to have arisen by tandem duplication of a single gene, followed, in vertebrates, by duplication of the cluster itself. As a consequence, Hox genes occu ...
... number of genes present in a cluster varies between animal species; the number of clusters in each species also varies. The Hox clusters are thought to have arisen by tandem duplication of a single gene, followed, in vertebrates, by duplication of the cluster itself. As a consequence, Hox genes occu ...
RT-PCR Master Mix (2X)
... primers should be designed to specifically match the desired target and not other sequences present in the target RNA and cDNA. In general, primers should range in length from 18 to 30 nucleotides, exhibit G+C content similar to each other (and ideally in the range of 40 to 60%), and exhibit Tm value ...
... primers should be designed to specifically match the desired target and not other sequences present in the target RNA and cDNA. In general, primers should range in length from 18 to 30 nucleotides, exhibit G+C content similar to each other (and ideally in the range of 40 to 60%), and exhibit Tm value ...
X inactivation Xplained
... hunt for regulatory mechanisms. Nevertheless, any given mechanism of XCI counting and choice requires a stochastic element. In principle, this could be achieved simply by inactivating each X chromosome with a certain fixed and fine-tuned probability. It has been shown that chaotic choice results if ...
... hunt for regulatory mechanisms. Nevertheless, any given mechanism of XCI counting and choice requires a stochastic element. In principle, this could be achieved simply by inactivating each X chromosome with a certain fixed and fine-tuned probability. It has been shown that chaotic choice results if ...
Nucleic acid enzymes
... and translocations. After size-dependent in vitro selection, the original 271-nucleotide-long ribozyme was reduced to sequences as short as 81 nucleotides. RNA is not only able to synthesize its building blocks, but can also catalyze a templated primer extension reaction analogously to polymerase en ...
... and translocations. After size-dependent in vitro selection, the original 271-nucleotide-long ribozyme was reduced to sequences as short as 81 nucleotides. RNA is not only able to synthesize its building blocks, but can also catalyze a templated primer extension reaction analogously to polymerase en ...
Alternative Splicing A very short introduction (in plants)
... Genome-wide analyses of alternative splicing in plants: Opportunities and challenges Genome Res. 2008. 18:1381-1392 ...
... Genome-wide analyses of alternative splicing in plants: Opportunities and challenges Genome Res. 2008. 18:1381-1392 ...
Investigation 1: Examining RNA-Seq data
... be used to help us identify exons and introns for the gene under study. All RNAs in the cell are collectively known as the 'transcriptome,’ as almost all RNA is produced by transcription from a DNA template. (In some cases, RNA is made from an RNA template.) The transcriptome includes messenger RNAs ...
... be used to help us identify exons and introns for the gene under study. All RNAs in the cell are collectively known as the 'transcriptome,’ as almost all RNA is produced by transcription from a DNA template. (In some cases, RNA is made from an RNA template.) The transcriptome includes messenger RNAs ...
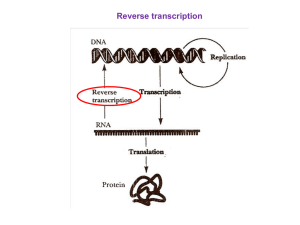
Reverse transcriptase
... • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upst ...
... • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upst ...
Homeotic selector genes
... – homologous means derived from a common ancestor – when Drosophila homeobox genes were identified, researchers screened for homologs in vertebrates – an important point to remember is that although not all developmental mechanisms are conserved, the genes employed to control development are the sam ...
... – homologous means derived from a common ancestor – when Drosophila homeobox genes were identified, researchers screened for homologs in vertebrates – an important point to remember is that although not all developmental mechanisms are conserved, the genes employed to control development are the sam ...
A DEAD Box RNA Helicase Is Essential for mRNA Export and
... These results suggest that the cryophyte mutation may have impaired the production of a germination inhibitor under high temperatures. In addition, the mutation appears to have less impact on the development of younger seedlings compared with older ones under high temperatures. We also tested the ge ...
... These results suggest that the cryophyte mutation may have impaired the production of a germination inhibitor under high temperatures. In addition, the mutation appears to have less impact on the development of younger seedlings compared with older ones under high temperatures. We also tested the ge ...
First Title - Buckeye Valley
... The mRNA strand binds to the small ribosomal subunit and is joined at the start codon by the first tRNA, which carries the amino acid methionine. Binding occurs between complementary base pairs of the codon and anticodon. ...
... The mRNA strand binds to the small ribosomal subunit and is joined at the start codon by the first tRNA, which carries the amino acid methionine. Binding occurs between complementary base pairs of the codon and anticodon. ...
comparing quantitative trait loci and gene expression data
... genes for which both measures are available. This method also has good performance except at some ends of a chromosome. Any QTL with a span that extends beyond the end of a chromosome is truncated. No obvious matches between the QTL set and the NA genes can be seen Figures 1. The visual impression d ...
... genes for which both measures are available. This method also has good performance except at some ends of a chromosome. Any QTL with a span that extends beyond the end of a chromosome is truncated. No obvious matches between the QTL set and the NA genes can be seen Figures 1. The visual impression d ...
The DNA sequence of the fragment Hind.30, 378 bases lcng, fran
... The DNA sequence of the fragment Hind.30, 378 bases lcng, fran the beginning of gene 1 of T7 is presented. It contains the C promoter, two ill vitro transcriptianal terminator sites and a sequence of 171 bases which probably codes for the N terminus of the T7 RNA polymerase. The sequence also codes ...
... The DNA sequence of the fragment Hind.30, 378 bases lcng, fran the beginning of gene 1 of T7 is presented. It contains the C promoter, two ill vitro transcriptianal terminator sites and a sequence of 171 bases which probably codes for the N terminus of the T7 RNA polymerase. The sequence also codes ...
Transcription
... common s factor in E. coli is s70. 2. Binding of the s factor converts the core RNA pol into the holoenzyme. 3. s factor is critical in promoter recognition, by decreasing the affinity of the core enzyme for non-specific DNA sites (104) and increasing the affinity for the corresponding promoter 4. s ...
... common s factor in E. coli is s70. 2. Binding of the s factor converts the core RNA pol into the holoenzyme. 3. s factor is critical in promoter recognition, by decreasing the affinity of the core enzyme for non-specific DNA sites (104) and increasing the affinity for the corresponding promoter 4. s ...
Supplementary Information (doc 1628K)
... the RNeasy kit (Qiagen, Inc., Germantown, MD). Samples were analyzed using the Genechip primeview assay for target synthesis and labeling. Samples were hybridized to the Genechip primeview human gene expression array and those demonstrating a cutoff greater or less than 1.5-fold difference from the ...
... the RNeasy kit (Qiagen, Inc., Germantown, MD). Samples were analyzed using the Genechip primeview assay for target synthesis and labeling. Samples were hybridized to the Genechip primeview human gene expression array and those demonstrating a cutoff greater or less than 1.5-fold difference from the ...
development, the Linker histone H1 is essential for Drosophila
... a genetically tractable organism where H1 may prove to play an essential role. As mentioned, deletion of the yeast HHO1 gene does not lead to obvious phenotypic effects. Although linker histones are essential for embryonic development in mice, the existence of multiple, nonallelic mouse H1 variant g ...
... a genetically tractable organism where H1 may prove to play an essential role. As mentioned, deletion of the yeast HHO1 gene does not lead to obvious phenotypic effects. Although linker histones are essential for embryonic development in mice, the existence of multiple, nonallelic mouse H1 variant g ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.