Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... • Chromosomes hold genes. Genes are made of DNA. A gene holds information that decides our colour of hair, colour of eyes etc. It also holds information for making proteins that may become enzymes or hormone for use within the body. ...
... • Chromosomes hold genes. Genes are made of DNA. A gene holds information that decides our colour of hair, colour of eyes etc. It also holds information for making proteins that may become enzymes or hormone for use within the body. ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... Protein Folding and Function As the amino acid chain grows, it folds into a three-dimensional (3-D) structure, which depends on both the chemical nature and order of the different amino acids. The 3-D structure determines the function of the protein. When there is a change in one or more amino acid ...
... Protein Folding and Function As the amino acid chain grows, it folds into a three-dimensional (3-D) structure, which depends on both the chemical nature and order of the different amino acids. The 3-D structure determines the function of the protein. When there is a change in one or more amino acid ...
Biochemistry 304 2014 Student Edition TRANSCRIPTION
... •shRNA Short (interfering) hairpin RNA. Used to supply siRNAs with vector-based approaches to produce stable gene silencing ( a research, experimental approach to add exogenous RNAs) •RISC RNA-induced silencing complex. A nuclease complex of proteins and siRNA, miRNA, etc. that targets and cleaves m ...
... •shRNA Short (interfering) hairpin RNA. Used to supply siRNAs with vector-based approaches to produce stable gene silencing ( a research, experimental approach to add exogenous RNAs) •RISC RNA-induced silencing complex. A nuclease complex of proteins and siRNA, miRNA, etc. that targets and cleaves m ...
12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... The genetic code is the “language” of mRNA instructions. The code is written using four “letters” (the bases: A, U, C, and G). A codon consists of three consecutive nucleotides on mRNA that specify a particular amino acid. The genetic code shows the amino acid to which each of the 64 possible codons ...
... The genetic code is the “language” of mRNA instructions. The code is written using four “letters” (the bases: A, U, C, and G). A codon consists of three consecutive nucleotides on mRNA that specify a particular amino acid. The genetic code shows the amino acid to which each of the 64 possible codons ...
Our laboratory studies the regulation of gene expression in
... classical genetics, modern biochemistry and genomics/proteomics in our studies. We have three principal interests. One is to define the mechanism of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) and how transcription is regulated. A focus of this work is the general transcription factor TF ...
... classical genetics, modern biochemistry and genomics/proteomics in our studies. We have three principal interests. One is to define the mechanism of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) and how transcription is regulated. A focus of this work is the general transcription factor TF ...
P{11/27/11 PPPP RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Review DNA 1
... are edited out before the mRNA gets to the ribosomes. 47.The _______________are the parts that are not edited out and thus used to make the protein. Now that we have our message, The mRNA can move through the nuclear pores to go to ribosome’s Ribosomes will “read” the mRNA to build a protein mRNA mo ...
... are edited out before the mRNA gets to the ribosomes. 47.The _______________are the parts that are not edited out and thus used to make the protein. Now that we have our message, The mRNA can move through the nuclear pores to go to ribosome’s Ribosomes will “read” the mRNA to build a protein mRNA mo ...
Genes Expression or Genes and How They Work: Transcription
... Many enhancers, scattered around the chromosome, can bind different activators, which provide a variety of responses to various signals. When a second kind of regulatory protein called a repressor binds to a “silencer” sequence located adjacent to or overlapping an enhancer sequence, the correspondi ...
... Many enhancers, scattered around the chromosome, can bind different activators, which provide a variety of responses to various signals. When a second kind of regulatory protein called a repressor binds to a “silencer” sequence located adjacent to or overlapping an enhancer sequence, the correspondi ...
ppt - Barley World
... phosphorylation a number of aminoglycoside antibiotics such as kanamycin, neomycin, geneticin (or G418) and paromomycin. Of these, G418 is routinely used for selection of transformed mammalian cells. The other three are used in a diverse range of plant species, however, kanamycin has proved to be in ...
... phosphorylation a number of aminoglycoside antibiotics such as kanamycin, neomycin, geneticin (or G418) and paromomycin. Of these, G418 is routinely used for selection of transformed mammalian cells. The other three are used in a diverse range of plant species, however, kanamycin has proved to be in ...
Par-1
... Components of RNAi machinery Many components of RNAi machinery have been identified through genetic screening for RNAi defective mutants and through biochemical studies using cell extracts (e.g. Drosophila embryo extract). ...
... Components of RNAi machinery Many components of RNAi machinery have been identified through genetic screening for RNAi defective mutants and through biochemical studies using cell extracts (e.g. Drosophila embryo extract). ...
What is RNA? - Biology for Life
... • In Miller’s experiments, ribose was created and deoxyribose was harder to produce. • RNA has a simpler structure then DNA. • RNA exists in viruses (and no DNA) • It has been proved experimentally that RNA has catalytic functions (it is a catalyst) • The DNA-protein system cannot work without RNA. ...
... • In Miller’s experiments, ribose was created and deoxyribose was harder to produce. • RNA has a simpler structure then DNA. • RNA exists in viruses (and no DNA) • It has been proved experimentally that RNA has catalytic functions (it is a catalyst) • The DNA-protein system cannot work without RNA. ...
Heads, Tails, and Tools: Morphogenesis of a Giant Single
... microRNA system for their own purposes. A look at portions of Stentor’s genome revealed to the authors that it contains genes that code for proteins needed for the microRNA pathway (such as Argonaute and Dicer proteins). To see if this machinery could function to silence Stentor’s gene transcripts, ...
... microRNA system for their own purposes. A look at portions of Stentor’s genome revealed to the authors that it contains genes that code for proteins needed for the microRNA pathway (such as Argonaute and Dicer proteins). To see if this machinery could function to silence Stentor’s gene transcripts, ...
An Introduction to RNA Interference (RNAi)
... research such as C. elegans and the fruitfly, D. melanogaster. Because of this work and the impact it would have on biomedical research, Andrew Fire and Craig Mello were awarded the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, even though they did not show or expect the RNAi mechanism to work in mamm ...
... research such as C. elegans and the fruitfly, D. melanogaster. Because of this work and the impact it would have on biomedical research, Andrew Fire and Craig Mello were awarded the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, even though they did not show or expect the RNAi mechanism to work in mamm ...
Biol-1406_Ch10Notes.ppt
... – Patches of fur growing from skin cells may differ in color if fur genes on X chromosomes differ ...
... – Patches of fur growing from skin cells may differ in color if fur genes on X chromosomes differ ...
3.4: Transcription and Translation
... sugar is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA; DNA is double stranded and RNA is single stranded; DNA has a (double) helix; DNA has thymine while RNA has uracil; (require full names written out) both contain four nitrogenous bases / A, G, C, T for DNA and A, G, C, U for RNA; [4 max] ...
... sugar is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA; DNA is double stranded and RNA is single stranded; DNA has a (double) helix; DNA has thymine while RNA has uracil; (require full names written out) both contain four nitrogenous bases / A, G, C, T for DNA and A, G, C, U for RNA; [4 max] ...
GENE EXPRESSION CH 17
... • Only one strand of the DNA is transcribed into RNA, the template strand • RNA strand is complementary to DNA strand copied • Enzyme is RNA polymerase ...
... • Only one strand of the DNA is transcribed into RNA, the template strand • RNA strand is complementary to DNA strand copied • Enzyme is RNA polymerase ...
Microbial Genetics
... structures, enzymes or regulators. • Most gene products will be a polypeptide, which fold-up into functions proteins. • The instructions are manifest as a unique sequence of nucleotide base pairs within a larger DNA molecule. • A universal genetic code is followed to convert base pair sequence infor ...
... structures, enzymes or regulators. • Most gene products will be a polypeptide, which fold-up into functions proteins. • The instructions are manifest as a unique sequence of nucleotide base pairs within a larger DNA molecule. • A universal genetic code is followed to convert base pair sequence infor ...
Ch 5
... mRNA has codons – a sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to mRNA’s codons. AUG is the universal ‘start’ codon that tells the ribosome to start translating. There are three ‘stop’codons – UAA, UAG and UGA – that tell the ribosome to stop t ...
... mRNA has codons – a sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to mRNA’s codons. AUG is the universal ‘start’ codon that tells the ribosome to start translating. There are three ‘stop’codons – UAA, UAG and UGA – that tell the ribosome to stop t ...
Lecture 10 Powerpoint Presentation
... These factors inhibit LuxR, which is required for LuxCDABE expression. At high cell density (ie high concentrations of AI-1 and AI-2), LuxQ and LuxN act as phosphatases and the system (phosphorelay) is reversed. ...
... These factors inhibit LuxR, which is required for LuxCDABE expression. At high cell density (ie high concentrations of AI-1 and AI-2), LuxQ and LuxN act as phosphatases and the system (phosphorelay) is reversed. ...
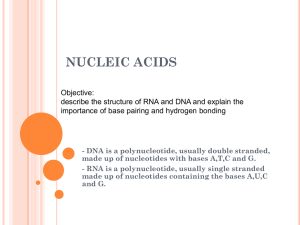
nucleic acids - onlinebiosurgery
... Devise and complete a table of key roles for each specified ion – information coming from bibliographic and web-based research in living organisms: calcium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, chloride, nitrate, phosphate ...
... Devise and complete a table of key roles for each specified ion – information coming from bibliographic and web-based research in living organisms: calcium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, chloride, nitrate, phosphate ...
Supplementary Materials and methods (doc 46K)
... threshold value across the ten permutations. When similar CV values were obtained, we selected the threshold yielding the smallest set of genes and lowest FDR given by pamr. Similarly, ten permutations of three fold CV were performed for determining the threshold in the BCP multivariate comparisons ...
... threshold value across the ten permutations. When similar CV values were obtained, we selected the threshold yielding the smallest set of genes and lowest FDR given by pamr. Similarly, ten permutations of three fold CV were performed for determining the threshold in the BCP multivariate comparisons ...
Terminator
... Types of Mutations • Point mutations (substitutions) – change in a single nucleotide – Due to redundancy of the genetic code it may change the amino acid, it may not “wobble” – Silent mutations do not change the protein Normal hemoglobin DNA ...
... Types of Mutations • Point mutations (substitutions) – change in a single nucleotide – Due to redundancy of the genetic code it may change the amino acid, it may not “wobble” – Silent mutations do not change the protein Normal hemoglobin DNA ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS What is a gene?
... Types of Mutations • Point mutations (substitutions) – change in a single nucleotide – Due to redundancy of the genetic code it may change the amino acid, it may not “wobble” – Silent mutations do not change the protein Normal hemoglobin DNA ...
... Types of Mutations • Point mutations (substitutions) – change in a single nucleotide – Due to redundancy of the genetic code it may change the amino acid, it may not “wobble” – Silent mutations do not change the protein Normal hemoglobin DNA ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.