Chapter 9 - HCC Learning Web
... expression. human accelerated region-1 gene is an example Humans differ from chimps with only 100 out of 118 bases matching (compared to chickens with 116/118 matching) This gene encodes a small, noncoding RNA and is expressed in a region of the brain that develops uniquely in humans Other pro ...
... expression. human accelerated region-1 gene is an example Humans differ from chimps with only 100 out of 118 bases matching (compared to chickens with 116/118 matching) This gene encodes a small, noncoding RNA and is expressed in a region of the brain that develops uniquely in humans Other pro ...
SDS-PAGE of protein purified with the AllPrep RNA/Protein
... buffer should not be used to equilibrate the Protein Cleanup spin column in step 5 of the protocol in the handbook (page 13). To avoid possible SDS precipitation in applications such as SDS-PAGE, protein purified using the AllPrep RNA/Protein Kit should be cleaned up by acetone precipitation, as des ...
... buffer should not be used to equilibrate the Protein Cleanup spin column in step 5 of the protocol in the handbook (page 13). To avoid possible SDS precipitation in applications such as SDS-PAGE, protein purified using the AllPrep RNA/Protein Kit should be cleaned up by acetone precipitation, as des ...
Plant Molecular Biology
... 1. These mutants show evidence of leaf development in darkness: they have expanded cotyledons, plastids that resemble chloroplasts, and chlorophyll protein genes turned on. 2. In the dark, these genes repress photomorphogenesis –related genes in all tissues. 3. In the light, they repress them only i ...
... 1. These mutants show evidence of leaf development in darkness: they have expanded cotyledons, plastids that resemble chloroplasts, and chlorophyll protein genes turned on. 2. In the dark, these genes repress photomorphogenesis –related genes in all tissues. 3. In the light, they repress them only i ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Ribosome moves along mRNA to the next codon, the anti-codon binds to the codon and the new amino acid attaches to the first amino acid forming a polypeptide chain until a stop codon occurs ...
... • Ribosome moves along mRNA to the next codon, the anti-codon binds to the codon and the new amino acid attaches to the first amino acid forming a polypeptide chain until a stop codon occurs ...
The Origins of Life
... but cannot propagate themselves • DNA – can propagate but cannot do any kind of biological work. ...
... but cannot propagate themselves • DNA – can propagate but cannot do any kind of biological work. ...
Chapter 6 From DNA to Protein: How Cell Read the Genome
... Transcription in procaryotic or eucaryotic cells (1) ...
... Transcription in procaryotic or eucaryotic cells (1) ...
epigenetics - Gene Silencing
... specific roles of these various RNA particles in the cell are being extensively investigated. Small RNA molecules (about 100 nucleotides in length) which can bind to a complementary sequence in mRNA and inhibit its translation, were discovered in E. Coli in the early 1980’s. Today about 25 cases of ...
... specific roles of these various RNA particles in the cell are being extensively investigated. Small RNA molecules (about 100 nucleotides in length) which can bind to a complementary sequence in mRNA and inhibit its translation, were discovered in E. Coli in the early 1980’s. Today about 25 cases of ...
The Nature of Genes The Nature of Genes
... • Introns are spliced out of pre-mRNAs to produce the mature mRNA that is translated. • Alternative splicing recognizes different splice sites in different tissue types. • The mature mRNAs in each tissue possess different exons, resulting in different polypeptide products from the same gene. ...
... • Introns are spliced out of pre-mRNAs to produce the mature mRNA that is translated. • Alternative splicing recognizes different splice sites in different tissue types. • The mature mRNAs in each tissue possess different exons, resulting in different polypeptide products from the same gene. ...
DNA constructs designed to produce short hairpin, interfering RNAs
... Abstract. Arylamine N-acetyltransferase (NAT) genes were targeted for inhibition using short hairpin RNA (shRNA) using two different RNA polymerase III promoters. Constructs were developed for NAT1 and NAT2, the endogenous mouse genes, and for human NAT1. There were fetal and neonatal deaths with th ...
... Abstract. Arylamine N-acetyltransferase (NAT) genes were targeted for inhibition using short hairpin RNA (shRNA) using two different RNA polymerase III promoters. Constructs were developed for NAT1 and NAT2, the endogenous mouse genes, and for human NAT1. There were fetal and neonatal deaths with th ...
Chapter 11: DNA and Genes
... ribosomes for protein manufacturing. In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dn ...
... ribosomes for protein manufacturing. In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dn ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... Occurs in the cytoplasm on a ribosome tRNA brings specific amino acids to ribosome If mRNA = AUG, then tRNA = UAC The tRNA has the anti-codon ...
... Occurs in the cytoplasm on a ribosome tRNA brings specific amino acids to ribosome If mRNA = AUG, then tRNA = UAC The tRNA has the anti-codon ...
TRANSCRIPTION & TRANSLATION: From DNA to Protein
... •An amino acid can be coded for by more than one codon •20 amino acids combine in different combinations to make various proteins ...
... •An amino acid can be coded for by more than one codon •20 amino acids combine in different combinations to make various proteins ...
gene expression
... Noncoding RNAs and gene expression • Discovering more about RNA’S that do not make protein • MicroRNAs (miRNA) – small, single stranded RNA generated from a hairpin on precursor RNA; associates with proteins that can degrade or prevent translation of mRNA with complementary sequence • Small interfe ...
... Noncoding RNAs and gene expression • Discovering more about RNA’S that do not make protein • MicroRNAs (miRNA) – small, single stranded RNA generated from a hairpin on precursor RNA; associates with proteins that can degrade or prevent translation of mRNA with complementary sequence • Small interfe ...
REGULATION OF GENES INVOLVED IN LIPID CATABOLISM
... replication was estimated using a probe for CaMV Gene VI. PR-1 is a marker for SAsignalled defence. In Northern blots, levels of transcripts from four genes, AtACX1, AtACX2, AtACX4 and THI (3,3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase) were greatly increased at 21 dpi, whereas the levels of AtACS3 and AIM1 (multi func ...
... replication was estimated using a probe for CaMV Gene VI. PR-1 is a marker for SAsignalled defence. In Northern blots, levels of transcripts from four genes, AtACX1, AtACX2, AtACX4 and THI (3,3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase) were greatly increased at 21 dpi, whereas the levels of AtACS3 and AIM1 (multi func ...
RNA and Central Dogma
... acts as the template for RNA synthesis (Making RNA) • Translation: RNA directs the assembly of a protein (Using RNA) ...
... acts as the template for RNA synthesis (Making RNA) • Translation: RNA directs the assembly of a protein (Using RNA) ...
Gene Set Analysis with Phenotypic Screening Data Results and Validation Purpose
... positive gene sets • The analysis was run on a viral infection cell proliferation assay then the significant sets were clustered (below). The themes are consistent with validated targets and pathways in viral infection. ...
... positive gene sets • The analysis was run on a viral infection cell proliferation assay then the significant sets were clustered (below). The themes are consistent with validated targets and pathways in viral infection. ...
2nd lesson Medical students Medical Biology
... known as the Central Dogma of molecular biology and is an underlying theme in all studies of gene expression. Transcription and translation These two processes are the critical steps involved in producing functional proteins in the cell. Transcription involves synthesis of an RNA from the DNA templa ...
... known as the Central Dogma of molecular biology and is an underlying theme in all studies of gene expression. Transcription and translation These two processes are the critical steps involved in producing functional proteins in the cell. Transcription involves synthesis of an RNA from the DNA templa ...
2nd lesson Medical students Medical Biology
... known as the Central Dogma of molecular biology and is an underlying theme in all studies of gene expression. Transcription and translation These two processes are the critical steps involved in producing functional proteins in the cell. Transcription involves synthesis of an RNA from the DNA templa ...
... known as the Central Dogma of molecular biology and is an underlying theme in all studies of gene expression. Transcription and translation These two processes are the critical steps involved in producing functional proteins in the cell. Transcription involves synthesis of an RNA from the DNA templa ...
Protein Synthesis
... The sequence of bases in an mRNA molecule serves as instructions for the order in which amino acids are joined to produce a polypeptide Ribosomes decode the instructions by using codons, sets of 3 bases that each code for 1 amino acid Each codon is matched to an anticodon, or complementary sequence ...
... The sequence of bases in an mRNA molecule serves as instructions for the order in which amino acids are joined to produce a polypeptide Ribosomes decode the instructions by using codons, sets of 3 bases that each code for 1 amino acid Each codon is matched to an anticodon, or complementary sequence ...
Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for RhoC
... tested with the 456 gene set identified in the previous study. Control was the same as last time {RNA from 11 different human tumor ...
... tested with the 456 gene set identified in the previous study. Control was the same as last time {RNA from 11 different human tumor ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
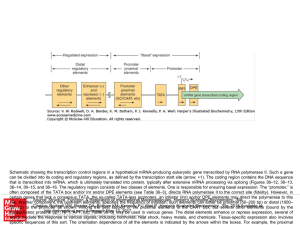
... Schematic showing the transcription control regions in a hypothetical mRNA-producing eukaryotic gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Such a gene can be divided into its coding and regulatory regions, as defined by the transcription start site (arrow; +1). The coding region contains the DNA sequenc ...
... Schematic showing the transcription control regions in a hypothetical mRNA-producing eukaryotic gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Such a gene can be divided into its coding and regulatory regions, as defined by the transcription start site (arrow; +1). The coding region contains the DNA sequenc ...
Genetics BIOL 335 Optional Worksheet 1 solutions 1
... 4. A mutant E coli has no activity for the enzyme isocitrate lyase. Does this result prove that the mutation is in the gene coding for isocitrate lyase? If not, what other mutations could result in the same phenotype? No, it does not. Mutations that affect gene expression could be involved. For exam ...
... 4. A mutant E coli has no activity for the enzyme isocitrate lyase. Does this result prove that the mutation is in the gene coding for isocitrate lyase? If not, what other mutations could result in the same phenotype? No, it does not. Mutations that affect gene expression could be involved. For exam ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.