Chapter 17 Guided Notes
... o ____________________ of 64 triplets code for amino acids. o The codon AUG not only codes for the amino acid _____________________________ but also indicates the “__________________” or initiation of ______________________________. o Three codons do not indicate amino acids but are “_______________ ...
... o ____________________ of 64 triplets code for amino acids. o The codon AUG not only codes for the amino acid _____________________________ but also indicates the “__________________” or initiation of ______________________________. o Three codons do not indicate amino acids but are “_______________ ...
MicroRNAs: something important between the genes
... regulation of plant development. In support of this claim, plant mutants that are impaired in miRNA accumulation, such as dcl1, hen1 and hyl1, display interesting and dramatic developmental phenotypes that range from defects in floral development to defects in leaf morphology [38,40,42,43]. In addit ...
... regulation of plant development. In support of this claim, plant mutants that are impaired in miRNA accumulation, such as dcl1, hen1 and hyl1, display interesting and dramatic developmental phenotypes that range from defects in floral development to defects in leaf morphology [38,40,42,43]. In addit ...
Protein Synthesis
... – Transfer RNA (tRNA): about 80 RNA nucleotides folded into a hairpin shape; binds to specific amino acids – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): RNA nucleotides in a globular form; rRNA makes up the ribosomes where proteins are made ...
... – Transfer RNA (tRNA): about 80 RNA nucleotides folded into a hairpin shape; binds to specific amino acids – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): RNA nucleotides in a globular form; rRNA makes up the ribosomes where proteins are made ...
MiR156 biogenesis is involved in the response to ambient
... Creative Research Initiative, School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Korea University, South Korea ([email protected]) ...
... Creative Research Initiative, School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Korea University, South Korea ([email protected]) ...
Bacterial Genetics Summary
... 1. Overview of Process a. Two parental strands uncoil and unzipper b. Replication starts at 3' end of parental strand c. Complementary deoxyribonucleotides brought in (1) hydrogen bond to complementary base (2) covalent bond to adjacent nucleotide on growing strand d. When finished, have two molecul ...
... 1. Overview of Process a. Two parental strands uncoil and unzipper b. Replication starts at 3' end of parental strand c. Complementary deoxyribonucleotides brought in (1) hydrogen bond to complementary base (2) covalent bond to adjacent nucleotide on growing strand d. When finished, have two molecul ...
DNA - Hermantown
... -along with some proteins make up ribosomes (cytoplasm) 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - transport amino acids to ribosomes (cytoplasm) All types of RNA are formed in the nucleus. ...
... -along with some proteins make up ribosomes (cytoplasm) 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - transport amino acids to ribosomes (cytoplasm) All types of RNA are formed in the nucleus. ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
... Introduction • Every cell in a multi-cellular eukaryote does not express all its genes, all the time (usually only 3-5%) – Long-term control of gene expression in tissue = differentiation ...
... Introduction • Every cell in a multi-cellular eukaryote does not express all its genes, all the time (usually only 3-5%) – Long-term control of gene expression in tissue = differentiation ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
... Substitutions can cause missense (wrong codon, wrong amino acid) or nonsense (codes for stop signal) mutations. Insertions or deletions can produce frameshift mutations that disrupt the mRNA reading frame “downstream” of the mutation. Spontaneous mutations can occur during DNA replication or repair, ...
... Substitutions can cause missense (wrong codon, wrong amino acid) or nonsense (codes for stop signal) mutations. Insertions or deletions can produce frameshift mutations that disrupt the mRNA reading frame “downstream” of the mutation. Spontaneous mutations can occur during DNA replication or repair, ...
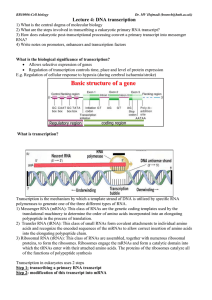
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Performed by spliceosomes (large RNA-protein complex made of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) Recognise exon-intron boundaries and splice exons together by transesterification reactions Cell type-specific splicing ...
... Performed by spliceosomes (large RNA-protein complex made of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) Recognise exon-intron boundaries and splice exons together by transesterification reactions Cell type-specific splicing ...
Transcription/Translation Notes Handout
... – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a _______________. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of _______________________________ where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings __________________________________________(protein building blocks) from the cytopl ...
... – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a _______________. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of _______________________________ where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings __________________________________________(protein building blocks) from the cytopl ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... • mRNA – messenger RNA carries the information for synthesis of protein • rRNA – ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes • tRNA – brings the amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis • The triplet code in tRNA is called the anticodon • Each tRNA and its anticodon is specific for one amino acid ...
... • mRNA – messenger RNA carries the information for synthesis of protein • rRNA – ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes • tRNA – brings the amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis • The triplet code in tRNA is called the anticodon • Each tRNA and its anticodon is specific for one amino acid ...
Early Earth and the Origin of Life
... and are very similar to primitive cells. Start for selection process that lead to cells? ...
... and are very similar to primitive cells. Start for selection process that lead to cells? ...
Detection of alien viruses and viroids in plants by siRNA
... In virus-susceptible plants, however, RNA silencing cannot prevent infection. Jari Valkonen ...
... In virus-susceptible plants, however, RNA silencing cannot prevent infection. Jari Valkonen ...
From Gene to Protein The Central Dogma
... 2. Operator - where a repressor binds, stopping the transcription of that gene 3. Structural Genes - genes coding for the enzyme, they are transcribed as a unit ...
... 2. Operator - where a repressor binds, stopping the transcription of that gene 3. Structural Genes - genes coding for the enzyme, they are transcribed as a unit ...
Applications of RNA interference high
... described using case studies as examples. Finally, discussions are made in the context of the existing problems with these screens. ...
... described using case studies as examples. Finally, discussions are made in the context of the existing problems with these screens. ...
Matched DNA and RNA sets
... Description: High quality intact total RNA and DNA were isolated simultaneously from a single biomaterial source. The RNA and DNA samples were treated with RNase-free DNase and DNase-free RNase to remove the contaminant DNA and RNA residuals respectively. Content: Each set contains 50µg RNA and 10µg ...
... Description: High quality intact total RNA and DNA were isolated simultaneously from a single biomaterial source. The RNA and DNA samples were treated with RNase-free DNase and DNase-free RNase to remove the contaminant DNA and RNA residuals respectively. Content: Each set contains 50µg RNA and 10µg ...
Eukaryotes - Daniel Guetta
... protein), a critical factor in eukaryotic transcription required by ALL RNA Pol genes in eukaryotes ...
... protein), a critical factor in eukaryotic transcription required by ALL RNA Pol genes in eukaryotes ...
Biology - secondary
... molecule than aerobic cellular respiration 107-110 • Building big muscles is an example of catabolic metabolism 119 • 109-Cellular formation is the breakdown of food without O2 • The RNA molecule that contains the code for a polypeptide chain of amino acids is called transfer RNA ...
... molecule than aerobic cellular respiration 107-110 • Building big muscles is an example of catabolic metabolism 119 • 109-Cellular formation is the breakdown of food without O2 • The RNA molecule that contains the code for a polypeptide chain of amino acids is called transfer RNA ...
Protein-coding genes
... enzymes of a network, and their phenotype includes cellular redox potential. 4. Dynamic systems to phenotype Control of global phenotype such as disease may be localized to a single regulatory system (such as metabolic, hormone signaling, etc.) or be distributed over many systems and levels ...
... enzymes of a network, and their phenotype includes cellular redox potential. 4. Dynamic systems to phenotype Control of global phenotype such as disease may be localized to a single regulatory system (such as metabolic, hormone signaling, etc.) or be distributed over many systems and levels ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... structure and function? If the characteristics of a cell depend upon the proteins that are synthesized, what does this tell you about protein synthesis? Work with a partner to discuss and answer the questions that follow. ...
... structure and function? If the characteristics of a cell depend upon the proteins that are synthesized, what does this tell you about protein synthesis? Work with a partner to discuss and answer the questions that follow. ...
RNA
... -along with some proteins make up ribosomes (cytoplasm) 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - transport amino acids to ribosomes (cytoplasm) All types of RNA are formed in the nucleus. ...
... -along with some proteins make up ribosomes (cytoplasm) 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - transport amino acids to ribosomes (cytoplasm) All types of RNA are formed in the nucleus. ...
Eukaryotic gene control
... dsRNA: double stranded RNA, longer than 30 nt miRNA: microRNA, 21-25 nt. Encoded by endogenous genes. Hairpin precursors Recognize multiple targets. ...
... dsRNA: double stranded RNA, longer than 30 nt miRNA: microRNA, 21-25 nt. Encoded by endogenous genes. Hairpin precursors Recognize multiple targets. ...
11/11/15 - cloudfront.net
... If you need to make up a quiz due to an absence… come see me Tues or Thurs during PLC Flip it over when you are finished and hang on to it ...
... If you need to make up a quiz due to an absence… come see me Tues or Thurs during PLC Flip it over when you are finished and hang on to it ...
Explain the steps in protein synthesis.
... • 3. Complementary nucleotides are added using the base pairing rules EXCEPT: • A=U • The rest are the same C=G, T=A, G=C ...
... • 3. Complementary nucleotides are added using the base pairing rules EXCEPT: • A=U • The rest are the same C=G, T=A, G=C ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.