Virus PowerPoint Notes
... Most viruses have proteins on their surface membrane or capsid that bind to receptor proteins on the __________ cell. ...
... Most viruses have proteins on their surface membrane or capsid that bind to receptor proteins on the __________ cell. ...
Document
... • This occurs at the beginning of transcription. The 5' cap is used as a recognition signal for ribosomes to bind to the mRNA. • At the 3' end, a poly(A) tail of 150 or more adenine nucleotides is added. The tail plays a role in the stability of the mRNA. ...
... • This occurs at the beginning of transcription. The 5' cap is used as a recognition signal for ribosomes to bind to the mRNA. • At the 3' end, a poly(A) tail of 150 or more adenine nucleotides is added. The tail plays a role in the stability of the mRNA. ...
group_presentation
... the cell’s original (also code X), the Dicer enzyme TIFFmRNA (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. recognizes both code Xs as intruders and destroys the doublestranded RNA along with the code X portion of the cell’s original mRNA • Step 4: because the Dice enzyme destroyed the ...
... the cell’s original (also code X), the Dicer enzyme TIFFmRNA (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. recognizes both code Xs as intruders and destroys the doublestranded RNA along with the code X portion of the cell’s original mRNA • Step 4: because the Dice enzyme destroyed the ...
Genes and How They Work
... called tRNA Smaller than mRNA or rRNA found in cytoplasm 40 different kinds of tRNA transports amino acids to ribosome positions amino acids on elongating polypeptide ...
... called tRNA Smaller than mRNA or rRNA found in cytoplasm 40 different kinds of tRNA transports amino acids to ribosome positions amino acids on elongating polypeptide ...
Necessary Components for Translation
... Necessary Components for Translation 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): • Ribosome is the site of protein synthesis. • Facilitates coupling of mRNA to tRNA. • Huge molecule: Large and small subunits must assemble for translation. • Ribosome composition: 60% rRNA and 40% protein • Transfer RNA (tRNA) Carries ...
... Necessary Components for Translation 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): • Ribosome is the site of protein synthesis. • Facilitates coupling of mRNA to tRNA. • Huge molecule: Large and small subunits must assemble for translation. • Ribosome composition: 60% rRNA and 40% protein • Transfer RNA (tRNA) Carries ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Look at the SIMULATION pane. Is the shown molecule DNA or RNA How do you know?_________________________________ 2. RNA polymerase is a type of enzyme. Enzymes help chemical reactions occur quickly. Click the Release enzyme button, and describe what happens.___________________________ Activity A: ...
... Look at the SIMULATION pane. Is the shown molecule DNA or RNA How do you know?_________________________________ 2. RNA polymerase is a type of enzyme. Enzymes help chemical reactions occur quickly. Click the Release enzyme button, and describe what happens.___________________________ Activity A: ...
Gene Section MIR191 (microRNA 191) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... due to common transcription event. A CpG-rich sequence in the DALRD3 promoter and a DNA methylation signal located in this region are responsible for its transcriptional regulation. Accordingly, hypomethylation at the miR-191 locus correlates to its overexpression (and the expression of its host gen ...
... due to common transcription event. A CpG-rich sequence in the DALRD3 promoter and a DNA methylation signal located in this region are responsible for its transcriptional regulation. Accordingly, hypomethylation at the miR-191 locus correlates to its overexpression (and the expression of its host gen ...
Document
... Short-term - genes are quickly turned on or off in response to the environment and demands of the cell. Long-term - genes for development and differentiation. ...
... Short-term - genes are quickly turned on or off in response to the environment and demands of the cell. Long-term - genes for development and differentiation. ...
RNA_and_Protein_Synthesis
... – Messenger RNA = Carry copies of the “instructions” or “messages” to assemble amino acids into proteins ...
... – Messenger RNA = Carry copies of the “instructions” or “messages” to assemble amino acids into proteins ...
chapt13_image
... • A gene mutation is a permanent change in the sequence of bases in DNA • Can range from no effect to complete inactivation • Germ-line mutations occur in sex cells and can be passed to subsequent generations • Somatic mutations occur in body cells and affect only a small number of cells in a tissu ...
... • A gene mutation is a permanent change in the sequence of bases in DNA • Can range from no effect to complete inactivation • Germ-line mutations occur in sex cells and can be passed to subsequent generations • Somatic mutations occur in body cells and affect only a small number of cells in a tissu ...
Document
... according to the size of the protein that it encodes. ◦ c. The trailer sequence, or 39 untranslated region (39 UTR), also varies in length and contains information influencing the stability of the mRNA. ◦ a. Bacteria use the RNA transcript as mRNA without modification. Transcription and translation ...
... according to the size of the protein that it encodes. ◦ c. The trailer sequence, or 39 untranslated region (39 UTR), also varies in length and contains information influencing the stability of the mRNA. ◦ a. Bacteria use the RNA transcript as mRNA without modification. Transcription and translation ...
Protein Synthesis PPT - Welcome to Highland Local Schools
... • Transcription-When the instructions for making a protein are transferred from a gene to an RNA molecule • Translation-When instructions on an RNA molecule are read and coded as ...
... • Transcription-When the instructions for making a protein are transferred from a gene to an RNA molecule • Translation-When instructions on an RNA molecule are read and coded as ...
ch 17
... Grew with ornithine supplements Grew with citrulline supplements Grew only with arginine supplements ...
... Grew with ornithine supplements Grew with citrulline supplements Grew only with arginine supplements ...
Transcription/Translation Notes
... Name __________________________________________________________________Date_______ Biology ...
... Name __________________________________________________________________Date_______ Biology ...
Eukaryotic Transcription
... • Four Kingdoms of Organisms which are eukaryotic are animal, plants, protists and fungi. ...
... • Four Kingdoms of Organisms which are eukaryotic are animal, plants, protists and fungi. ...
Molecular Genetics
... • The primary transcript is called hnRNA – 5’ cap (methylated G) – added and a poly-A tail added to the 3’ end – (Note: cap and tail are protection from degradation and recognition by ribosome) – Spliced out introns (non-coding segments; the coding segments are called exons) ...
... • The primary transcript is called hnRNA – 5’ cap (methylated G) – added and a poly-A tail added to the 3’ end – (Note: cap and tail are protection from degradation and recognition by ribosome) – Spliced out introns (non-coding segments; the coding segments are called exons) ...
transcriptiontranslation lecture
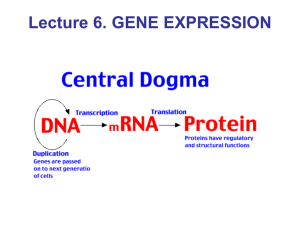
... When converting from DNA to RNA you are simply transcribing the code from the language of DNA nucleotides to RNA nucleotides Proteins are “written” in the language of amino acids. When converting from RNA to protein we are translating from the nucleotide language to amino ...
... When converting from DNA to RNA you are simply transcribing the code from the language of DNA nucleotides to RNA nucleotides Proteins are “written” in the language of amino acids. When converting from RNA to protein we are translating from the nucleotide language to amino ...
Western Blots. After toxin treatment, non-adherent
... mM PMSF, 2 μg/mL CLAP (Chymostatin, Leupeptin, Antipain, and Pepstatin), and 1% Triton X100. Each well was scraped and the sample with homogenization buffer was added to the resuspended non-adherent cells. This was centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 5 min at 4˚C and the supernatant was boiled for 5 min, ...
... mM PMSF, 2 μg/mL CLAP (Chymostatin, Leupeptin, Antipain, and Pepstatin), and 1% Triton X100. Each well was scraped and the sample with homogenization buffer was added to the resuspended non-adherent cells. This was centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 5 min at 4˚C and the supernatant was boiled for 5 min, ...
Genetics
... locus mask the expression of alleles on another locus and express their own phenotype instead. pleiotropy (dwarfism, giantism) one allele affects various phenotypes in an organism. polygenic (skin color) multiple alleles are required for the expression of a characteristic ...
... locus mask the expression of alleles on another locus and express their own phenotype instead. pleiotropy (dwarfism, giantism) one allele affects various phenotypes in an organism. polygenic (skin color) multiple alleles are required for the expression of a characteristic ...
insight review articles
... The similarity of induction, degradation and associated short dsRNAs in RNAi, quelling and PTGS indicates an underlying evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Analysis of mutants defective in these processes in Caenorhabditis elegans, Neurospora and Arabidopsis confirm this closeness, showing that ther ...
... The similarity of induction, degradation and associated short dsRNAs in RNAi, quelling and PTGS indicates an underlying evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Analysis of mutants defective in these processes in Caenorhabditis elegans, Neurospora and Arabidopsis confirm this closeness, showing that ther ...
Drosophila
... our study is siRNA of each candidate gene, while the specific tissue will be lymph gland tissue. ...
... our study is siRNA of each candidate gene, while the specific tissue will be lymph gland tissue. ...
Off-target Effects: Disturbing the Silence of RNA
... RNA interference (RNAi) is a post-transcriptional gene regulatory mechanism that can be mediated by endogenously encoded small RNA molecules (microRNAs), or synthetic duplexes referred to as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). In both cases, these molecules partner with the RNA Induced Silencing Comple ...
... RNA interference (RNAi) is a post-transcriptional gene regulatory mechanism that can be mediated by endogenously encoded small RNA molecules (microRNAs), or synthetic duplexes referred to as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). In both cases, these molecules partner with the RNA Induced Silencing Comple ...
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments
... • The initiation of transcription requires that RNA polymerase recognize and bind tightly to a promoter sequence on DNA. • RNA elongates in a 5’ 5’--toto-3’ direction, antiparallel to the template DNA. • Special sequences and protein helpers terminate transcription. ...
... • The initiation of transcription requires that RNA polymerase recognize and bind tightly to a promoter sequence on DNA. • RNA elongates in a 5’ 5’--toto-3’ direction, antiparallel to the template DNA. • Special sequences and protein helpers terminate transcription. ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.